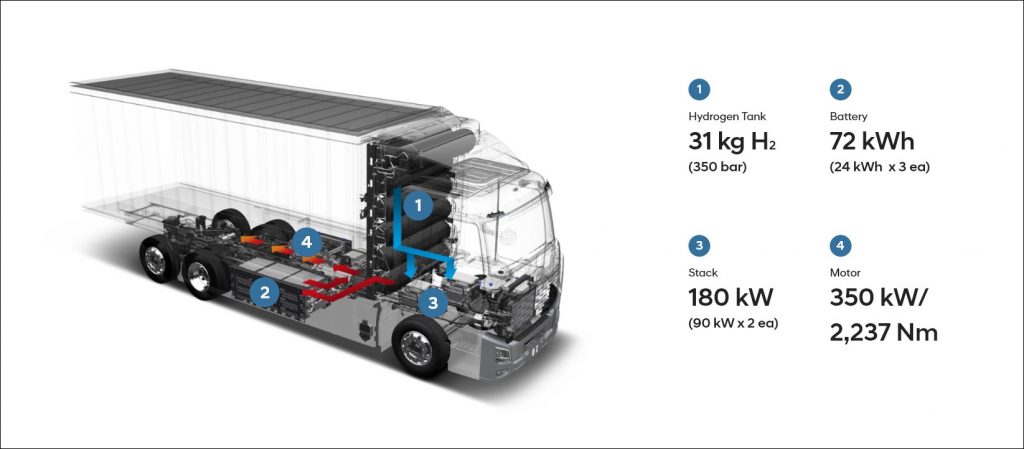
The sale of electric vehicles (EVs) in high volumes began 12 years ago, when Nissan introduced its LEAF. Since then, the number of EVs in use has grown rapidly and the question of what to do with the batteries at the end of their life powering vehicles is becoming a serious matter. The batteries can still be used for other purposes and some manufacturers are exploring practical ways of reusing them.
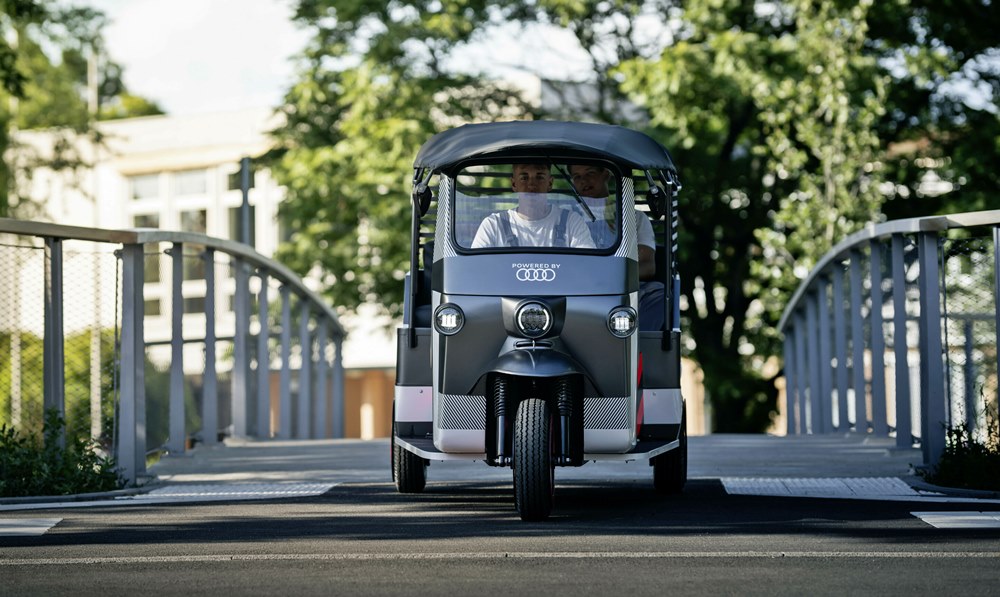
One possible second-life use case is being tested in India by a German–Indian start-up called Nunam. The aim of the project is to explore how modules made with automotive high-voltage batteries can be reused by installing them in electric rickshaws.
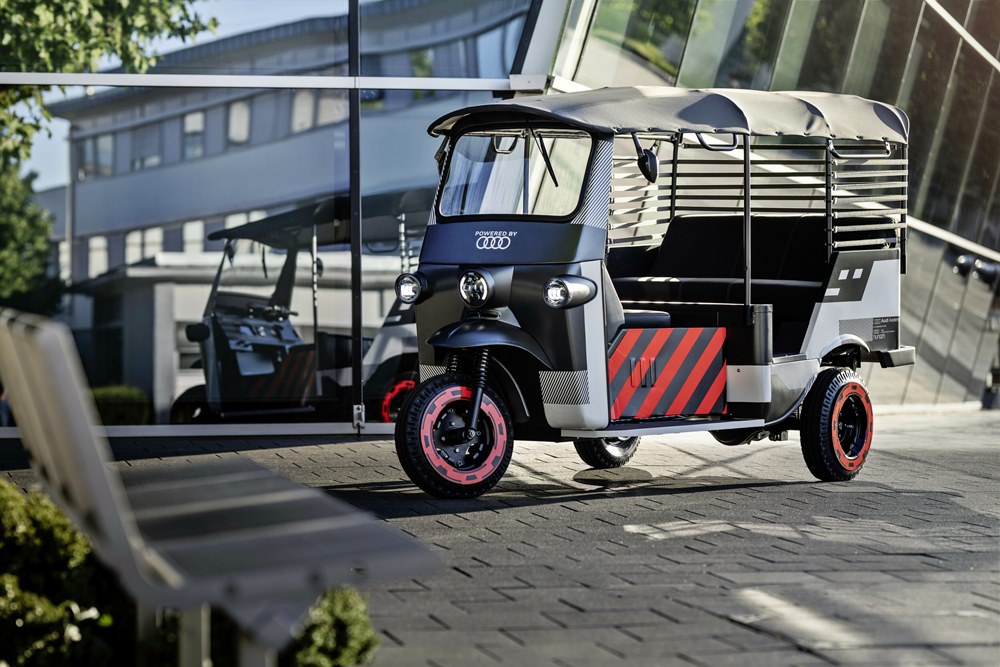

“The old batteries are still extremely powerful,” says Nunam co-founder Prodip Chatterjee. “When used appropriately, second-life batteries can have a huge impact, helping people in challenging life situations earn an income and gain economic independence – everything in a sustainable way.”
3 prototypes
The non-profit start-up based in Berlin and Bangalore is funded by the Audi Environmental Foundation. Nunam developed the three prototype rickshaws in collaboration with the training team at Audi’s Neckarsulm site which, in turn, benefits from the intensive intercultural exchange. This is the first joint project between both AUDI AG and the Audi Environmental Foundation in addition to Nunam.

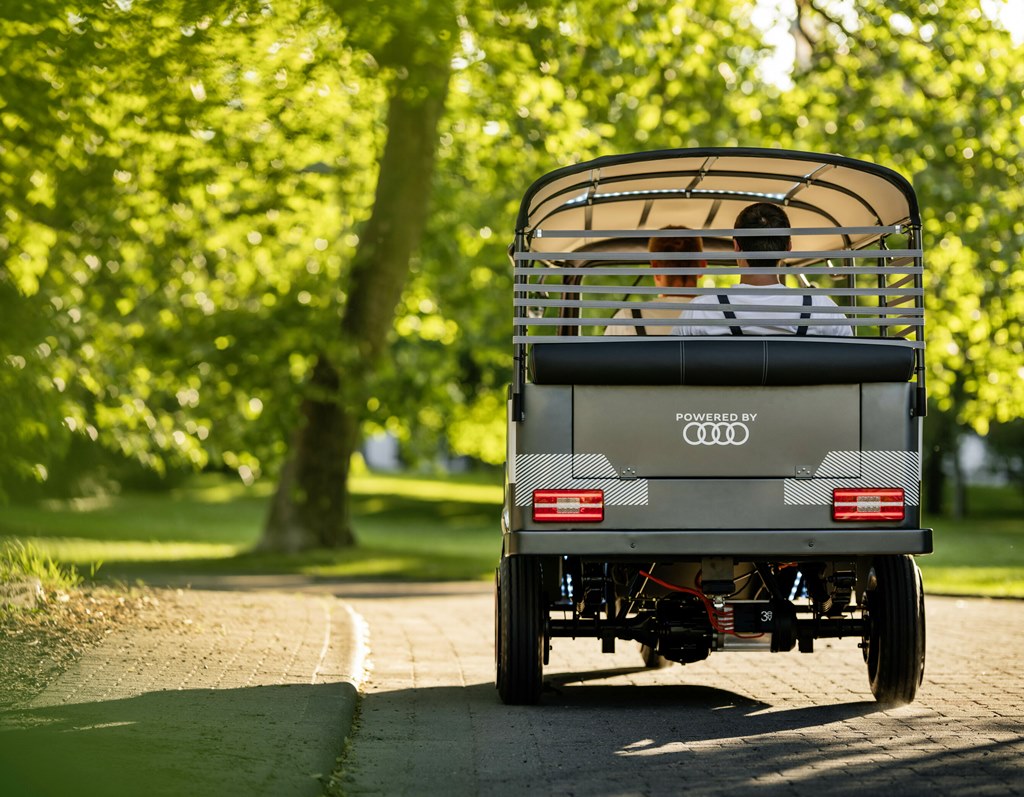
The 3 electric rickshaws are powered by used batteries taken from test vehicles in the Audi e-tron test fleet. They will appear on Indian roads in early 2023 when the pilot project gets underway with a non-profit organization. Women in particular will be able to use the all-electric rickshaws to transport their goods to market for sale, all without the need for intermediaries.
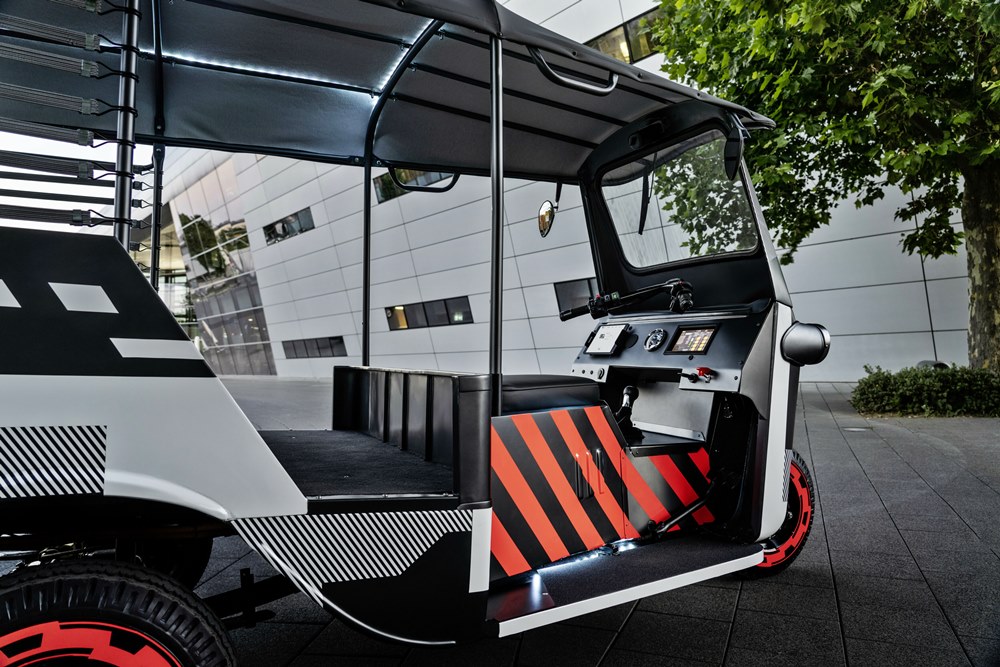

Looking for new uses
The start-up’s primary goal is to develop ways to use old batteries as second-life power storage systems, thus both extending their lives and using resources more efficiently. “Car batteries are designed to last the life of the car. But even after their initial use in a vehicle, they still have a lot of their power,” Chatterjee explained. “For vehicles with lower range and power requirements, as well as lower overall weight, they are extremely promising.”
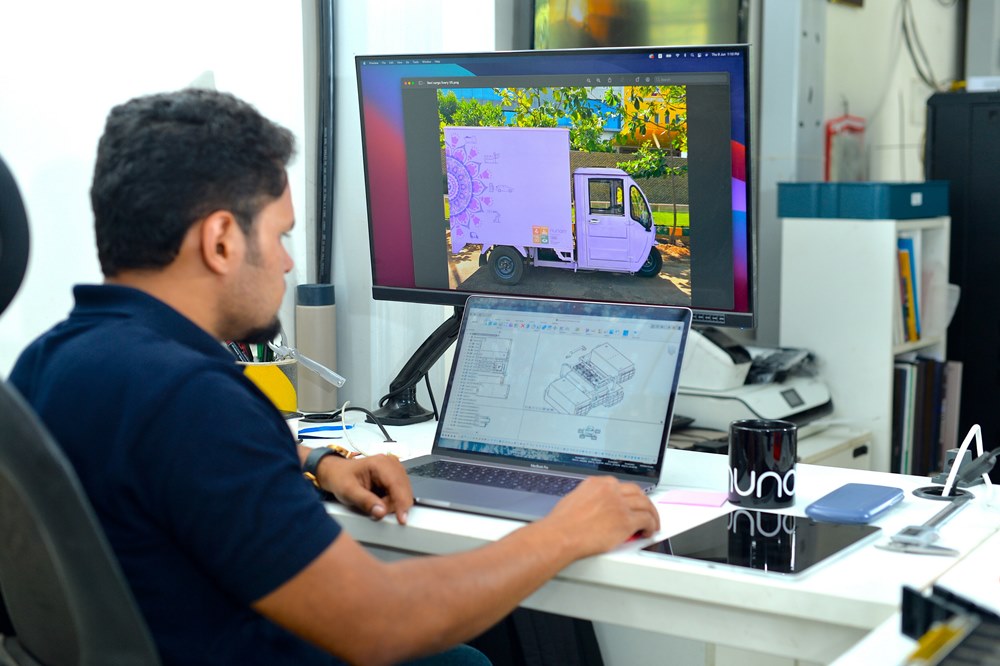

“ In our second-life project, we reuse batteries from electric cars in electric vehicles; you might call it electric mobility ‘lite’. In this way, we’re trying to find out how much power the batteries can still provide in this demanding use case,” he said.
Reusing e-waste
E-rickshaws have an ideal eco-efficiency. With a high-energy-density battery pack and comparatively low vehicle weight, the electric motor doesn’t have to be particularly powerful – especially since rickshaw drivers in India travel neither fast nor far. While electrically-powered rickshaws are not an uncommon sight on the roads of the sub-continent today, they often run on lead-acid batteries, which have a relatively short service life and are often not disposed of properly.
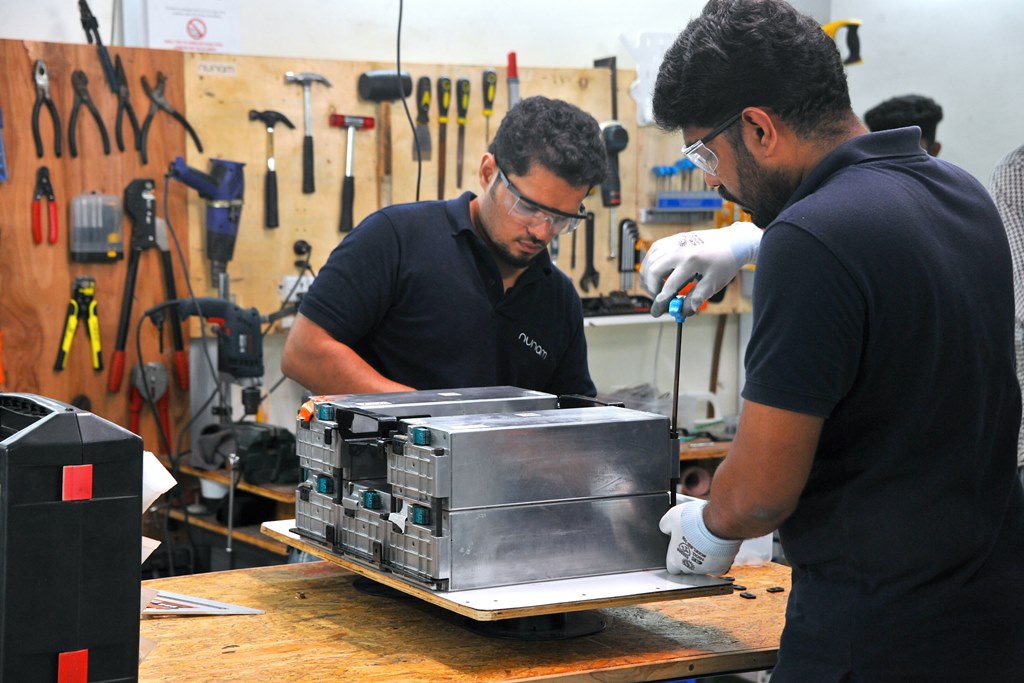

At the same time, rickshaw drivers charge their vehicles primarily with public grid electricity, which has a high proportion of coal-fired power in India. Nunam has a solution for this as well: The e-rickshaws charge using power from solar charging stations. The solar panels are located on the roofs of the local partner’s premises. During the day, sunlight charges an e-tron battery, which acts a buffer storage unit. And in the evening, the power is passed on to the rickshaws.
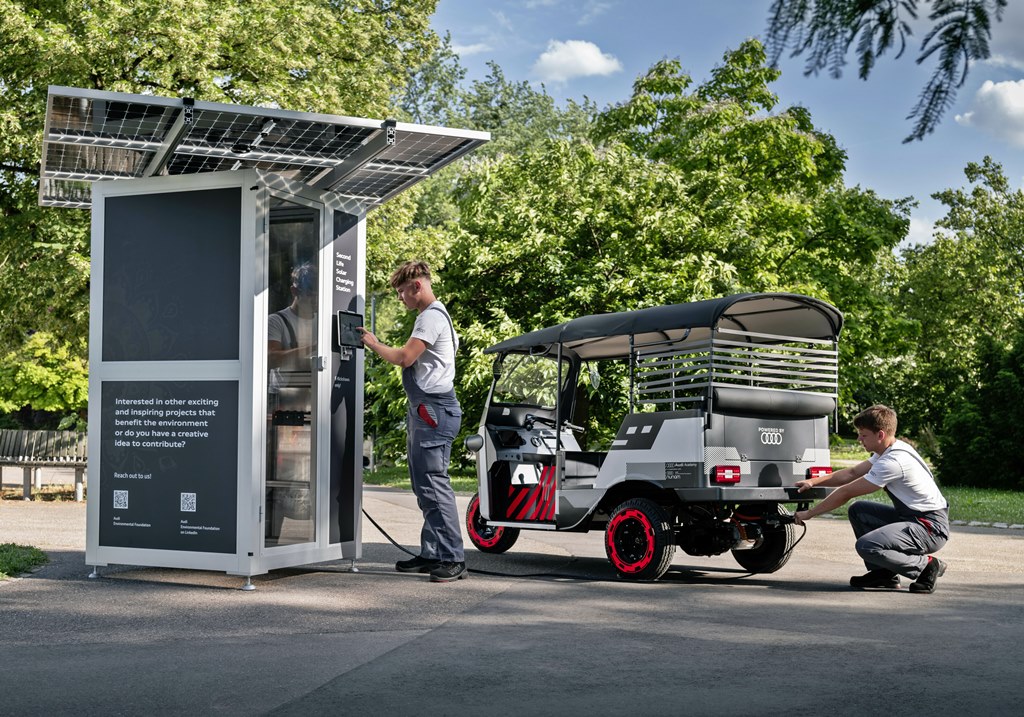

This approach makes local driving largely carbon-free. The benefit is that the electric rickshaws can be used throughout the day – and still be charged with green power during the evening and night. In India, where the sun shines all year round, placing solar panels on the roof is an obvious solution.
Open-source platform encourages imitators
Nunam will continuously monitor the e-rickshaws’ performance and range. The social entrepreneurs make all the e-rickshaw data they collect available to potential imitators on the open-source platform. In fact, imitation is expressly encouraged.
“Initiatives like the one pioneered by Nunam are needed to find new use cases for e-waste. Not only in India, but worldwide. So Nunam shares its knowledge to motivate more initiatives to develop products with second-life components that can drive the eco-social revolution forward,” said Audi Environmental Foundation Director Rudiger Recknagel.

And even after the battery has spent its first life in an Audi e-tron and its second in an e-rickshaw, it has not necessarily reached the end of the road. In a third step, the battery could still be used for stationary applications such as LED lighting. “We want to get everything possible out of each battery before recycling,” said Chatterjee.