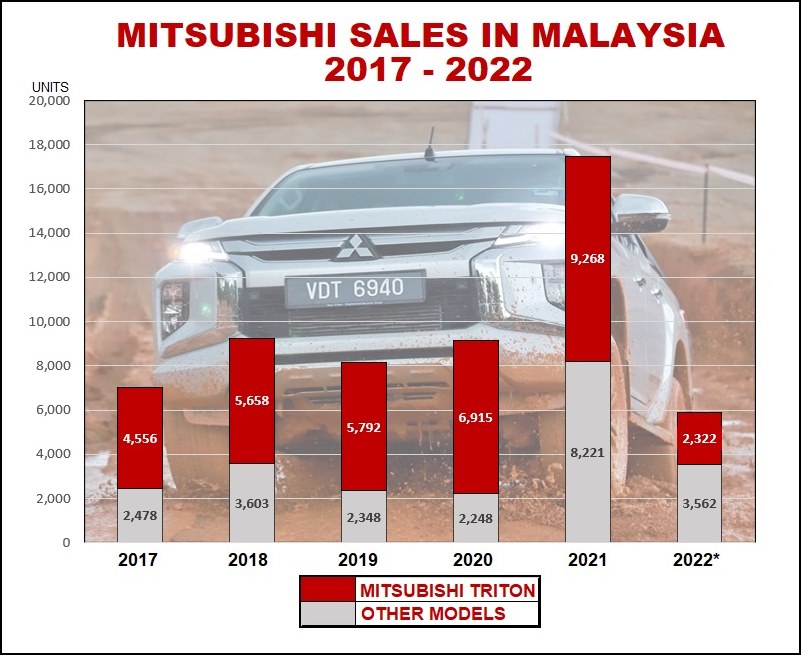
In spite of the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic, Mitsubishi Motors Malaysia (MMM) was able to achieve a higher sales volume during it its last financial year (FY21: April 2021 – March 2022). The total volume of 19,217 units was a 66% increase compared to the volume sold in the same period when the Total Industry Volume of the Malaysian market declined by 6.7%. This achievement put the company comfortably in the top 3 spots of the non-national automotive category.
The Triton pick-up truck was the bestseller for the brand with 9,420 units sold in FY21, which was a 24% increase compared to FY20. Its popularity among Malaysians was evident as it maintained a market share of around 21.4%.
The XPANDER was also a strong seller and the dominant model in the non-national MPV segment. 9,065 units of the locally-assembled 7-seater were sold, accounting for 47.2% to the company’s overall total sales.

“In general, the past 2 years have been tough on the automotive industry, not only with the rising cases of Omicron COVID-19 but floods that affected the Klang Valley and East Coast region, as well as parts or chips shortage. There were many hurdles for the industry to overcome, thus for our sales performance to grow is a significant triumph for us. We take this chance to thank the Malaysian government for initiating and extending the SST exemption these last couple of years. With this, our customers could enjoy extra savings while it also gives us the time to fulfil all booking orders made,” said Shinya Ikeda, CEO of Mitsubishi Motors Malaysia.
“The company will continue to charge forward with strong momentum for 2022. We are aware that a large number of our customers aim to purchase their cars before the SST exemption expires by end of June. We are continuing our best efforts to meet the booking numbers, and we have already increased our production capacity while maintaining a high level of product quality. Our customers are the ones that put us here, thus providing them with utmost convenience and confidence towards the brand is our utmost priority,” he added.
The Mitsubishi Motors network consists of 54 showrooms (out of which 49 are 3S Centres) and 55 service outlets throughout Malaysia. In East Malaysia, there are 14 showrooms (7 in Sarawak and 7 in Sabah). The present range consists of the Triton which is imported as a CBU (Completely Built-Up) model from Thailand, and the XPANDER MPV which is assembled locally.
To know more about Mitsubishi models in Malaysia and to locate a showroom, visit www.mitsubishi-motors.com.my.
Mitsubishi Motors Malaysia offers 1-hour test-drives without salesman being present