The rush of new model introductions, some delayed by the MCO earlier in the year, continues and today, Honda Malaysia has announced that an updated Honda CR-V will be in showrooms before the end of this year. Bookings are now accepted at all 101 authorised dealerships nationwide.
The CR-V was the first model that Honda Malaysia assembled at its new plant when the facility opened in Melaka in 2003. Since then, over 100,000 units have been sold, of which more than 36,000 have been of the 5th generation which was launched in 2017.

“We are confident that the New CR-V will not only continue to live up to this stellar track record, but also regain its status as No.1 in the Non-National SUV segment as it offers a complete package comprising bold exterior, VTEC Turbocharged engine as well as Next Generation Advanced Safety Technology – Honda SENSING. We believe the enhanced New CR-V is an ideal SUV for families and professionals with a keen sense of sophistication and style,” said Honda Malaysia’s Managing Director & CEO, Toichi Ishiyama.
The changes
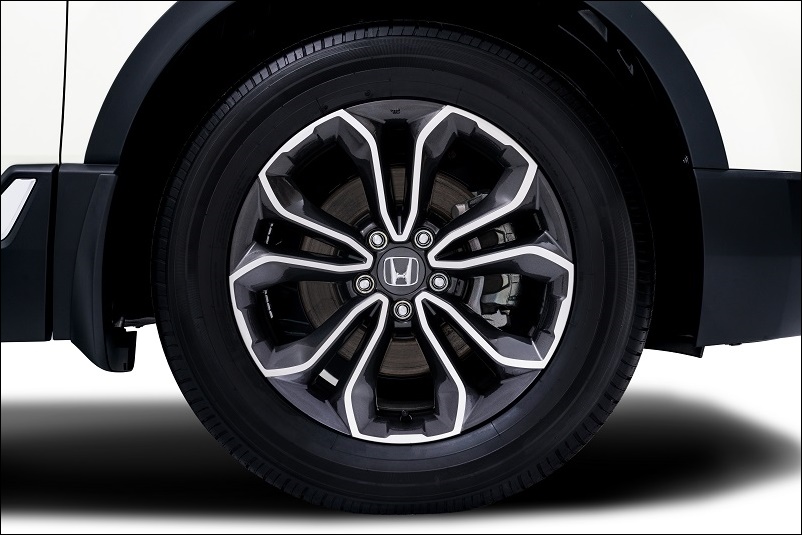
The exterior of the New CR-V receives cosmetic changes with a new black grille combined with Honda’s signature LED headlights. The restyled front and rear bumpers have a wing-style chrome fascia, while the rear end has new dark chrome and new smoked finish taillights, plus a new tailpipe finisher. The 18-inch dual-tone alloy wheels have a new design as well.
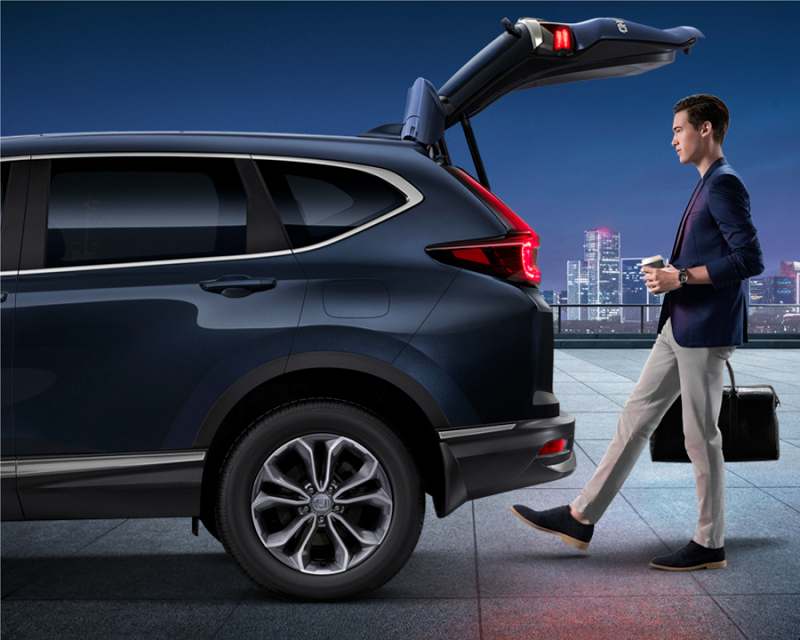
Owners of the New CR-V will no longer have to press a button to open the tailgate. It now comes with a Handsfree Power Tailgate which will open (and close) when a foot is positioned under the rear bumper.
The CR-V has a 1.5-litre VTEC turbocharged Earth Dreams engine with an output of 193ps/243 Nm, which makes its more powerful than a conventional 2.4-litre engine. Having a smaller displacement helps in fuel efficiency which can be enhanced with activation of the ECON mode.
The CR-V is available with all-wheel drive (AWD) that is managed by an Intelligent Control System. Torque is distributed optimally to the wheels, providing better traction and control on all surfaces.
Full Honda SENSING suite
The New CR-V will come with a full suite of Honda SENSING that that consists of eight systems, all of which work with a camera mounted at the top of the windscreen. The systems are Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC), Low-Speed Follow (LSF), Forward Collision Warning (FCW), Collision Mitigation Braking System (CMBS), Lane Departure Warning (LDW), Road Departure Mitigation (RDM), Lane Keeping Assist System (LKAS), and Auto High-Beam (AHB).
In addition, Honda LaneWatch (shown above) is now a standard feature. This is a noteworthy innovation by Honda which provides a real-time image of the blind spot along the left side of the vehicle from a small camera mounted on the left door mirror. The image, which is clear day and night, is displayed on the infotainment screen in the middle of the dashboard, so the driver does not have to turn the head so much to view.
Pricing for the New CR-V is not revealed yet but it would, of course, have full exemption of the 10% sales tax until December 31, 2020. Visit www.honda.com.my for more information or let a Honda dealer know of your interest to be updated.