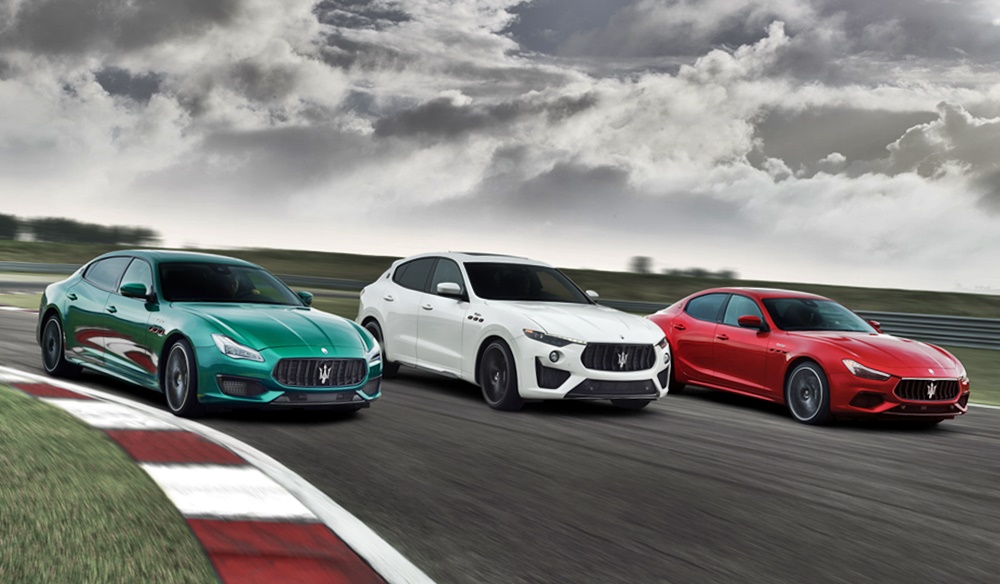
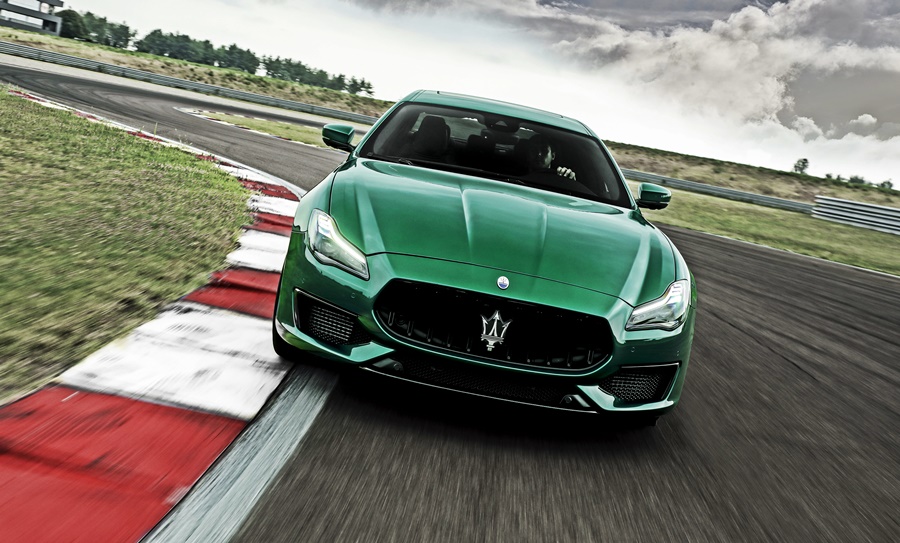
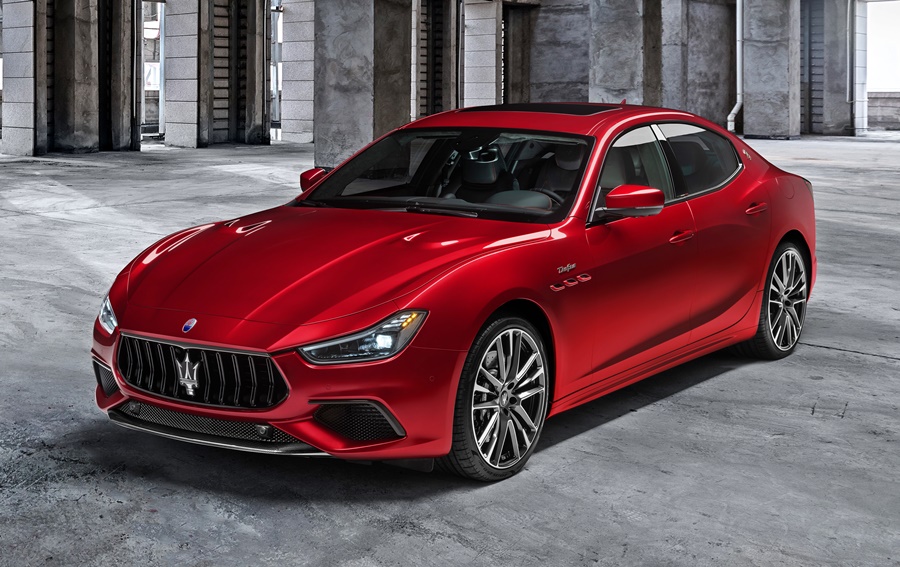
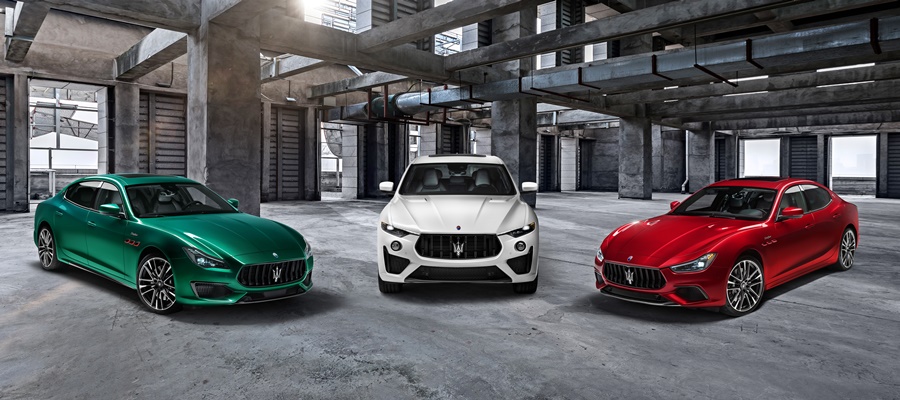
Following the 2018 launch of Levante Trofeo, the most powerful version of Maserati’s first SUV, the range is now joined by the new Quattroporte and Ghibli Trofeo. The expanded collection highlights Maserati’s all-Italian identity with the colours chosen for the Trofeo collection launch being those of the country’s flag: green for Quattroporte, white for Levante and red for Ghibli.
The striking colours are combined with burnished chrome-work and gloss red trim. The whole Trofeo collection is distinguished by the red details that characterize the bottom profiles of the side air vents and the arrow on the Trident badge on the C-pillars.
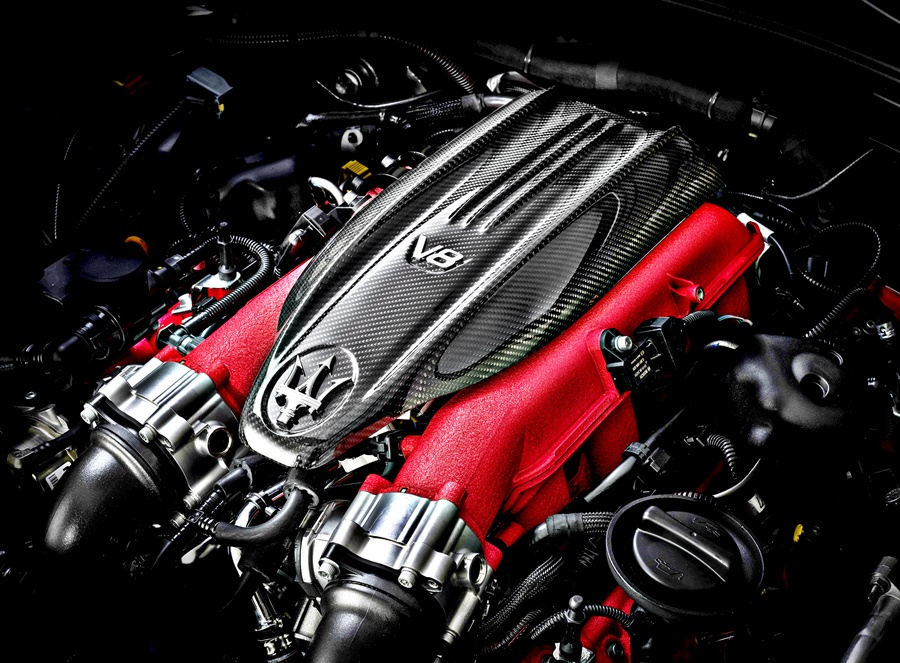
580-bhp V8 engine
The heart of Ghibli and Quattroporte Trofeo is the 3.8-litre V8 Twin Turbo with no less than 580 bhp and 730 Nm of torque at peak output. The engine, already available with the Levante Trofeo, is built at the Ferrari factory to Maserati’s specifications. It has been modified and developed to deliver equally impressive performance on the rear-engine sedans.
Although completely new for Ghibli, the V8 engine has already been used in the past on Quattroporte GTS, tuned for 523 bhp output. The uprated V8 for the Trofeo versions are in full compliance with fuel efficiency and emissions standards.
Fastest Maserati sedans
The Ghibli and Quattroporte Trofeo are claimed to be the fastest Maserati sedans ever, able to reach a maximum speed of 326 km/h, 24 km/h faster than the Levante Trofeo.
Like Levante Trofeo, the new Ghibli and Quattroporte Trofeo also incorporate the Integrated Vehicle Control (IVC) system, with a specific set-up for enhanced driving dynamics and greater active safety.
The sedans have the Corsa button that sets the car for an even sportier driving style. Also included is Launch Control, a function that first appeared on Levante Trofeo, to exploit all the engine’s power and produce an authentic Maserati driving experience.
Special stylistic touches
While the unique signature of every Maserati is the sound of its engine, the Trofeo collection adds distinctiveness, thanks to special stylistic touches. These include the front grille with twin vertical bars in Black Piano finish, and the introduction of carbonfibre on the front air duct trims and rear extractor, giving an even more aggressive effect.
There are major changes at the rear of the car, where the light clusters have been completely restyled, with a boomerang-like profile inspired by the 3200 GT and the Alfieri concept car.
For the Ghibli Trofeo, the bonnet has also been restyled, featuring two aggressive air ducts for better cooling, just like on Levante Trofeo.
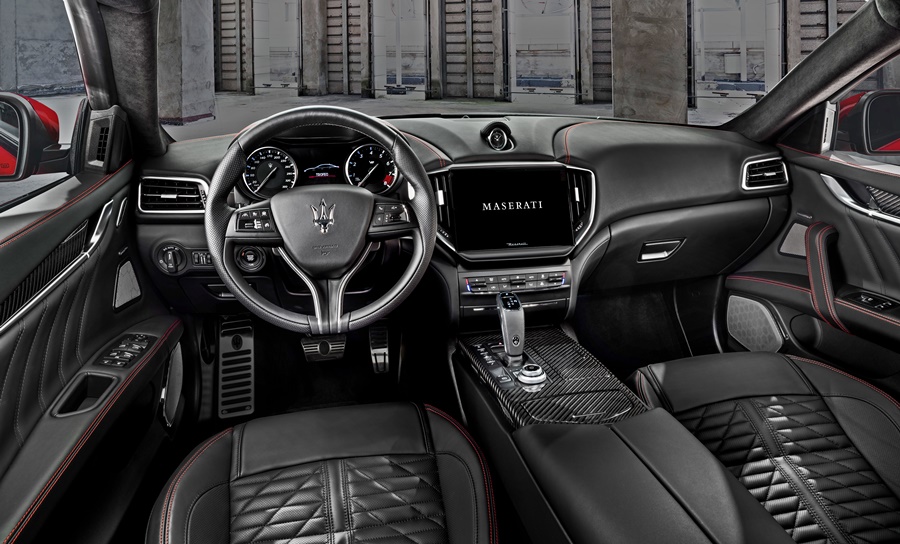
The Trofeo characterization continues in the interior, with a new on-board panel that displays an exclusive interface at switch-on, while the headrests bear the Trofeo badge with the name in 3-dimensional relief. The exclusivity also extends to the interior upholstery, in full-grain Pieno Fiore natural leather.
New technologies also appear in MIA (Maserati Intelligent Assistant) while the multimedia screen has upgraded resolution and a larger size.