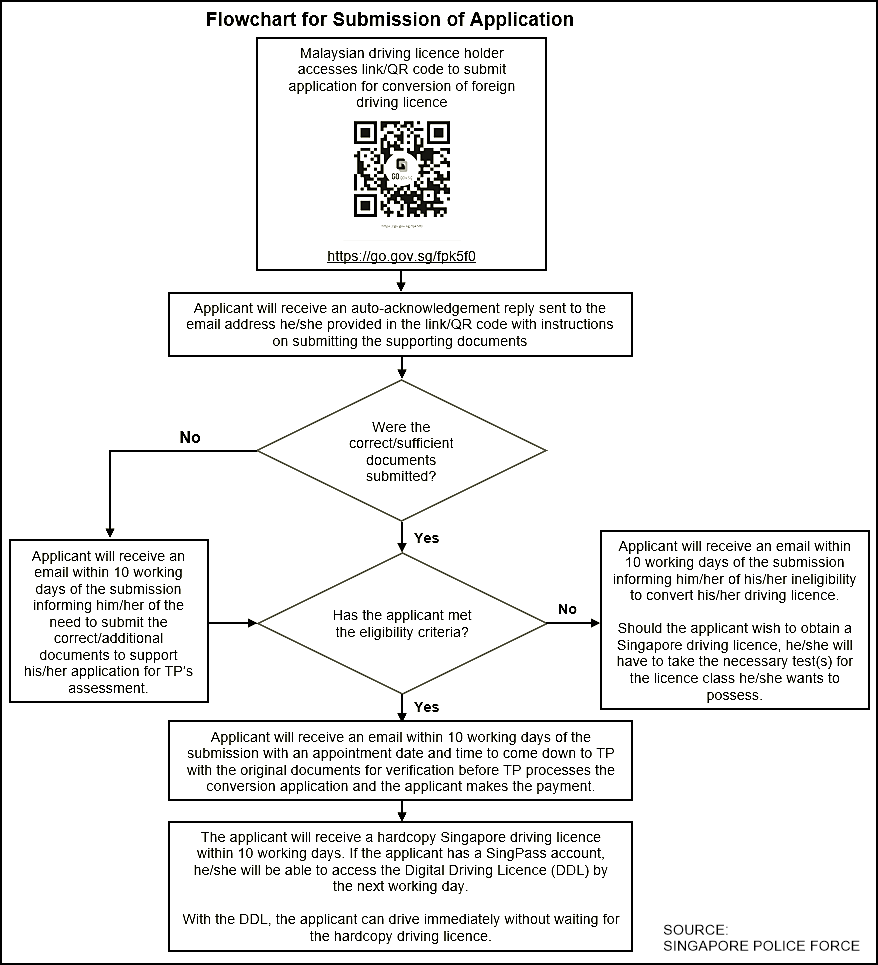
Although wind tunnels have been associated with aeronautical research and development, such facilities existed long before the first aircraft flew, and they were used by scientists in the 19th century to study airflow. Aircraft designers then used wind tunnels to see the effects of different shapes that would be used for aircraft bodies and wings.
Wind tunnels were also used by other industries and by the 1930s, as cars started to go at high speeds, the wind tunnel was used to study how air flowed over their bodies. It was a Prof. Dr.-Ing. Wunibald Kamm at the Technische Hochschule Stuttgart in Germany who was the first to use a wind tunnel for aerodynamic design studies which would be pioneering.
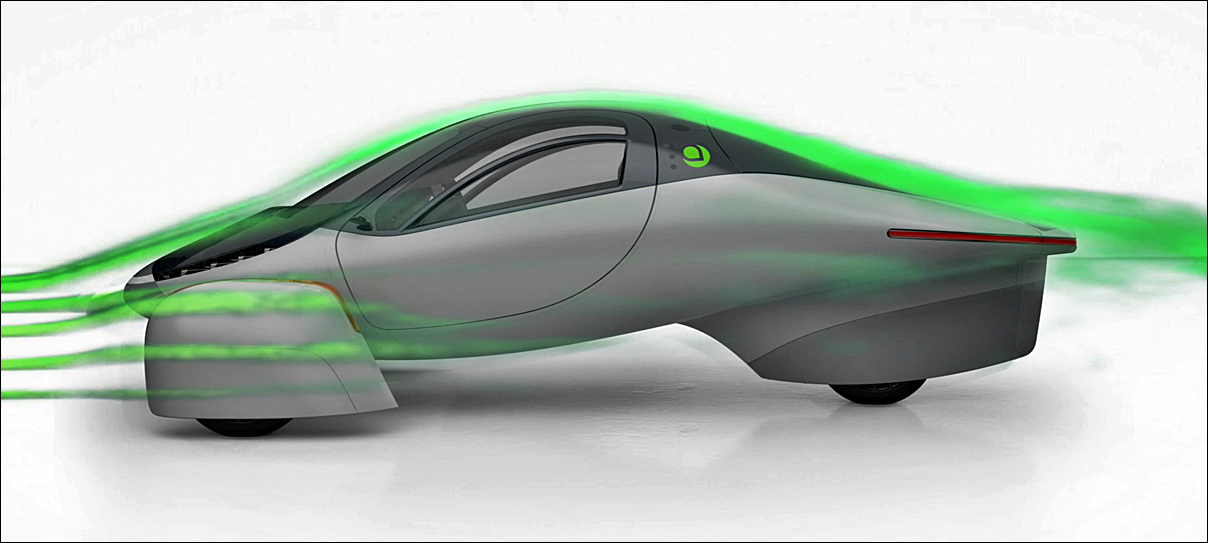
From then on, carmakers would add aerodynamic studies to the development process of a new model, using scale models in small wind tunnels and full-sized models in larger tunnels. Various types of equipment measured airflow so that it could be optimised because it was understood that smoother airflow could improve performance and also reduce noise levels. By having a wind tunnel, the engineers could also study the behaviour of the car design (eg stability) at high speeds without actually having to drive the prototype on the track.
In earlier years, carmakers didn’t yet have their own wind tunnels, so they used those in other research facilities. In time, some started to build their own so they could conduct testing with more secrecy and also without having to pay for renting facilities. Some built small tunnels and some built big ones, depending on how much they could spend.
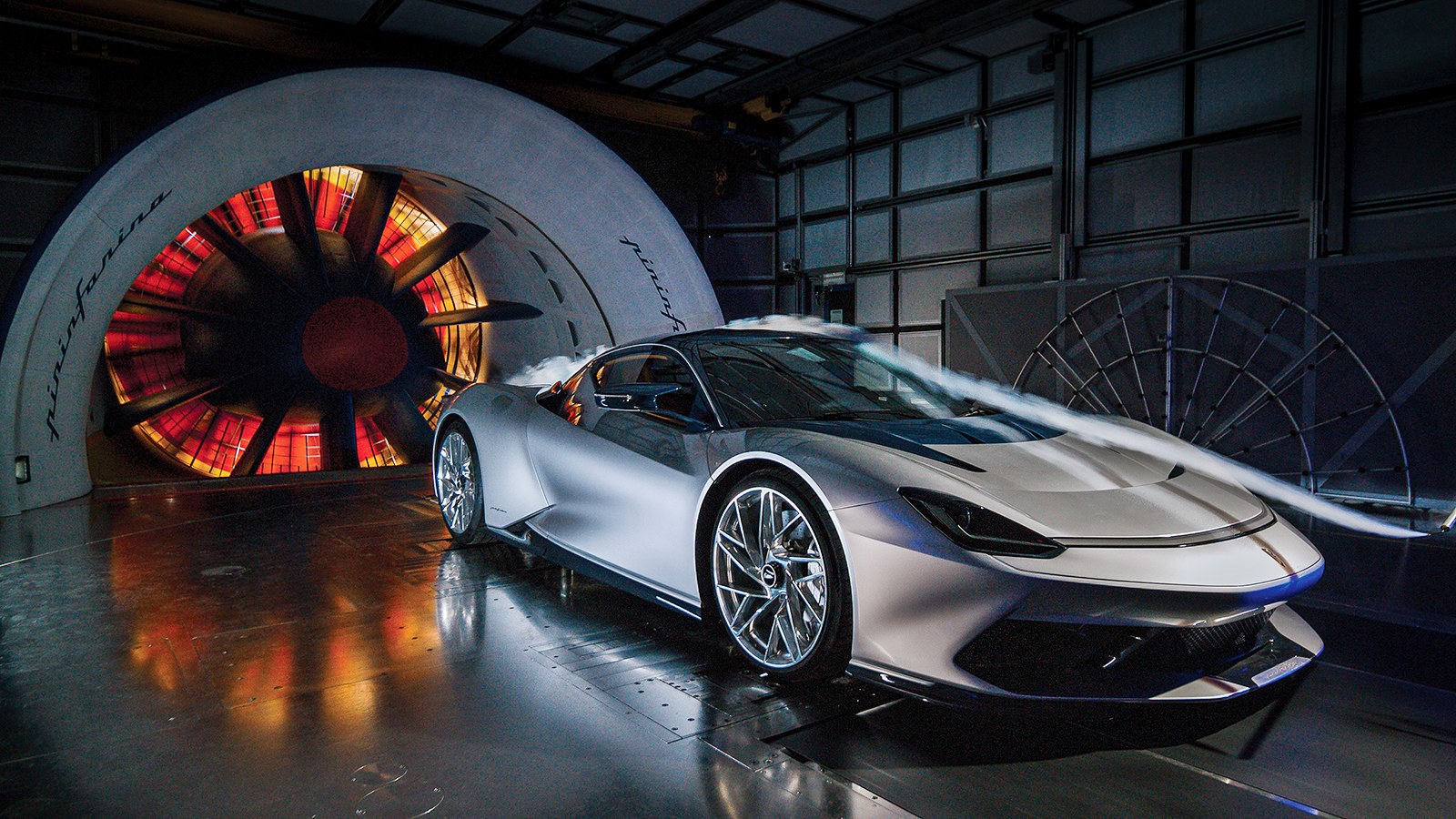
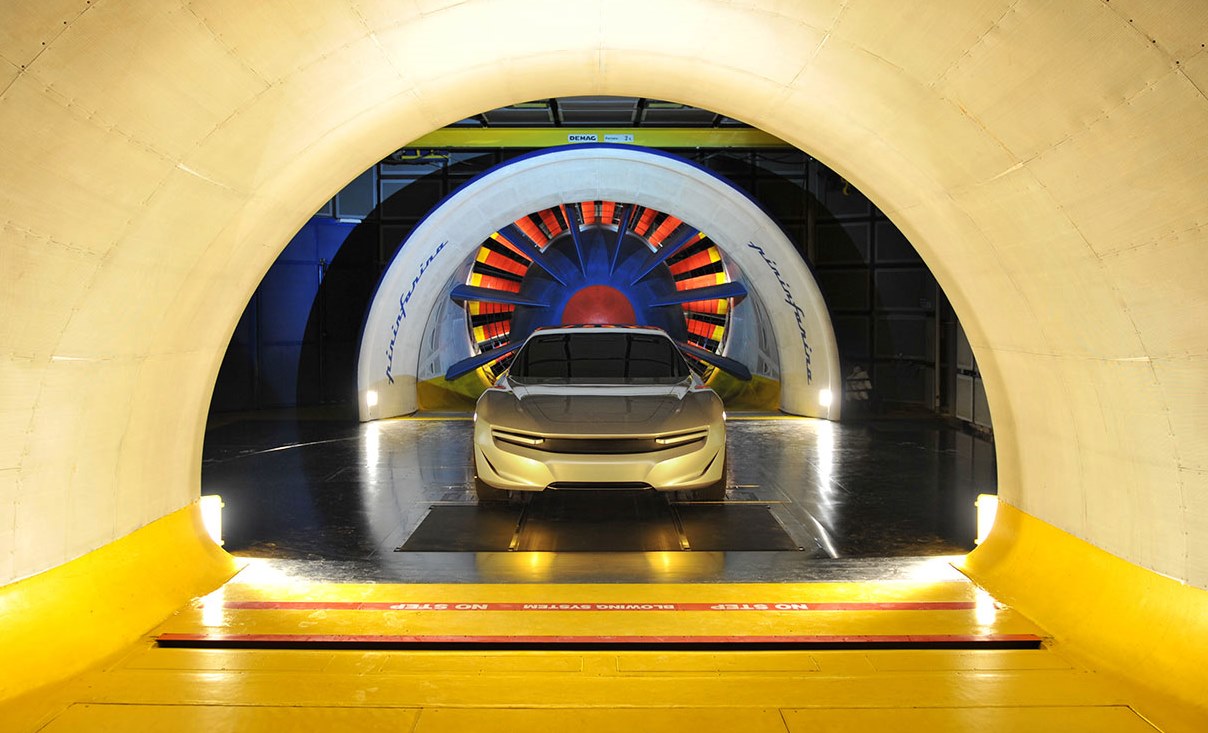
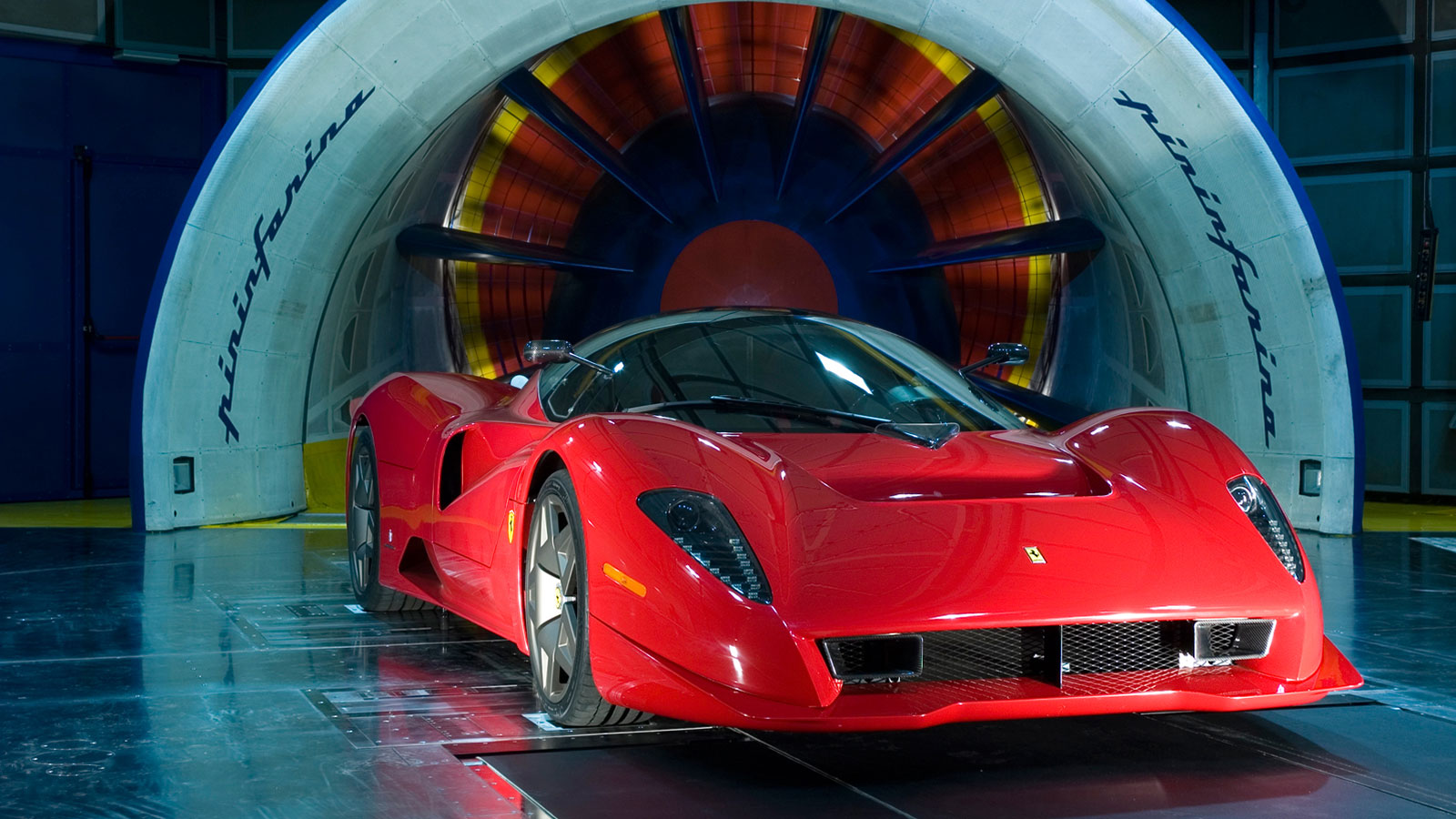
Pininfarina, the automotive design consultancy, also decided to build its own wind tunnel and it was large enough to test full-sized vehicles. At the time it began operations, it was Italy’s first wind tunnel to be built for testing full-sized cars, and one of only seven in the world. That was in the year 1972 and this year sees it celebrating its 50th anniversary.
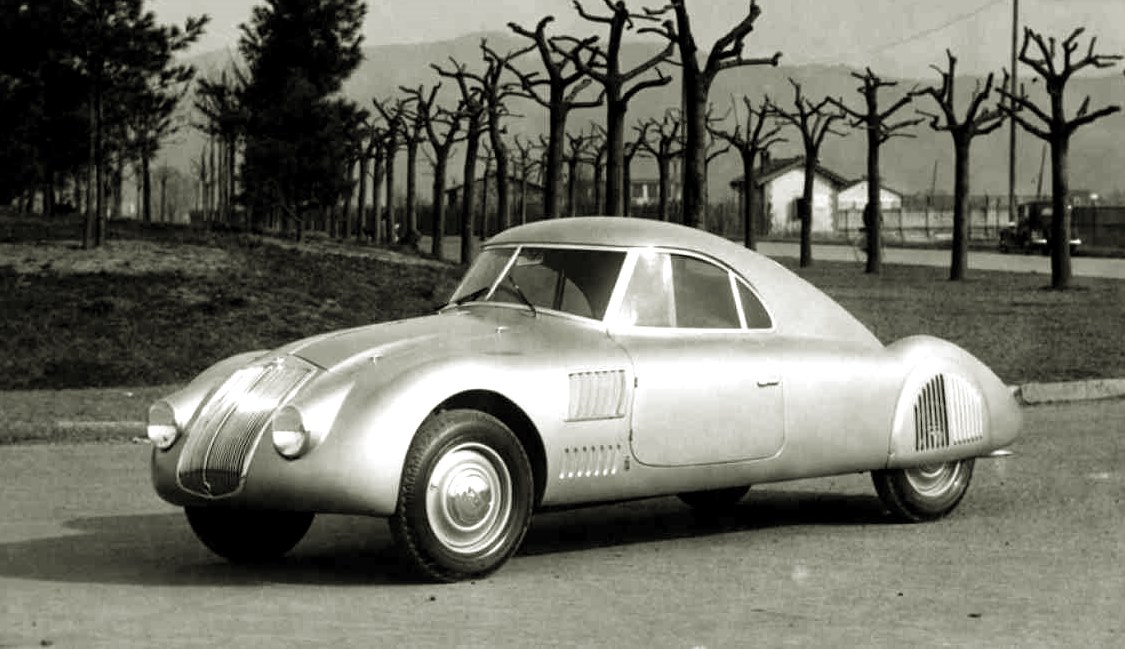
“Without a doubt, Pininfarina has a real passion for aerodynamics. And it’s a passion that has lasted more than 50 years, long before my father decided to build the structure. It all began with my grandfather Pinin, whose visionary intuition in aerodynamics is exemplified since the Lancia Aprilia Aerodinamica produced in 1936,” said Chairman Paolo Pininfarina, whose father was Sergio Pininfarina.

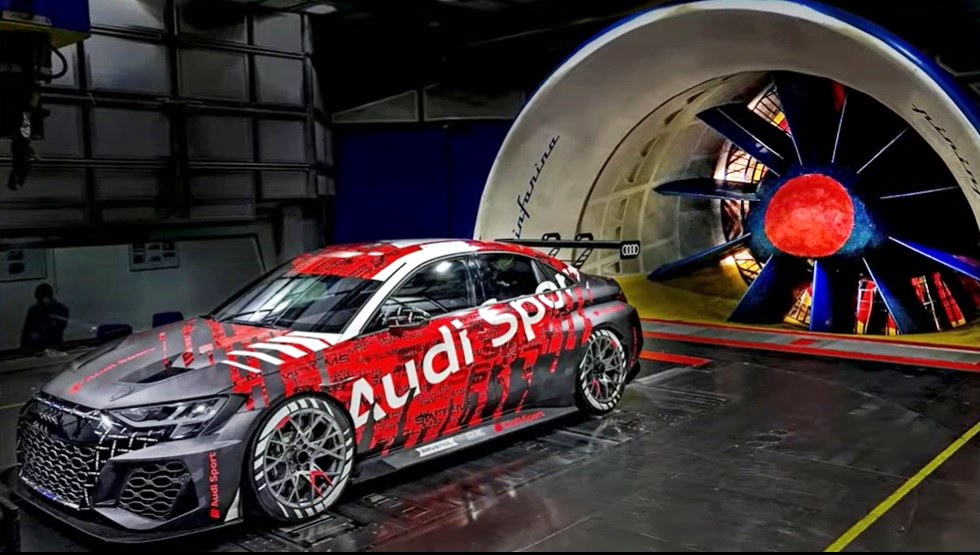
While it was initially used for motor vehicles, Pininfarina’s wind tunnel would become a powerful tool for testing and developing products across all sectors in which the company is fully involved. These include aircraft, high-speed trains, yachts, buildings, wind engineering, industrial design and even sporting goods. With the advent of electric mobility, there is even greater emphasis on aerodynamics as well as aeroacoustic development.
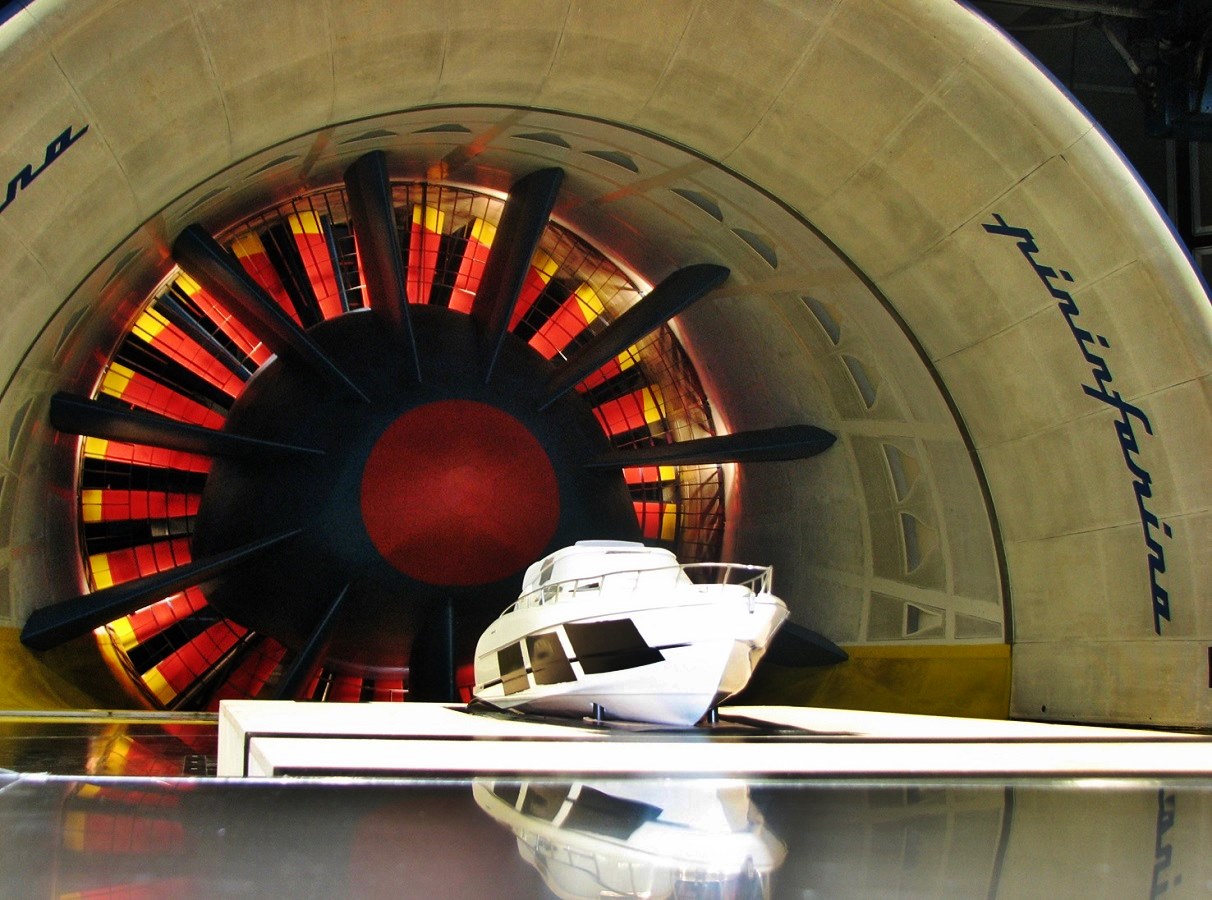

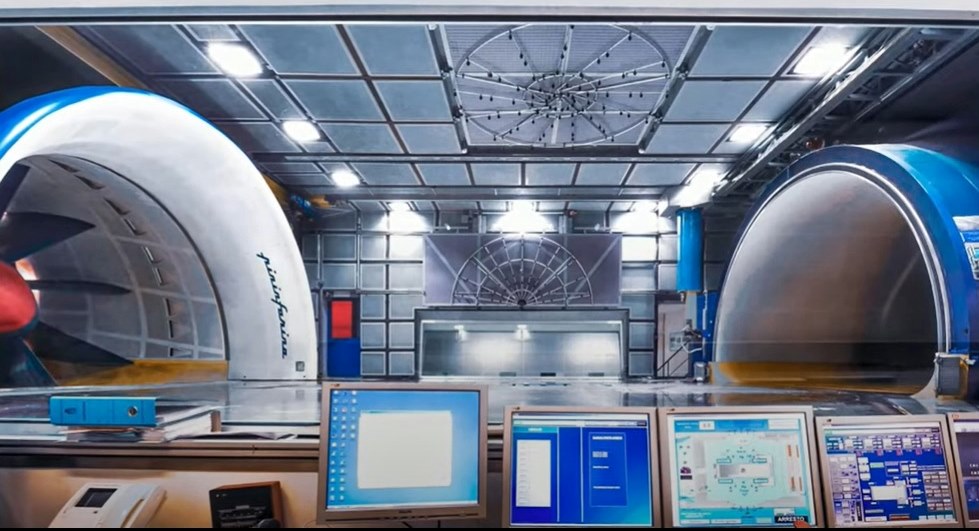
It is one of the few wind tunnels in the world to have a TGS – Turbulence Generator System – able to create various conditions of controlled turbulence associated with gusts of wind, overtaking manoeuvres, cross-winds and vortices generated by cars ahead.
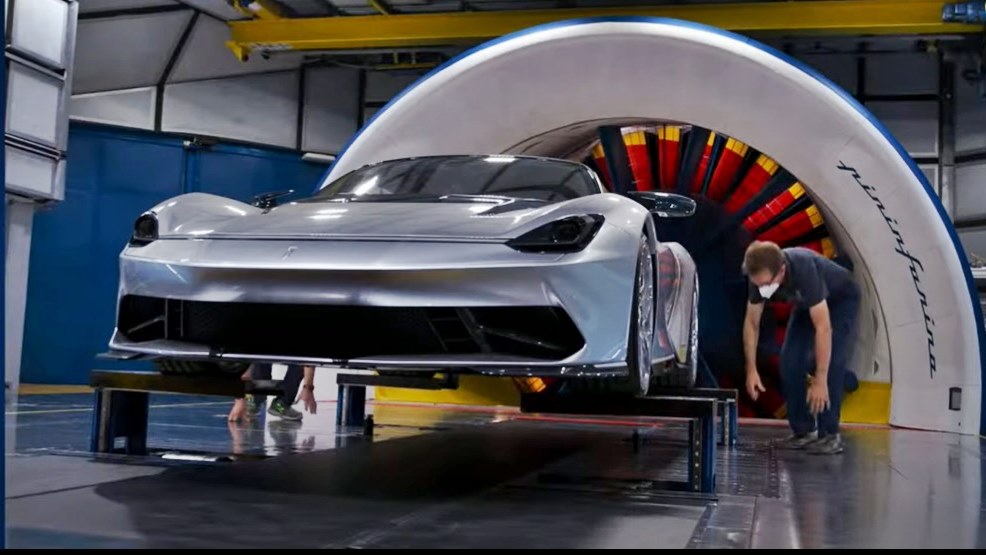
There is also a Ground Effect Simulation System allows reproduction of real vehicle motion conditions. This is achieved by having 4 rollers and 3 mats to allow the wheels of the vehicle and the ground to move at the same wind speed. This system was developed to make the tunnel test conditions as faithful as possible to the road conditions, and to analyze the movement of air underneath.
While most cars have closed cabins, there are also convertibles with open tops as well as the increasingly popular fitment of sunroofs that create an opening on the roof. These all have significant implications on airflow and noise generation, as those who have been in such cars will know. In the wind tunnel, the turbulence generated can be studied and solutions developed to make things more comfortable.
When it first started operation, the wind speed inside the tunnel was less than the 250 km/h maximum of today. It was upgraded with the addition of 13 fans, with each fan able to spin at a different speed or have a different blade pitch. Noise levels were also reduced allowing better aeroacoustic studies with new noise measuring techniques. Aeroacoustic tests are becoming a fundamental element for increasing driving comfort, particularly for hybrid and battery electric vehicles.
The wind tunnel is equipped with three external microphone arrays and also cameras, helping to identify the sources of noise and consequent definition of countermeasures. Noise Vision and Beam Forming support enables visualization to aid analysis. In addition, the wind tunnel is also equipped with 4 acoustic dummies for internal acoustic comfort evaluation.
“The Wind Tunnel has given our company a considerable competitive edge, being the only design company to own one. Born as a tool with which Pininfarina developed its own projects, today it’s a strategic asset for the group, thus expanding the portfolio of services that we offer to the market: an activity that supports other sectors beyond the automotive, from transportation to architecture, from nautical to industrial design,” said CEO Silvio Pietro Angori.