Being able to develop electric vehicles (EVs) is a vital expertise for carmakers as the industry speeds towards electrification of its products. However, just as vehicles with internal combustion engines are useless without liquid fuel, EVs will not run without electricity. The electricity can come from various sources – even the sun – but what’s more important is being able to store the energy.
That’s where batteries come in and currently, there is much focus on the development of batteries for EVs, with the technology advancing very quickly. As we have seen with the shortage of microprocessors disrupting vehicle production globally, a shortage of batteries would also mean EVs cannot leave the factory, even if the vehicle is completed.
For this reason, the major carmakers have looked for ways to secure supply of batteries for coming years as demand for EVs increases rapidly. The biggest companies have established their own subsidiaries to develop and manufacture batteries, setting up factories around the world to ensure that different regions are covered.
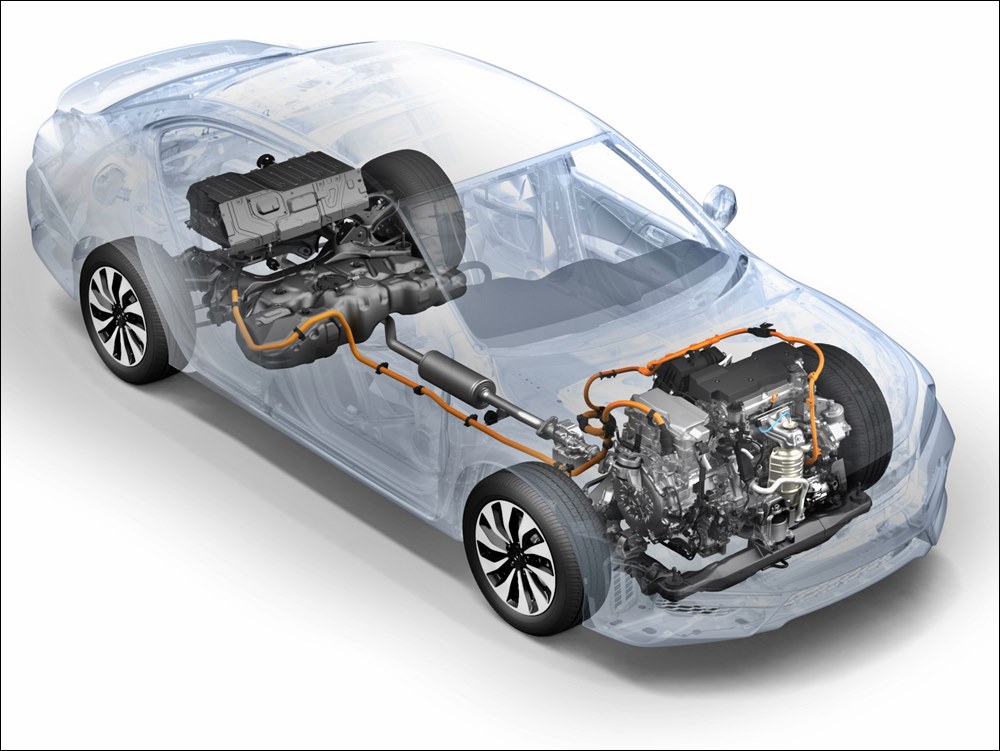

Following on from the January announcement, it has been reported by Nikkei that the joint venture between Honda and GS Yuasa International will invest over 400 billion yen (around RM13.3 billion) to establish an efficient production operation including the supply chain for key raw materials. This will include building a new factory in Japan which will have a production capacity likely to be up to 20 gigawatt hours (GWh), according to the newspaper’s report.
Honda and GS Yuasa have had a close relationship since 1981 when Yuasa began supplying batteries as original equipment for Honda motorcycles. Over 4 decades, the two companies have grown together and with the EV age starting, Yuasa’s long expertise in making batteries (going back to 1915) has become even more valuable. The company evolved into GS Yuasa Corporation in 2004 and five years later, formed a joint venture with Honda that was called Blue Energy Co. (BEC) to produce lithium-ion batteries for Honda’s hybrid models.
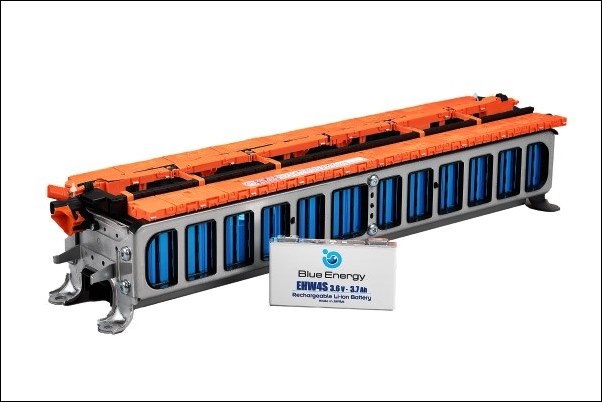

In January this year, Honda and GS Yuasa announced the basic agreement toward collaboration for a high-capacity, high-output lithium-ion battery. With the EV market becoming more competitive, this is an important step for Honda not only in R&D and battery production methods but also establishing a supply chain for key raw materials and a highly-efficient battery production system.

“Honda is striving to realize carbon neutrality for all products and corporate activities which the company is involved in by 2050. Honda and GS Yuasa have already been working together on lithium-ion batteries for hybrid electric vehicles, and this new collaboration will further accelerate Honda’s electrification strategies toward the achievement of our carbon neutrality goal,” said Toshihiro Mibe, Director, President and Representative Executive Officer of Honda Motor.

While Blue Energy has not been named, it is believed that this company will also be involved in the factory which would make sense. Production is expected to begin in 2027.
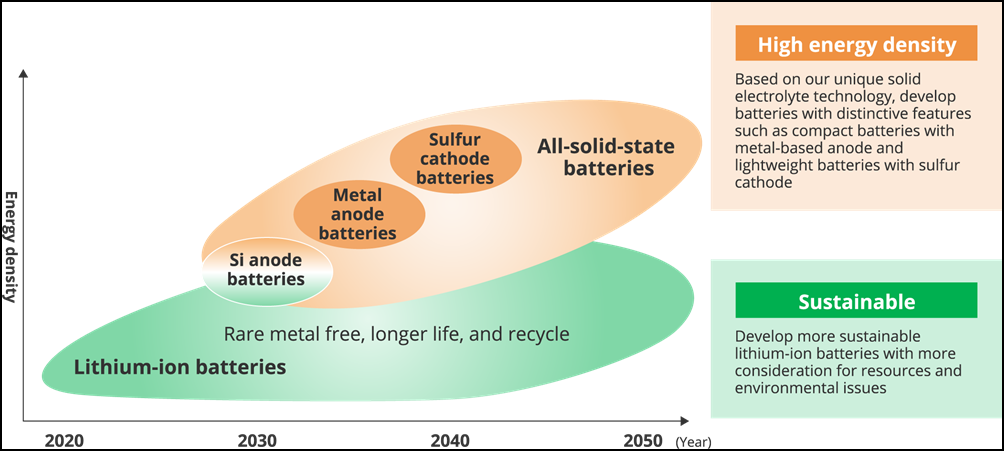
Earlier this month, in its presentation of Vision 2035 (GS Yuasa’s long-term vision and 6th Mid-Term Management Plan), the company showed its R&D roadmap for battery development over the next 3 decades. It will move towards all-solid-state batteries to achieve higher energy density with the company’s unique solid electrolyte technology. Liquid electrolyte lithium-ion batteries as they currently exist will evolve into batteries free from the use of rare metals, possessing longer lives, and capable of being recycled.