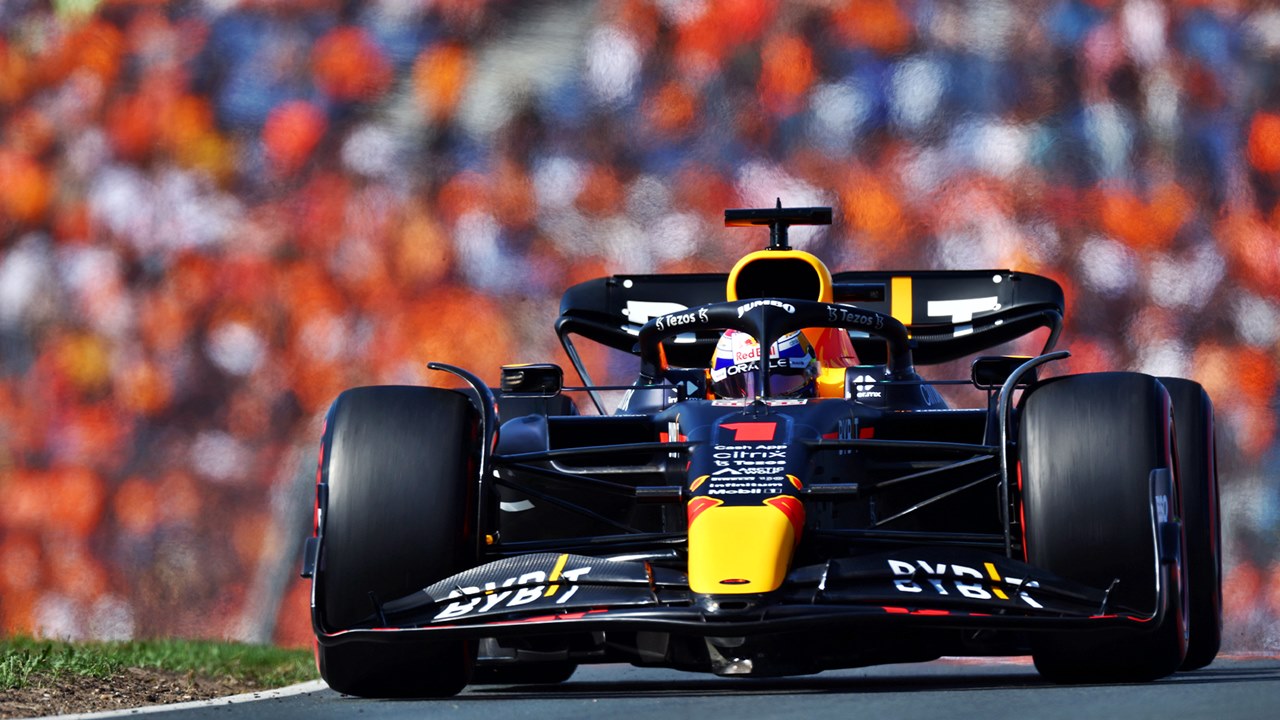
Last year saw the return of the Dutch Grand Prix after a 36-year gap – the longest in the Formula 1 championship. The reason it had dropped off the F1 calendar was due to financial difficulties that prevented the Zandvoort circuit from being modernized and upgraded as the sport evolved. It was only in 1995 that proper investment was made with a new owner and the circuit, which had its first race in 1948, was redesigned and redeveloped.

The last F1 race in 1985 was won by Niki Lauda when he was with McLaren, which also won the championship that year. Besides Lauda, the drivers of that era were men like Jim Clark, Jackie Stewart and Rene Arnoux, all retired (or passed away).

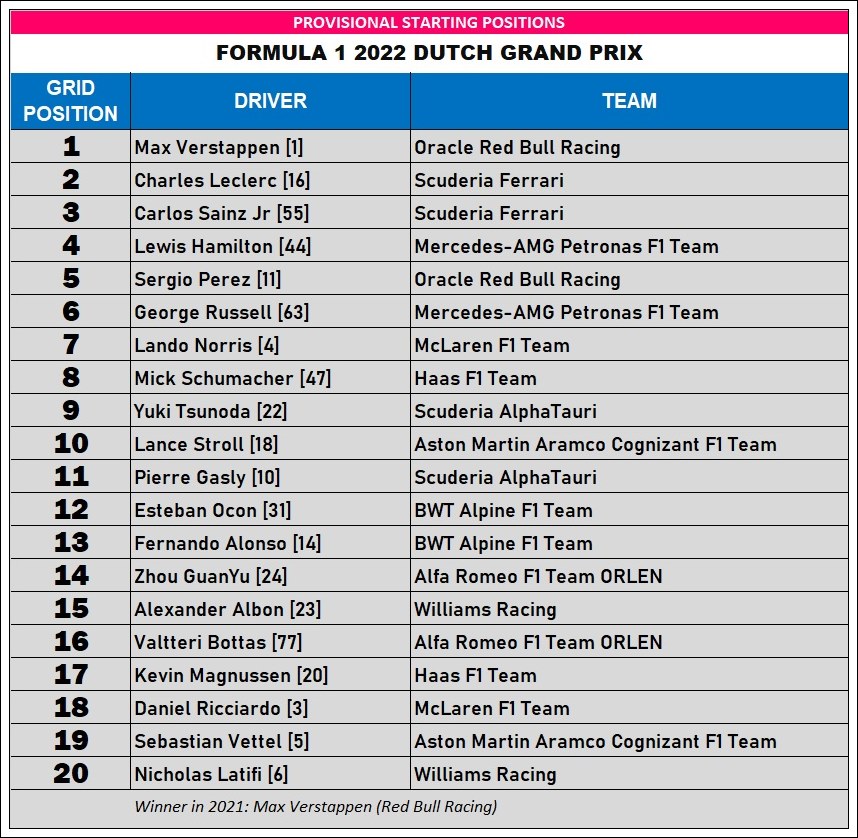
While the 4.3-km layout of today’s circuit for Round 15 of the 2022 championship differs greatly from the one that existed in the first 50 years, some of the drivers who raced in last year’s championship round were familiar with it from their Formula 3 years.
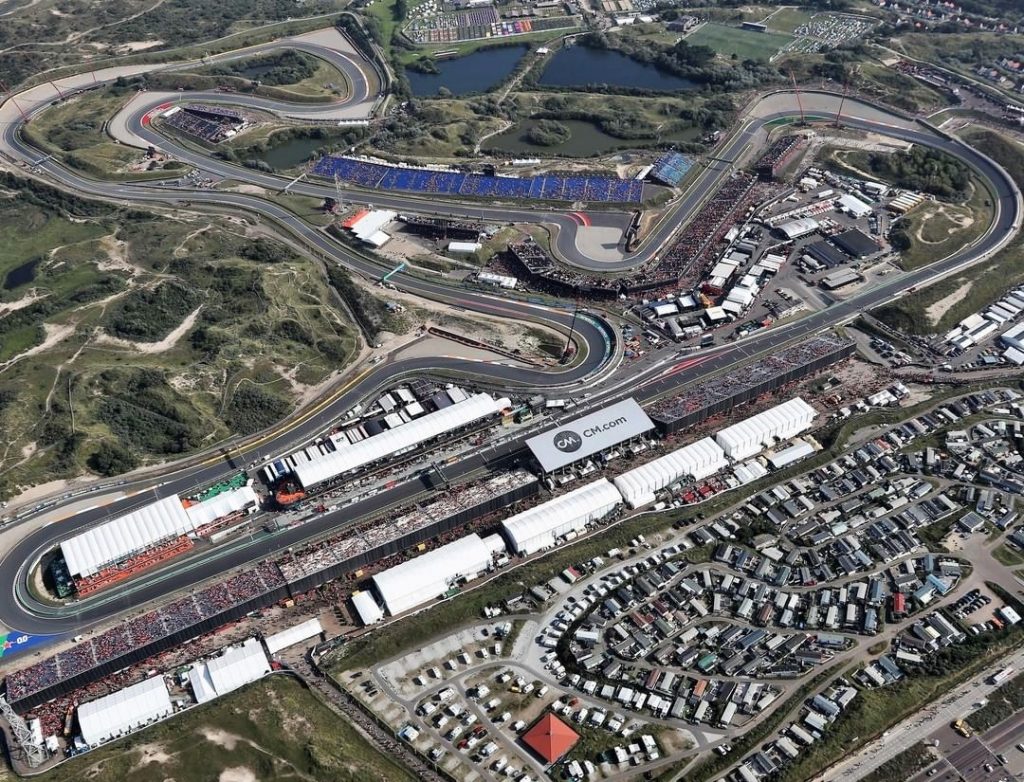
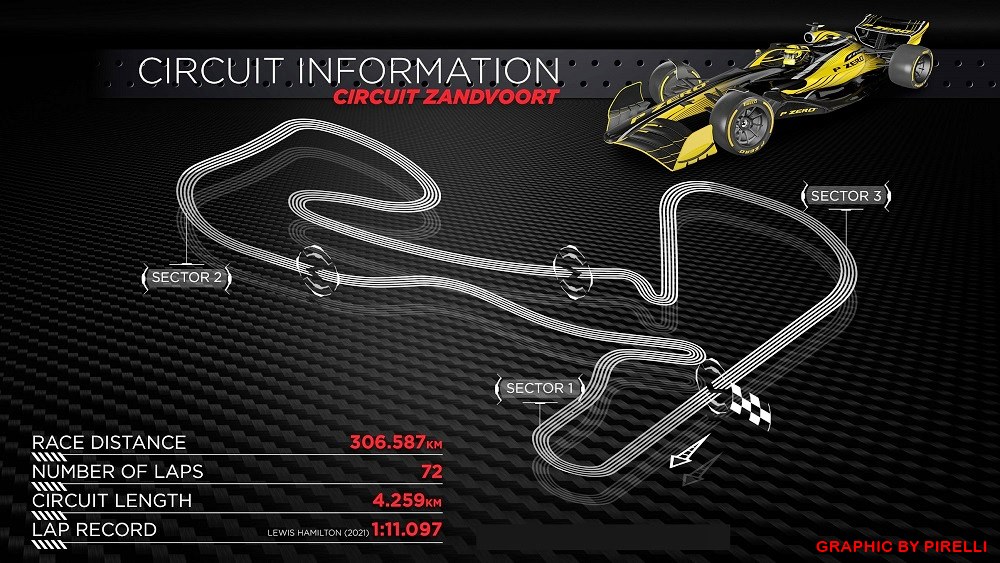


Zandvoort is a challenging track with 14 corners, many of them fast and sweeping with the ‘Tarzan Corner’ hairpin at the end of the start/finish straight. Undulating, rising and falling between the sand dunes, with a rollercoaster-like vibe similar to Portimao, it has an old-school feel, which many of the drivers like. “It’s definitely a unique challenge for the drivers and puts many aspects of an F1 car to the test,” said Mercedes-AMG’s Toto Wolff.

The elevation change is almost 8 metres and being located across the road from the North Sea, strong wind can be expected, sometimes blowing sand onto the track and affecting grip (an issue normally associated with places like Bahrain).
Zandvoort doesn’t feature many long straights and a lot of the lap is spent cornering. Due to this, it’s a track with low power sensitivity and engine duty, so the Power Unit has an easier time than at other tracks, where it is worked harder.

Because of the many high-speed changes of direction, where the mass of the car can work against you, Zandvoort has the highest mass sensitivity of the year – which means, carrying more fuel will be more penalising. But it’s below average for tyre duty and wear, because most of the corner speeds and loads sit in the middle of the. Many sequences are also very flowing rather than stop/start, which puts traction demand into the tyre.
“The most challenging parts for the tyres are the banked Turns 3 and 14, which are taken at high speed and place sustained combined forces on the car: downforce as well as lateral demands. Along with the other overall demands of the circuit layout, this is why we have nominated the hardest three compounds in the range for only the fourth time in 2022, after Bahrain, Spain and Great Britain,” said Mario Isola, Pirelli’s Motorsport Director.
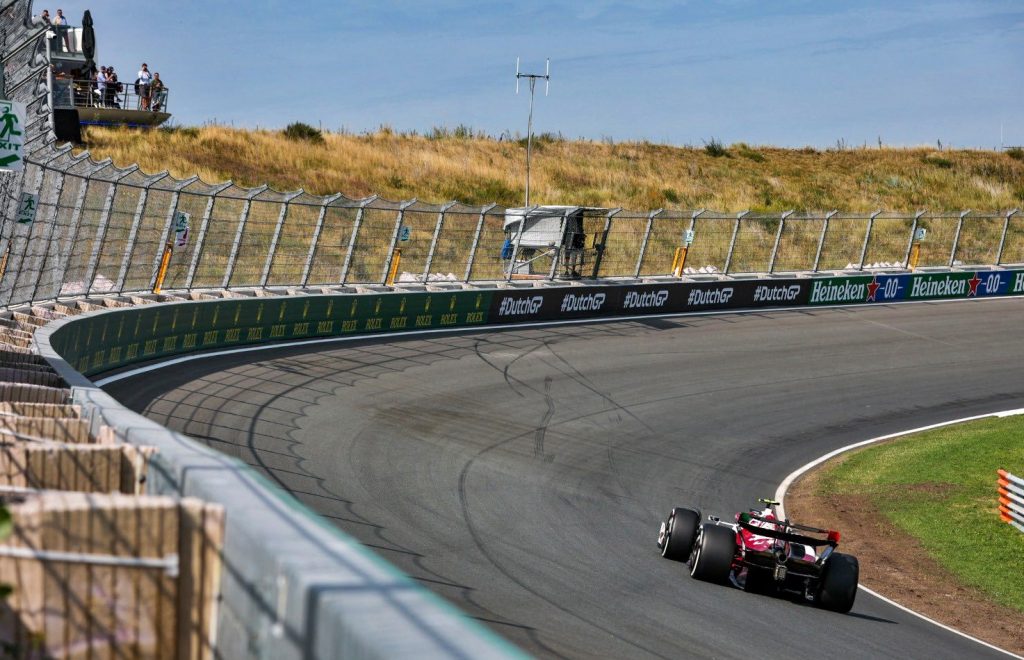

Overtaking is challenging at Zandvoort due to the almost constant sequence of cornering, apart from the main straight (which leads into not a particularly big braking zone) and the back straight (which isn’t very long). This means qualifying performance and pace is vital and makes it one of the most important F1 qualifying sessions of the year.
“The new F1 car-tyre package this season should make overtaking easier on a track where it was hard to pass last year. The majority of drivers stopped just once to maintain track position but this time, there could be more of a focus on the softer compounds – which might lead to more two-stoppers and drivers pushing even harder,” predicts Isola.


There are two very different tarmacs at Zandvoort, which means the tyres behave quite differently on one relative to the other. There’s some new, smoother tarmac laid in 2020, and the rest of the track features an older, more aggressive surface. This makes it tricky to rebalance the car for all corners, because the surfaces can be different from one corner to the next.
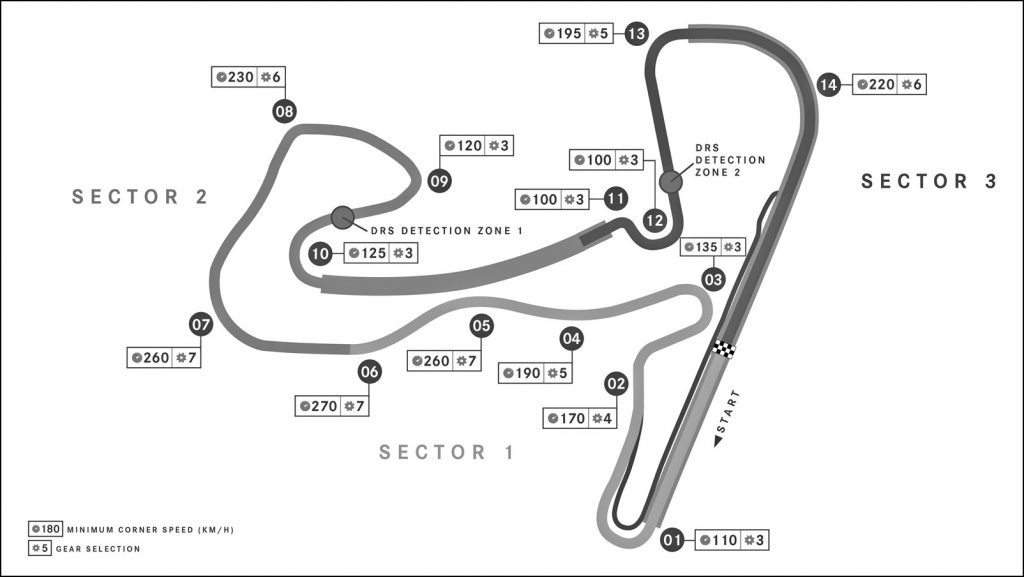
Drivers experience 5.2g through the long, sweeping Turn 7 at Zandvoort, one of the highest lateral g-forces of the entire season. Of the 10 braking sections, two are classified as highly demanding on the Brembo brakes, six are of medium difficulty and the remaining two are light.
The most difficult one for the braking system is on the first turn because the cars come off a 1.1-km straight with no braking on the last turn. The single-seater F1 cars hit the brakes at 317 km/h and drop to 133 km/h in just 111 metres. To achieve this, the drivers brake for 1.99 seconds and sustain 4.8g of deceleration.

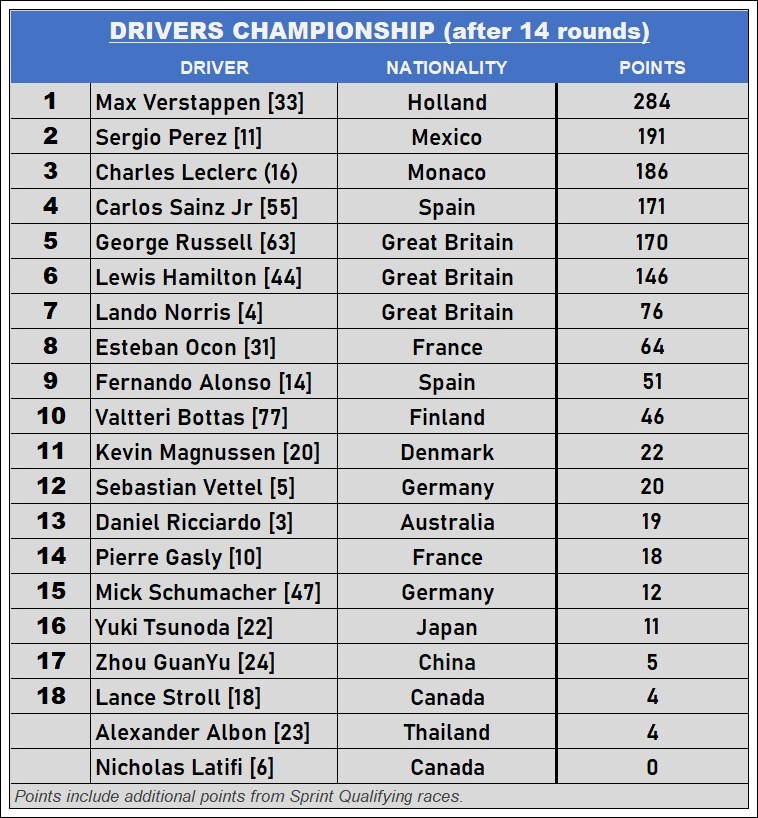
Because of the very long gap from the 1985 Dutch F1 GP, the most successful driver remains one from that era and it is Jim Clark who won 4 times in the 1960s. Max Verstappen won last year at his home race, and if he repeats his winning form for the next few years, he could replace Clark.
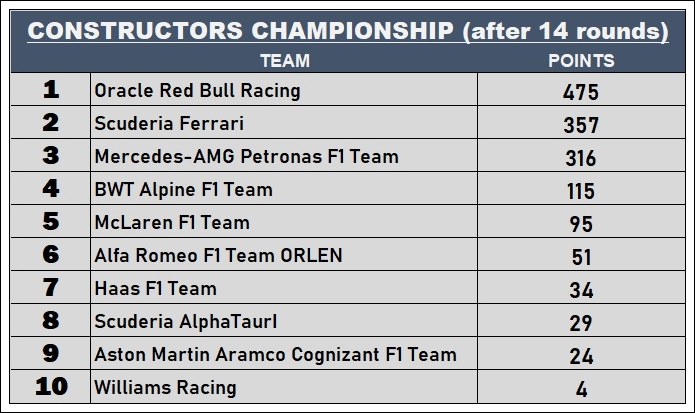
Scuderia Ferrari has been the most successful team in the Dutch F1 GP with 10 victories between 1952 and 1983. During that period, the team had drivers like Alberto Ascari. Juan Manuel Fangio, Mike Hawthorn, Phil Hill, John Surtees, Niki Lauda and Jody Scheckter.