Over the next 10 years, Honda will allocate approximately 5 trillion yen in the area of electrification and software technologies to further accelerate its electrification, which is approximately 62% of the company’s overall R&D expenses budgeted for the same. This expenditure will enable it to have up to 30 EV models globally by 2030 with production volumes of more than 2 million units annually. This huge investment will help Honda achieve carbon neutrality for all products and corporate activities by 2050.
The strong focus on EVs – and presumably, Honda is referring to battery electric vehicles (BEVs) – may suggest that the carmaker will be decreasing development of internal combustion engines (ICE) and hybrid vehicles (HEVs). In fact, last year, it announced the intention to stop producing and selling new ICE vehicles, including hybrids, worldwide by 2040.
However, like what a number of major carmakers are saying, hurried adoption of BEVs is not a practical approach. Due to regional differences such as the level of customer acceptance, affordability, readiness of infrastructure and economic conditions, a singular approach to switching to BEVs globally is not going to work.
Honda will therefore be working on rapid transitioning to BEVs in markets and regions such as the USA, Europe, China and Japan while continuing with a more realistic solution for other areas. In those major markets for electrification, the ratio of BEVs and fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs) will be increased at a faster rate. In relation to overall unit sales, these zero emission vehicles will account for 40% of volume by 2030, 80% by 2035, and 100% by 2040.

And even though North America is one of the regions that is part of the main electrification plan, Honda has still allocated R&D resources to develop new hybrid models for the near-term. This is to increase HEV volume of core models such as the CR-V, Accord and Civic which are produced there. Honda currently sells 4 HEV models in North America. However, Insight production will end in June to start production of the new CR-V Hybrid this year, followed by the Accord Hybrid, which will eventually make up 50% of the sales mix of each model.
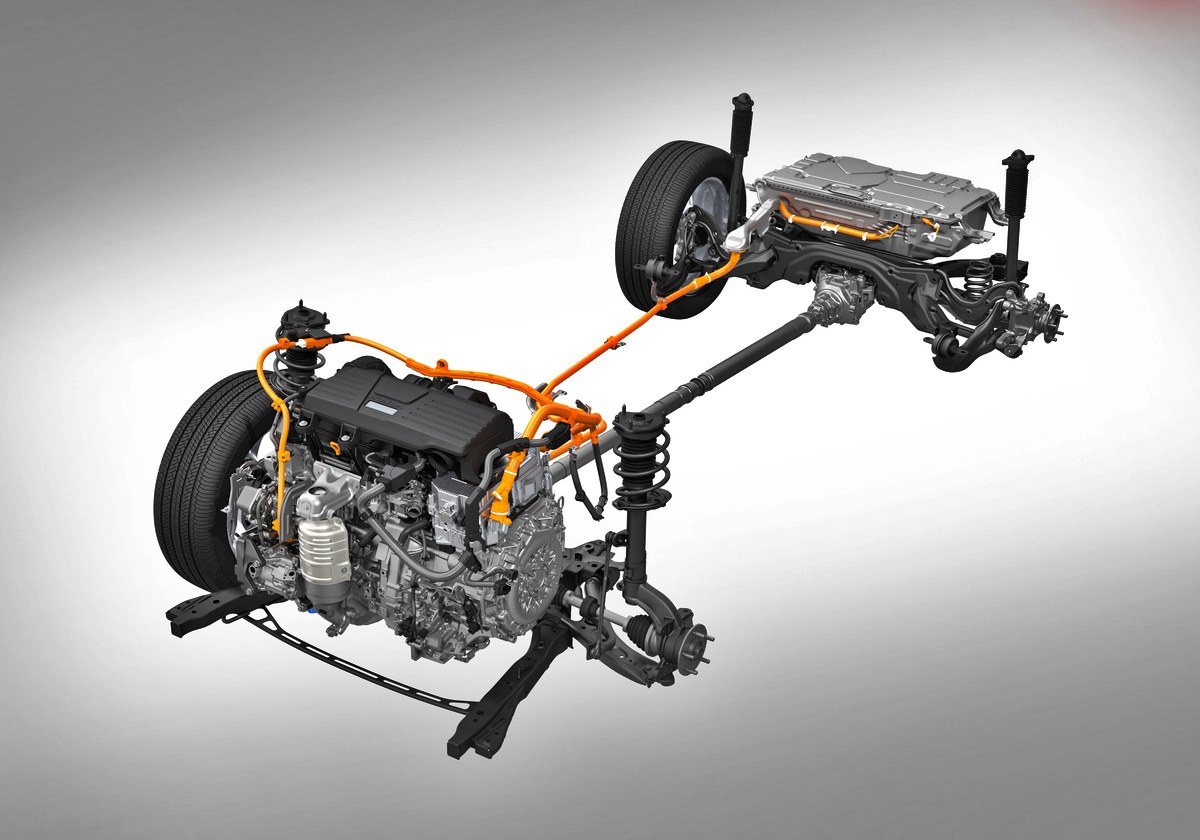
“We need to take into account multiple factors, such as the living environment and the penetration rate of renewable energy, rather than simply switching to electric vehicles,” said Toshihiro Mibe, Honda’s CEO. “We are ending conventional engines but we will still focus on hybrids, and it will be our strength in 2030 or even in 2035.”
Honda, along with Toyota, were the first brands to introduce HEVs and while the Prius was the first into the market, Honda’s first generation of Insight arrived in the USA 7 months before the Toyota HEV. Following the futuristic looking Insight was the Civic Hybrid in 2002 and then the Accord Hybrid.


Honda continued to improve its hybrid technology (which it also refers to as e:HEV technology in some markets) as well as try to bring costs down and developed better hybrid powertrains for the next generations of the models. It also came out with a HEV sportscar, the CR-Z, in 2010 but as sales of coupes slowed down, the model line did not continue into a second generation.
So HEVs still have a future, more so now that they have moved from being of interest to early adopters to become more mainstream in the marketplace. While most HEV buyers would be aware that their car is powered by a petrol engine as well as an electric motor, the fact that a HEV needs no recharging (a plug-in hybrid or PHEV does) makes the technology ‘invisible’. It’s like turbochargers; in the 1970s, they were distinct features in high-performance engines but today, their presence is taken for granted in the new generation of downsized engines.

Honda’s continued attention to HEVs will also be beneficial in other markets where BEV adoption may be slow. HEVs can still help in a small way on the climate change issue as they generate lower carbon dioxide gases which have been identified as a major cause of global warming.
Honda Civic Hatchback e:HEV Hybrid for Europe – will it come to Malaysia too?