In the late 1990s, the ‘merger of equals’ between Chrysler and Daimler led to the start of the mega corporations in the auto industry. The new company was the result of the largest industrial merger ever, worth US$130 billion in 1998. While DaimlerChrysler lasted less than 10 years, it set in motion a rush of mergers in the industry and the next group to come together was Renault and Nissan, forming an alliance in 1999. The Alliance helped to save Nissan from financial collapse which went on to become a successful partnership with shared resources during the 2000s.
In 2016, it was Nissan’s turn to help save another manufacturer – Mitsubishi Motors (MMC) – which lacked scale to progress healthily. With Nissan acquiring a 34% controlling stake in MMC, the smaller company was able to become a ‘junior partner’ in the Alliance.
One of the Alliance’s most competitive advantages is its ability to strengthen its members by sharing what each one is best at. This approach has allowed each company acquire and use new technologies while reducing costs, lowering prices and thus increasing business performance. For example, shared resources (60% of its models use common platforms) have helped the company focus on other areas of innovation.

The sharing will continue in a bigger way as the Alliance has announced more common projects and actions to accelerate and to shape their shared future towards 2030, focusing on the mobility value chain. The trio will use a common roadmap to 2030 on pure-EV and Intelligent & Connected mobility, with massive investments that none could make alone.
“Among the world’s automotive leaders, the Renault-Nissan-Mitsubishi Alliance is a proven, unique model. For 22 years, we have been building on our respective cultures and strengths for our common benefit,” said Jean-Dominique Senard, Chairman of the Alliance. “Today, the Alliance is accelerating to lead the mobility revolution and deliver more value to customers, our people, our shareholders and all our stakeholders. The three member-companies have defined a common roadmap towards 2030, sharing investments in future electrification and connectivity projects.
Moving forward together
The Alliance members have developed a ‘smart differentiation’ methodology that defines the desired level of commonality for each vehicle, integrating several parameters of possible pooling, such as platforms, production plants, powertrains or vehicle segment. This is supplemented and enhanced by a stricter approach to design and upper-body differentiation. For example, the common platform for the C and D segment will carry 5 models from the 3 brands of the Alliance (Nissan Qashqai and X-Trail, Mitsubishi Outlander, Renault Austral and an upcoming 7-seater SUV).
Strengthening this process, the Alliance members will enhance usage of common platforms in the coming years from 60% today to more than 80% of its combined 90 models during the next 4 years. As part of this, MMC will reinforce its presence in Europe with two new models, among them the new ASX based on Renault models.
5 common EV platforms
Renault, Nissan and Mitsubishi have been pioneers in the EV market, having begun offering products even before the acceleration began in recent years. Nissan, for example, began selling the fully electric LEAF in 2010 which has today become the volume leader globally. In the main markets (Europe, Japan, the US, China), 15 Alliance plants already produce parts, motors, batteries for 10 EV models, with more than 1 million EV cars sold so far and 30 billion e-kilometres driven. To date, the Alliance has invested more than 10 billion euros in the field of electrification.
Building on this long expertise, the Alliance will accelerate its EV business by adding a total of 23 billion euros during the next 5 years on electrification. This investment will see 35 new EV models by 2030. 90% of these models will be based on 5 common platforms, covering most markets, in all major regions

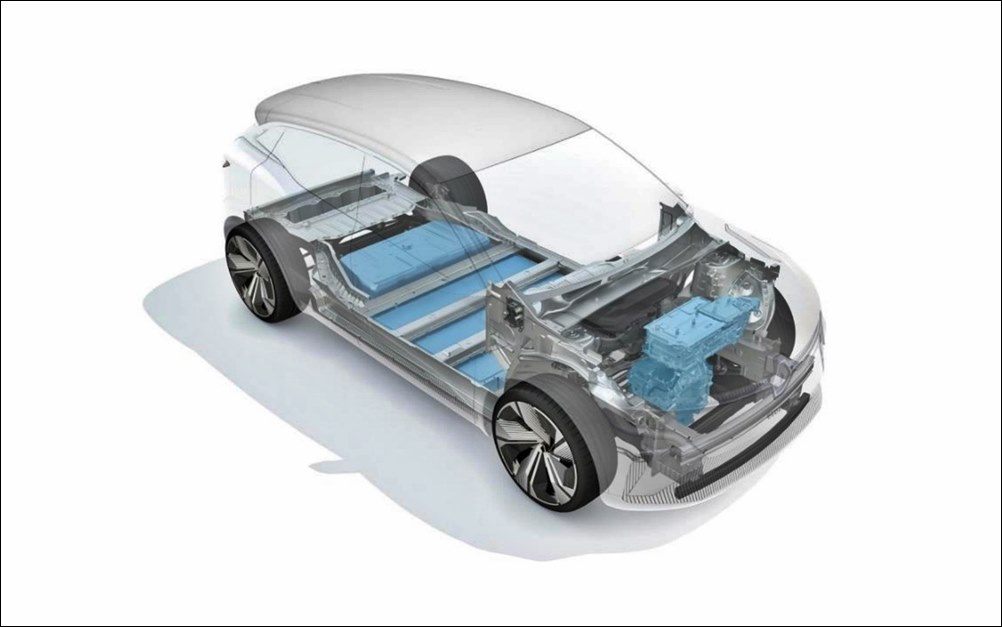
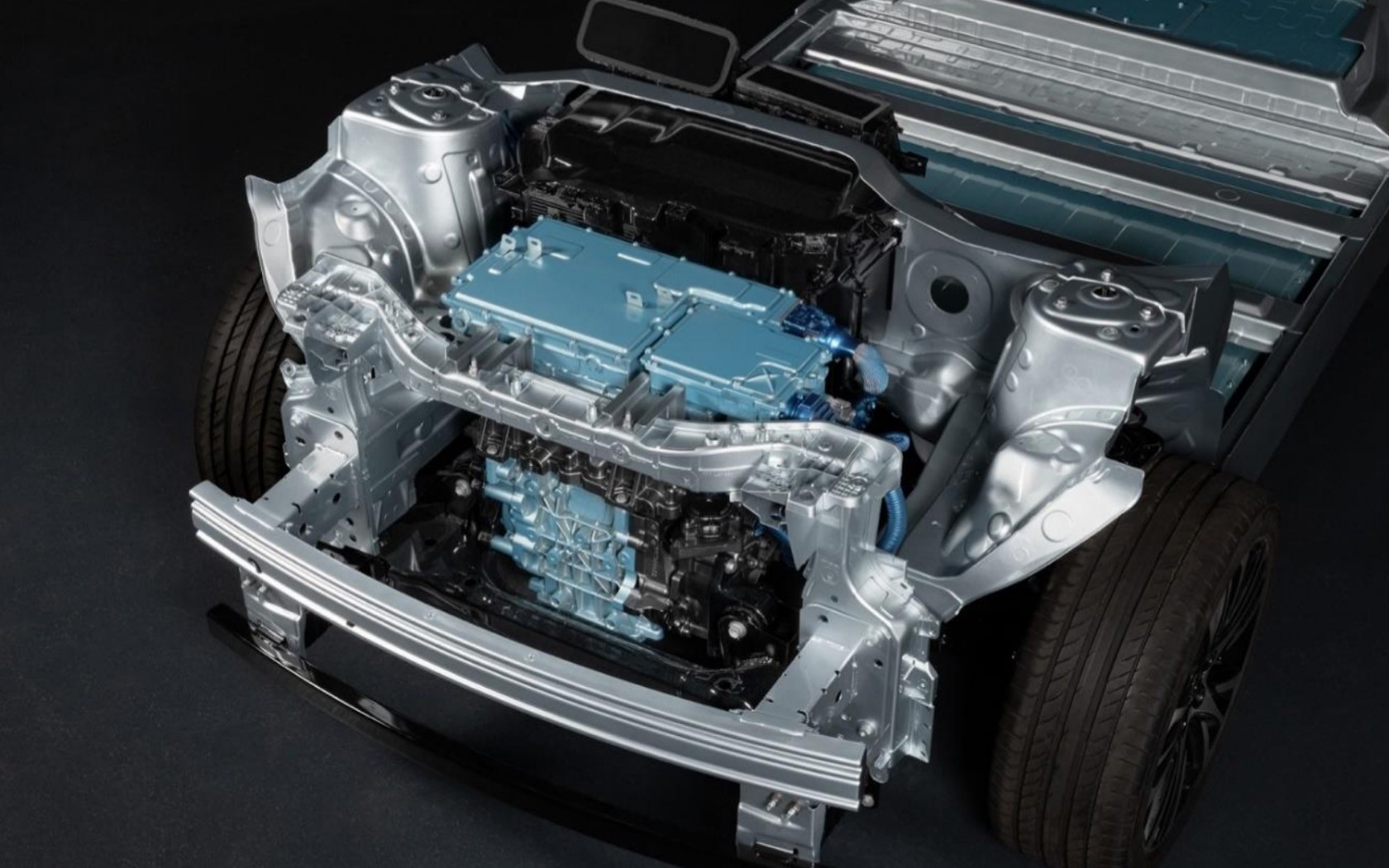
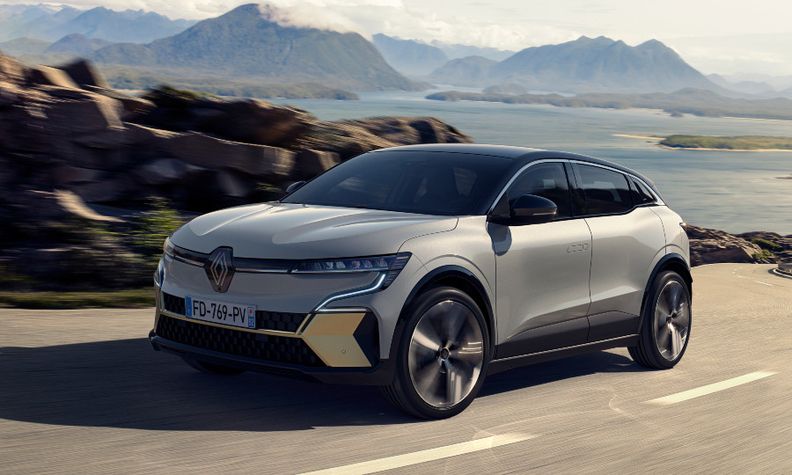
There will be platforms for small models as well as large light commercial vehicles, with the CMF-EV being the global and flexible platform fully engineered for EVs. It is already being used as the base for the Nissan Ariya EV crossover and Renault Megane E-Tech Electric, and its modularity allows the Alliance partners to develop for a new generation of EVs.
The platform has been created to integrate and optimize all the elements specific to a 100% electric powertrain, hosting a new, high-performance motor and an ultra-thin battery. By 2030, more than 15 models will be based on the CMF-EV platform, with up to 1.5 million vehicles produced on this platform each year.
The CMFB-EV, to be launched in 2024, will be the most competitive compact electric platform in the world, it is claimed. It will be able to provide up to 400 kms range from a fully-charged battery pack, thanks for efficient aerodynamic performance. Power consumption will also be more than 10% lower than the current Renault ZOE, while the cost will be lower by 33%.


This platform will be the base for 250,000 vehicles a year under the Renault, Alpine and Nissan brands. Among the new models will be the Renault R5 and a new compact EV that will replace the Nissan Micra. Designed by Nissan and engineered by Renault, the new model is planned to be manufactured at Renault ElectriCity, and electric industrial centre in northern France.
Common battery strategy
Battery technology and production are key elements in electrification strategies and with breakthrough battery innovations and a planned 220 GWh production capacity, the Alliance expects to bring a highly competitive and attractive offer to all customers. Competitiveness is key, and that can be achieved with a common battery strategy which will see (in core markets), Renault and Nissan using a common battery supplier so volumes will be higher for better economies of scale. The aim, with common partners, will be to reduce battery costs by 50% in 2026 and 65% by 2028.
Beyond that, the Alliance shares a common vision for all-solid-state battery technology (ASSB). Based on its deep expertise and unique experience as a pioneer in battery technology, Nissan will lead innovations in this area that will benefit all Alliance members. ASSB will have double the energy density versus current liquid lithium-ion batteries, while recharging time could be be greatly reduced to one-third of today’s time.