After pioneering the mass production of hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) in the late 1990s, Toyota is starting its big push into full electrification with a more extensive line-up of battery electric vehicles (BEVs). Until now, it has focussed on HEVs although it has had a small range of BEVs but now the carmaker is making the big leap towards larger models and aiming for higher numbers.
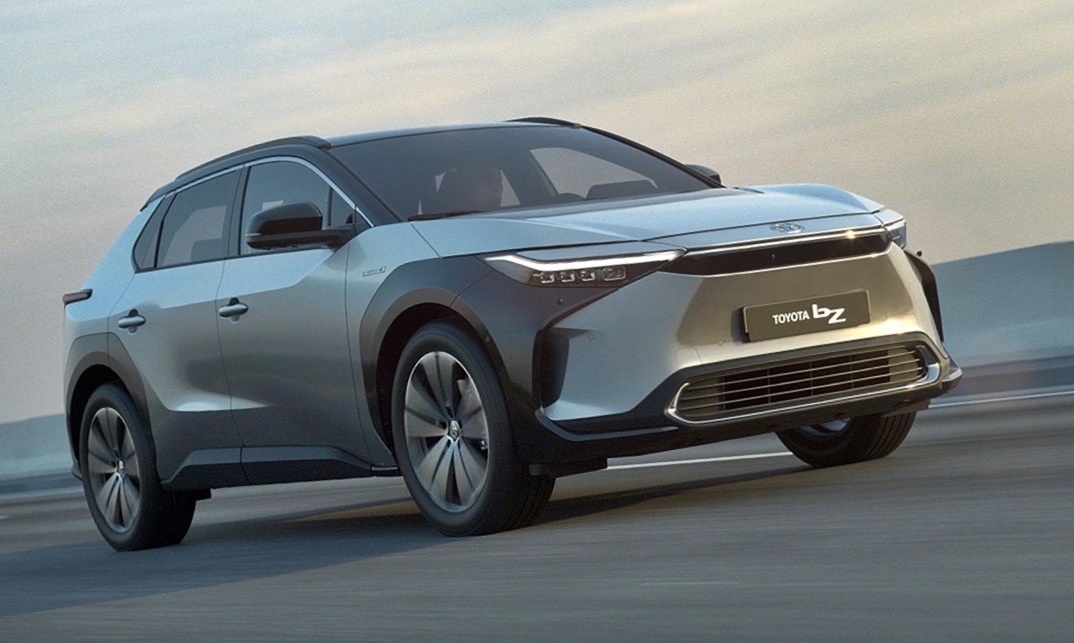
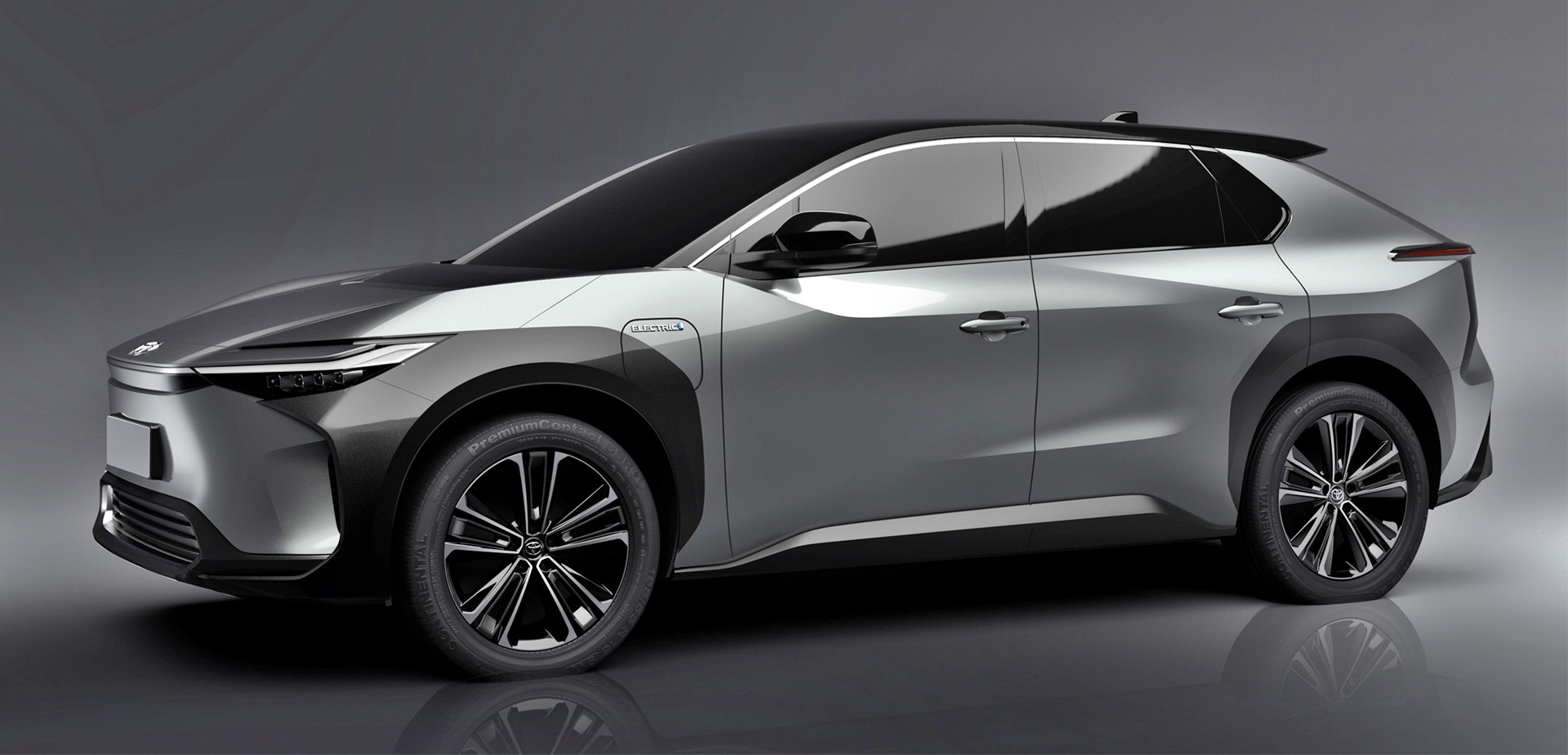
The first of the 7-model bZ range (by 2025) was previewed at Auto Shanghai in April this year in the form of the Toyota bZ4X concept. To be made in China and Japan, worldwide sales of the production version of the new BEV is expected to start by the middle of 2022.
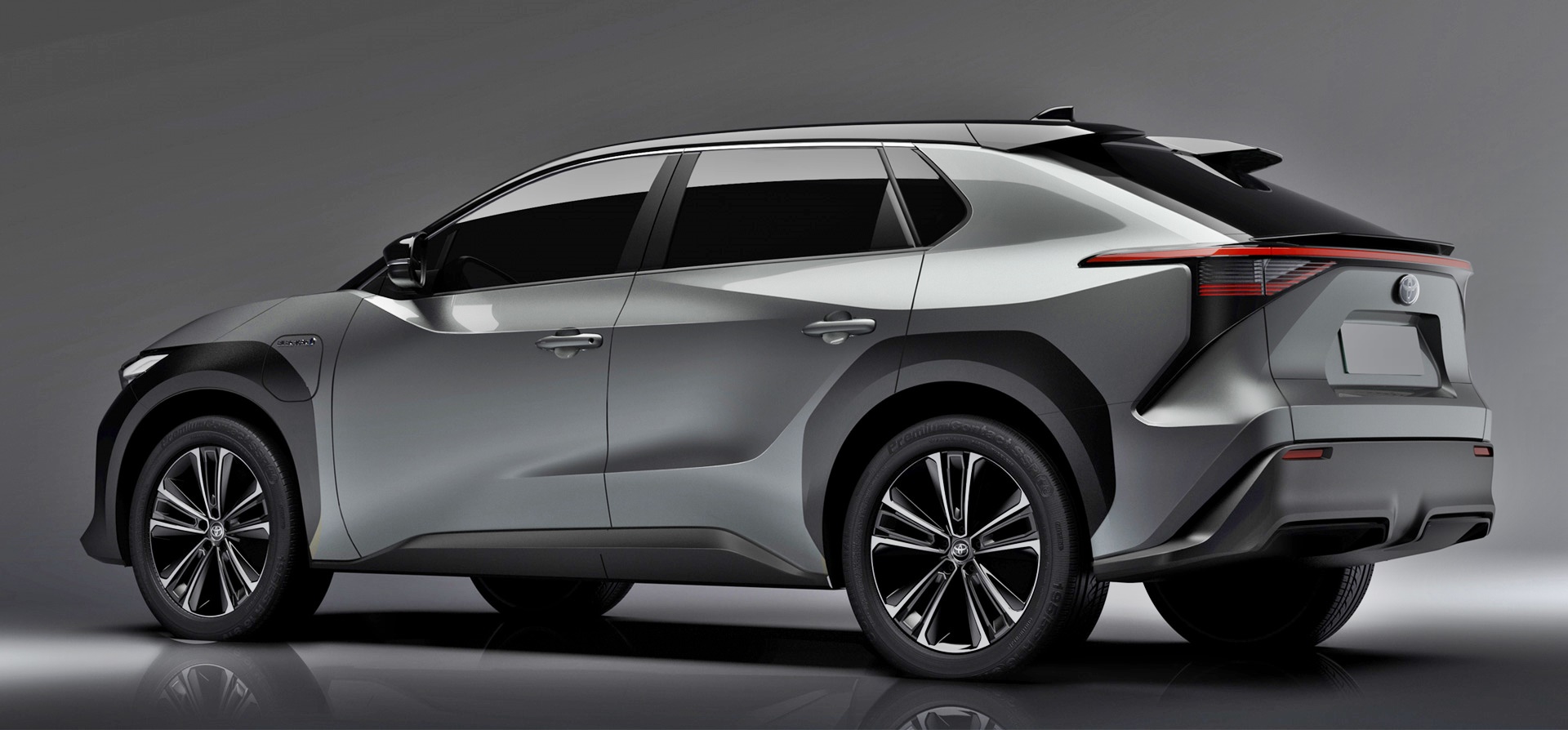
Details of the new model, which will be a SUV, released today show that the production model is pretty much like the concept car. This is not surprising as Japanese carmakers have not wasted time and money on making too many fancy concepts to wow people but which never get built. They have instead previewed near-production concept cars as a final step to get last-minute feedback on designs and features.
e-TNGA architecture
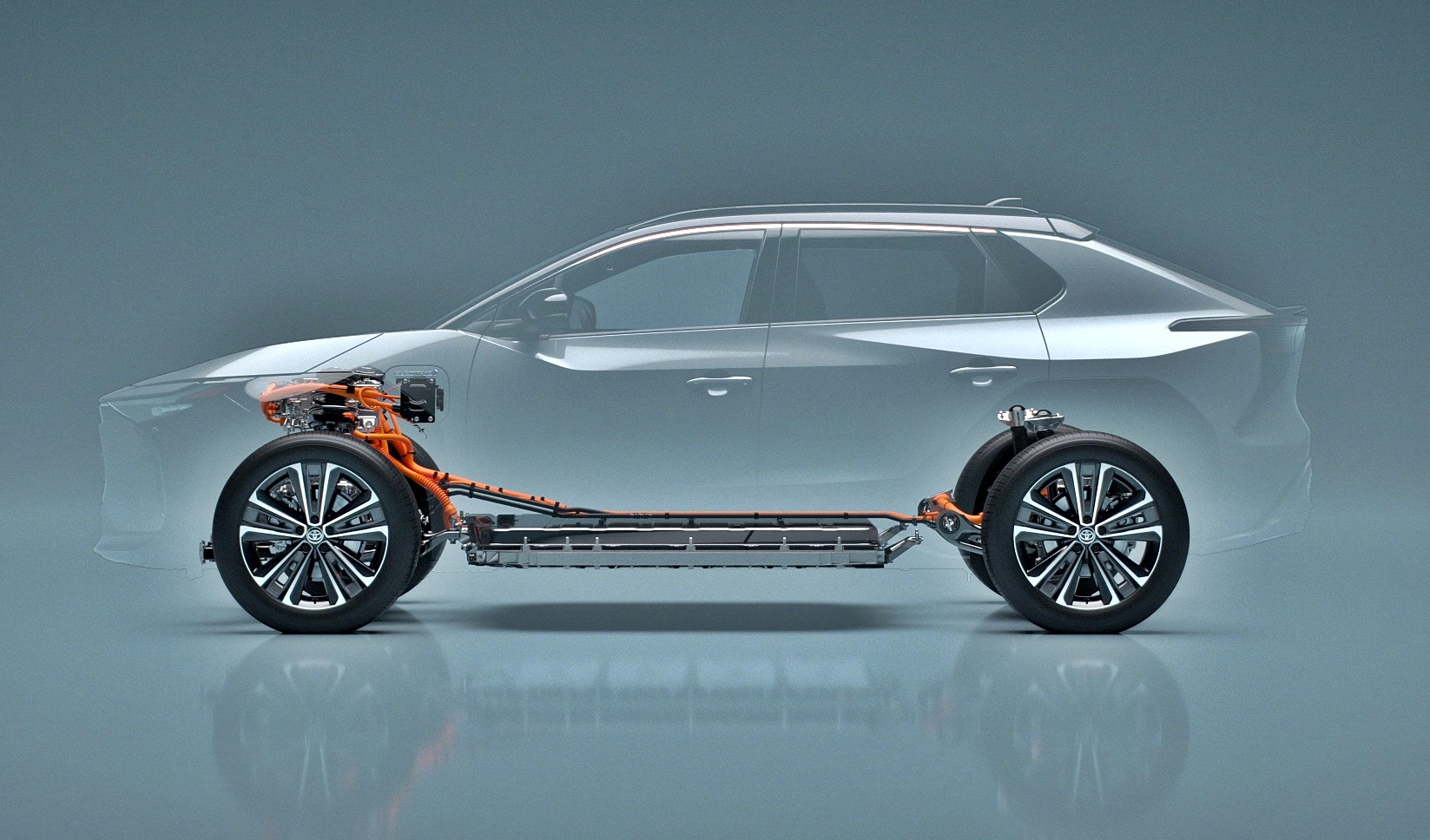
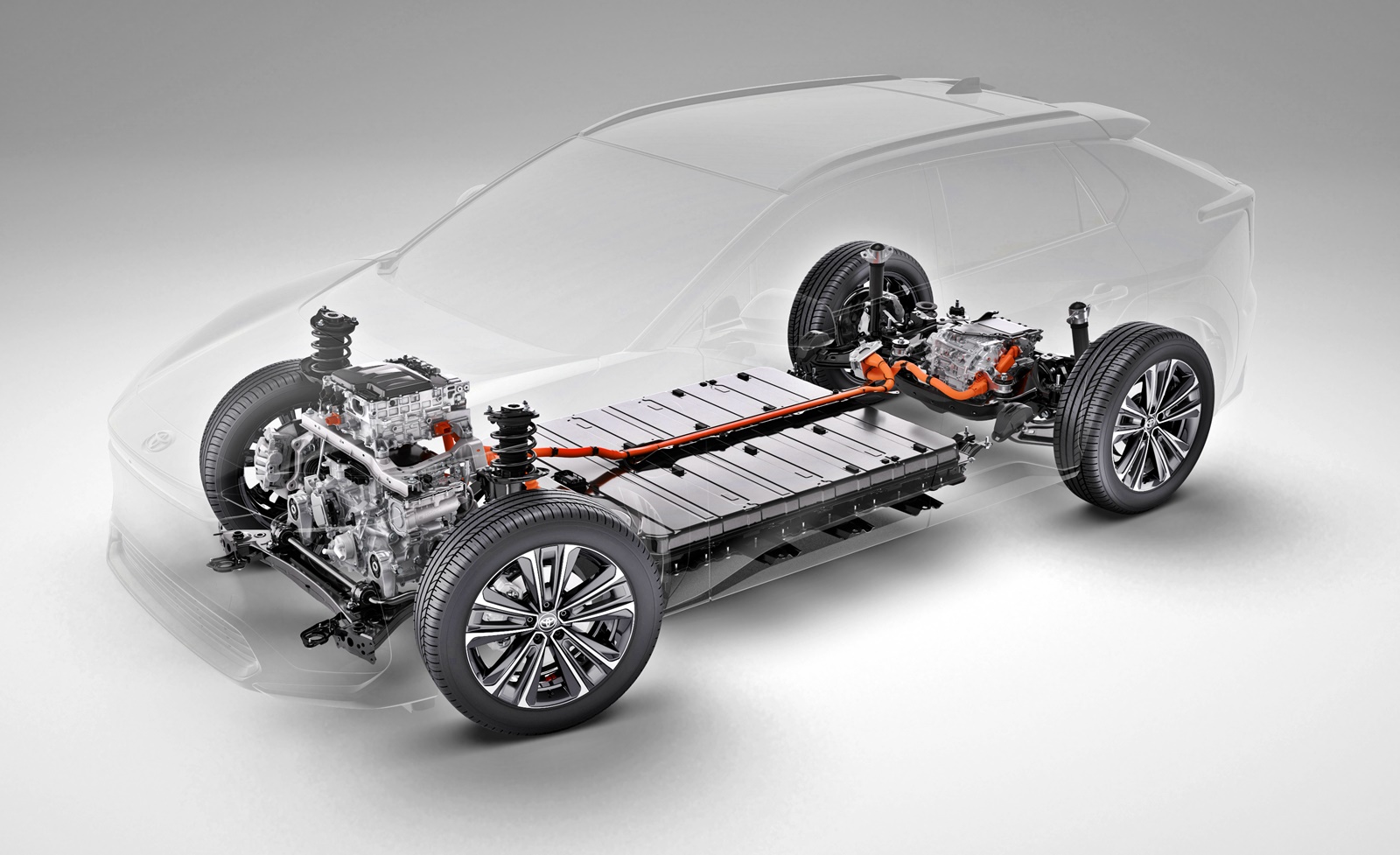
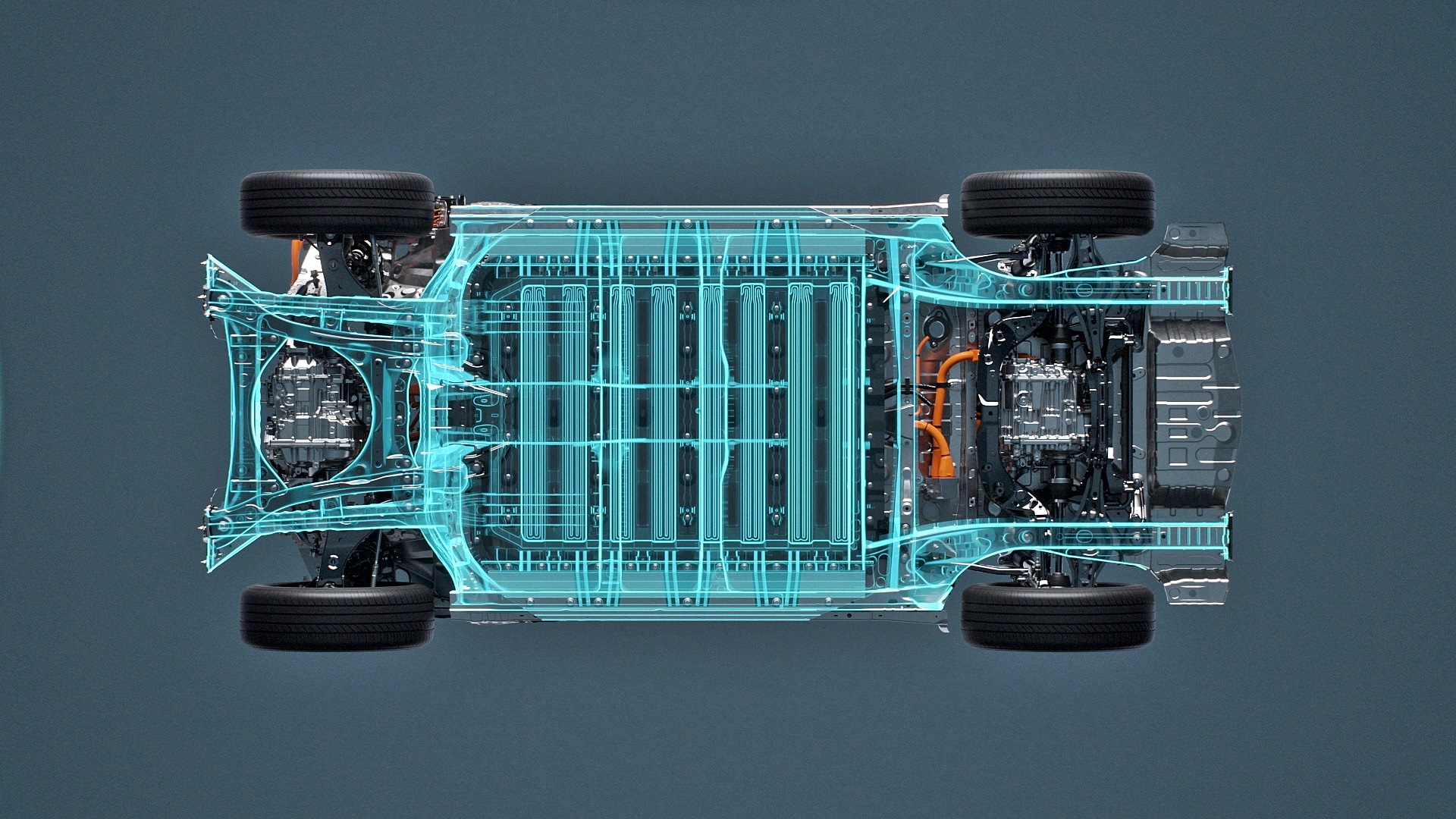
The new model, to also be known as the bZ4X, sits on a BEV-dedicated platform (first for Toyota) based on e-TNGA philosophy. TNGA stands for Toyota New Generation Architecture, a flexible architecture used for all of the latest models. The one for the bZ4X has been jointly developed with Subaru Corporation which will also have its own BEV to be called the Solterra.
The platform has the advantages that TNGA provides such as a low centre of gravity and high rigidity, all of which will contribute to better driving dynamics and even good off-road performance since this is to be a SUV.
FWD or AWD
The powertrain is straightforward with one or two motors, the latter for the all-wheel drive version. System output is 150 kW for the front-wheel drive version and 160 kW for the AWD version. The E-axle integrates the electric motor, transaxle and inverter while the Electricity Supply Unit consolidates charging and power distribution functions.
Battery performance and safety
As with all BEVs, the key points that motorists will want to know are the performance of the battery pack. The 71.4 kWh lithium-ion battery pack (made by an affiliated company) is expected to provide a cruising range of about 500 kms’, even in cold regions.
Compatible with high-output chargers worldwide, an 80% charge is said to be possible within 30 minutes. Besides the usual methods of recharging, there is an optional solar panel on the roof that can also convert sunshine to electricity for the battery pack.
It is also targeting a top-class battery capacity retention ratio (90% after 10 years of use or 240,000 kms). More attention has been given to preventing battery failure by strengthening measures to prevent and detect abnormal conditions (eg overheating). There are also new technologies with a multiple monitoring system that ensures safety and security in case of emergency.
Toyota’s subsidiaries have been developing and making batteries for many years and have gained a lot of knowledge. They have now developed a production process that eliminates contamination, which is a cause of abnormal heating. There is also a high-resistance coolant which prevents fire from short circuits even if there is leakage of the battery’s liquid coolant.
Safety is not forgotten and this is new territory for carmakers. While the basic structure has similarities to combustion vehicles, the high-voltage systems require specific protection. To ensure a high degree of battery pack safety, the Toyota Safety Sense active safety package is used and the body structure has been adapted to withstand collision from any direction. The battery pack itself is also designed in a way that contributes to ensuring protective performance in a collision.
Toyota has also developed more proactive initiatives with regard to the end-of-life scenario for battery packs. The company has a Battery 3R – Rebuild, Reuse, Recycle – approach which will ensure a worldwide top-class battery capacity retention ratio. It proactively undertakes battery rebuild (inspection and reassembly) and reuse and promotes initiatives for battery recycling.
RAV4 size but more spacious
The bZ4X has an overall length of 4690 mm and overall width of 1860 mm, which is about the same size as a RAV4 but it is around 100 kgs lighter. Due to the entirely different powertrain and layout of components, the wheelbase is significantly longer than the RAV4’s – 2850 mm versus 2690 mm. This naturally means a more spacious cabin which is also extra wide. Toyota says that the tandem distance is equivalent to that of a sedan like a Camry.
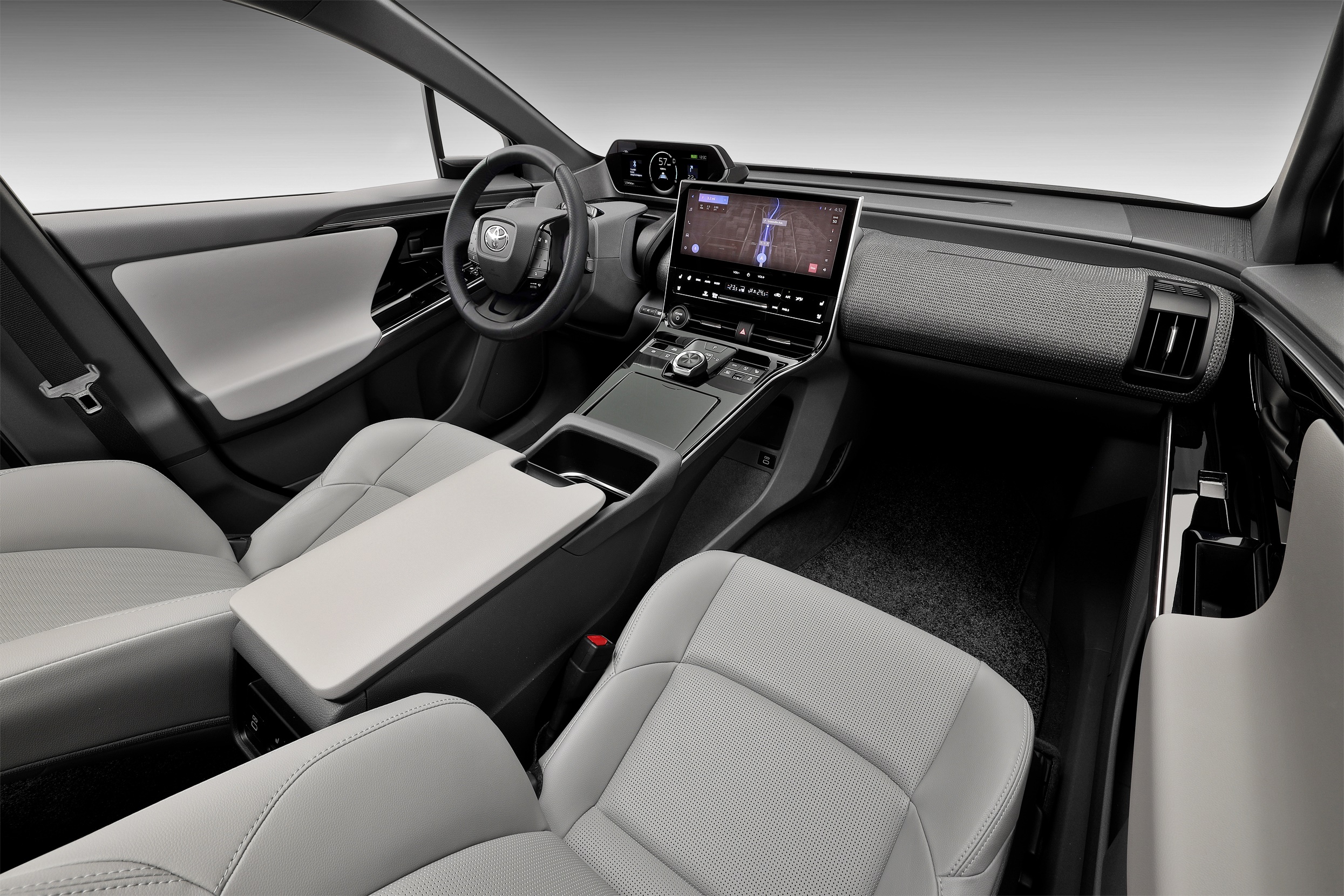
As the pictures show, the cockpit area is futuristic with the meters positioned to be visible through the upper part of the steering wheel. This is the first time a Toyota vehicle has such an arrangement and it is emphasizes ease of viewing by reducing eye movement and enabling a distance point of focus.
This is the second time that Toyota’s interior designers have given more thought to viewing the meters. When the first Prius hybrid was designed, the meter display was located at the centre of the dashboard instead of its traditional place ahead of the steering wheel. This was to improve eye focus (especially for older drivers) by not having a short viewing distance to the meter and a longer one to see the road ahead. Positioning the display further away meant that the driver’s focus would be further away most of the time, reducing changes and improving safety.
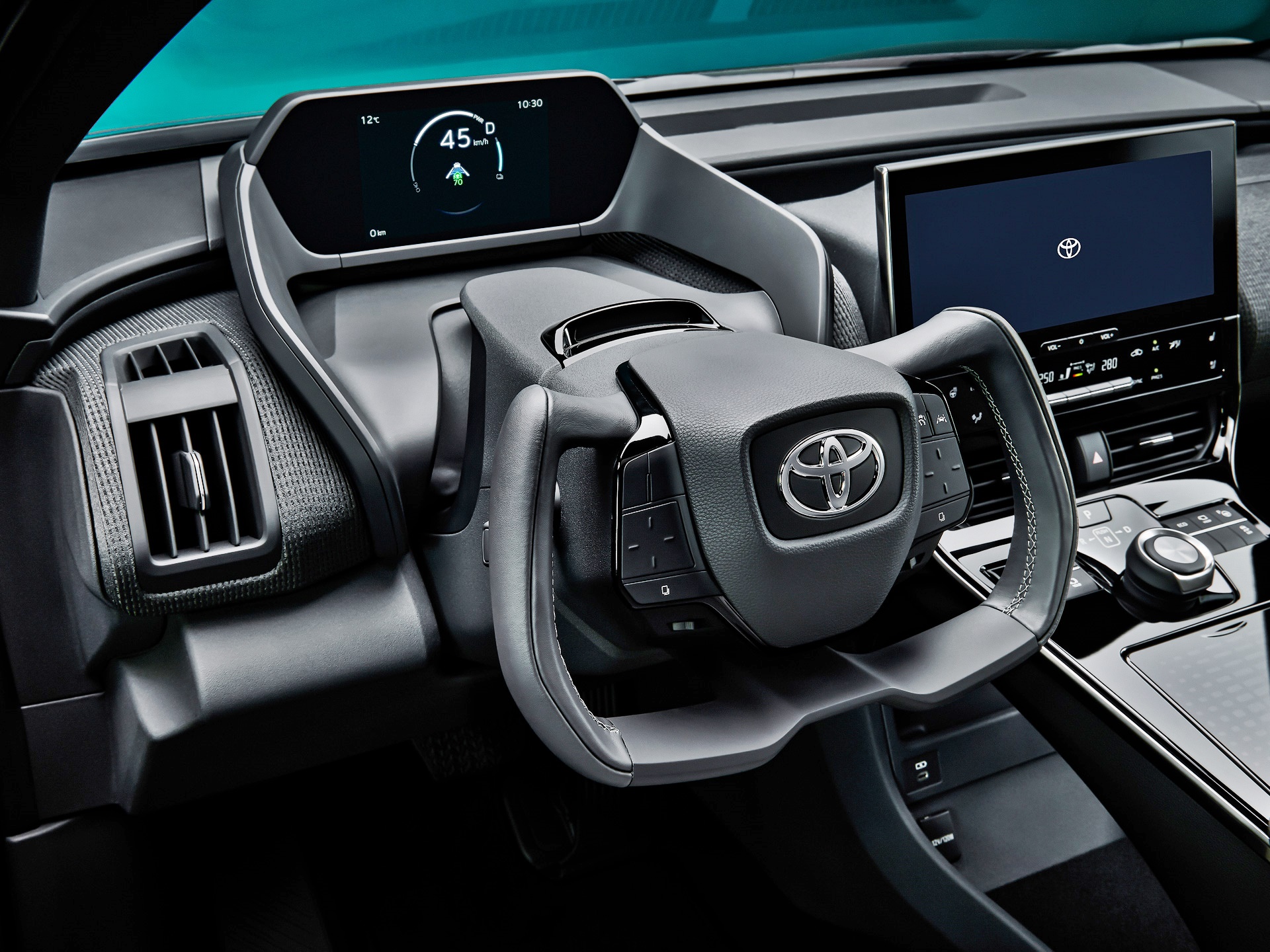

The modularized driving controls including a steering column with a wing-shape. The one-motion grip combining steer-by-wire system and uniquely shaped steering wheel will be first offered in cars sold in China and progressively added to those in other markets. Before then, the other markets will have a conventional circular steering wheel.
Different regions, different approaches
Clearly, Toyota intends to quickly move to the forefront of the EV market as it did with hybrid electric vehicles. It has different strategies for different markets and regions, depending on the supply of electricity and the recharging network. For Malaysia, the decision has been made that the first phase of electrification will be to assemble hybrid electric vehicles locally.
While the latest news today of full tax exemption for EVs does make it possible for models like the bZ4X to be sold, it is likely that Toyota’s production and marketing plans for the next few years have already been set. The major markets will already have given big numbers that will probably take most of the output from plants in China and Japan, so a smaller market like Malaysia may have to wait till later. At best, we may a small number of units imported more to gauge market response while UMW Toyota Motor focusses on growing HEV sales for which a RM270 million investment has already been made.
Toyota: “No customer is left behind” in quest for carbon neutrality