Scrapping cars at the end of their useful life has been a common practice for decades. The metal and plastic parts that can be extracted can be reused for other goods – but not necessarily cars again. BMW thinks that cars of the future should be made from nearly 100% recycled materials. This will support the idea of a ‘circular economy’, where materials are continually reused, rather than discarded at the end of a single product’s lifespan, as in the conventional linear economy.
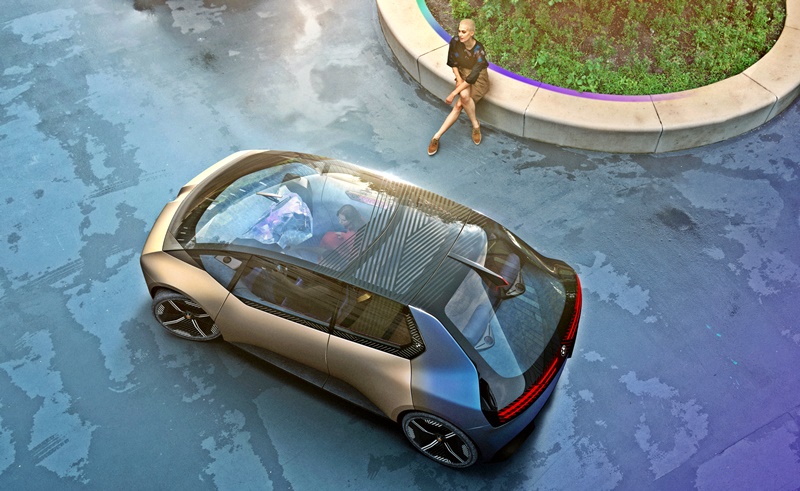
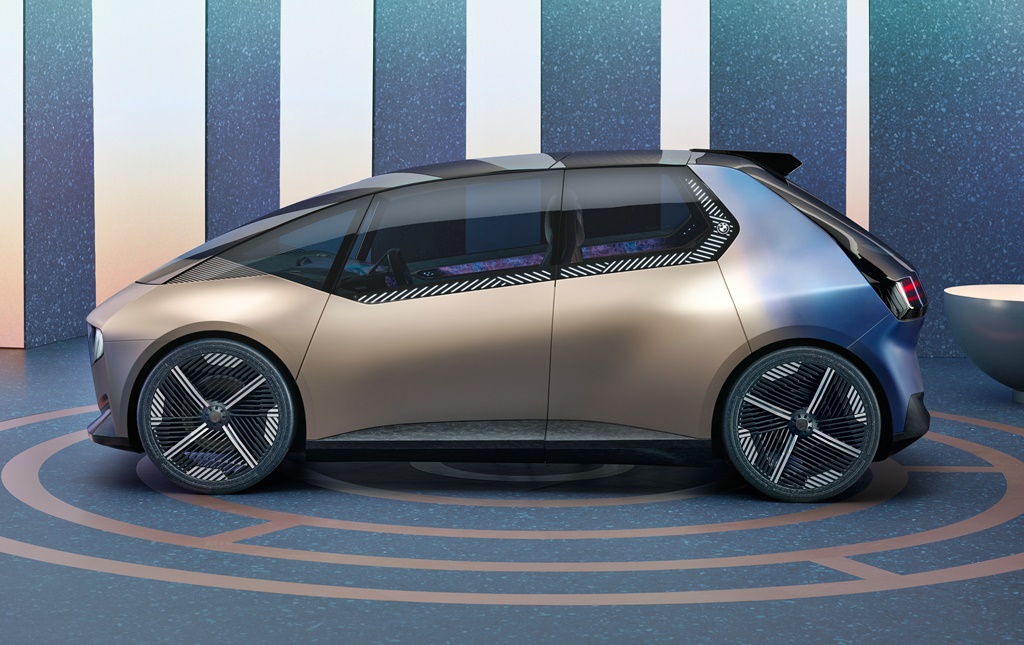
To demonstrate how the circular economy can be applied by the auto industry, the carmaker built the i Vision Circular concept which is a compact EV that might be in use in 2040. Working with companies like BASF and the ALBA Group, materials like recycled plastics are identified as sustainable materials that go into the construction of the i Vision Circular concept.
The recycling approach applies to the all-solid-state battery pack which is also manufactured almost entirely using materials sourced from the recycling loop. It will achieve much higher energy density with significantly reduced use of the most valuable resources, especially rare earth materials.
BMW also used 3D printing for many interior components, which further helps reduce waste, the automaker noted. The process produces less scrap material, and whatever isn’t used can be fed back into the production cycle as raw material.
Circularity from design stage
“We gave thorough consideration to circularity from the outset during the design process for the BMW i Vision Circular. As a result, this Vision Vehicle is packed with innovative ideas for combining sustainability with a new, inspirational aesthetic – we call this approach ‘circular design’,” explained Adrian van Hooydonk, Head of BMW Group Design.
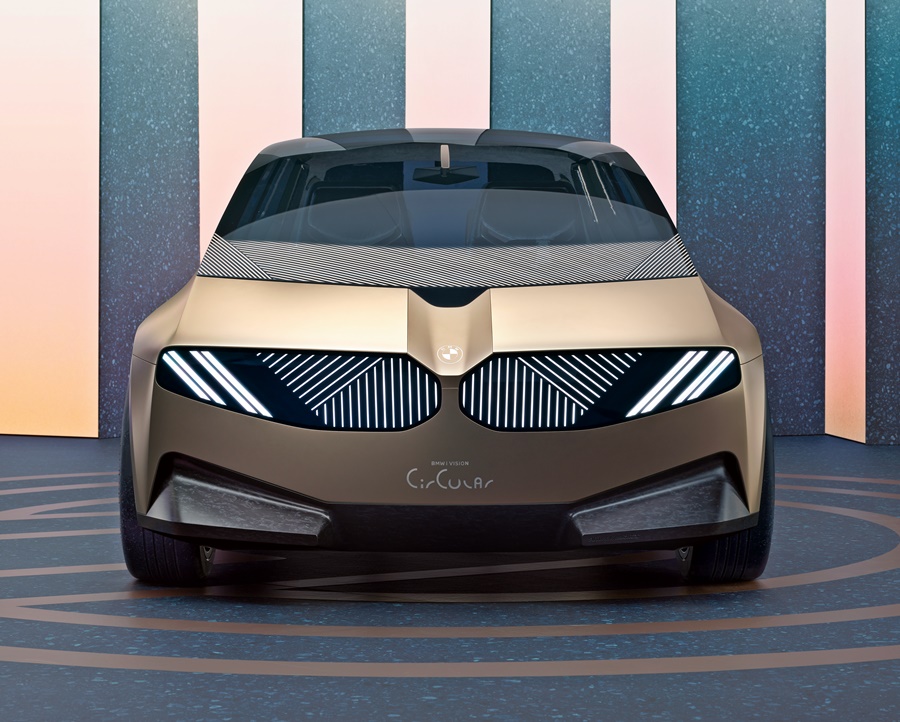
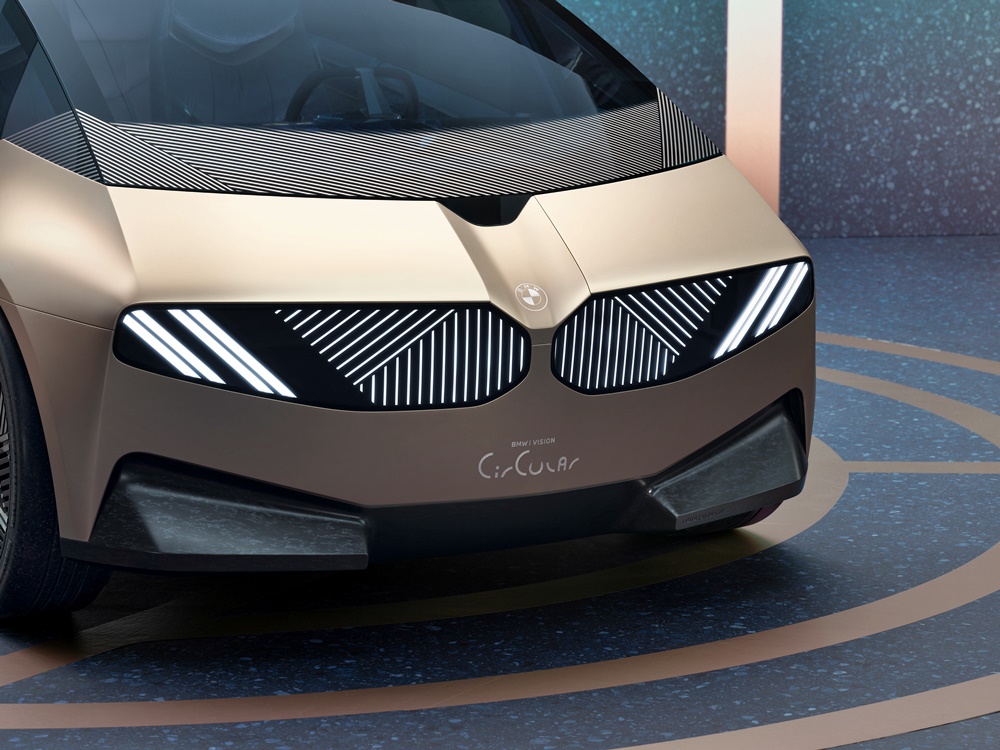
The number of parts on the bodywork has been reduced as much as possible. Instead of having a chrome surround with bars, for example, the iconic kidney grille has been newly interpreted as a digital surface. Even the brand logo on the front end is engraved and the vehicle badge is laser-etched to avoid using extra add-on parts.
The surfaces below the windscreen are made from secondary aluminium. An additional sensor cluster between the two kidney elements groups together technological features, enabling simple disassembly within a single removable element. The bumper area further down is manufactured from recycled plastic with a sophisticated marbled surface.
Minimum parts and ease of disassembly
Having a small number of different mono-material groups with connections that can easily be undone is crucial for good recycling. For this reason, there are no bonded connections or composite materials and, instead, intelligent types of connection, such as cords, press studs and quick-release fasteners are used. A special socket wrench can separate the component parts joined by the fastener with a single rotation.
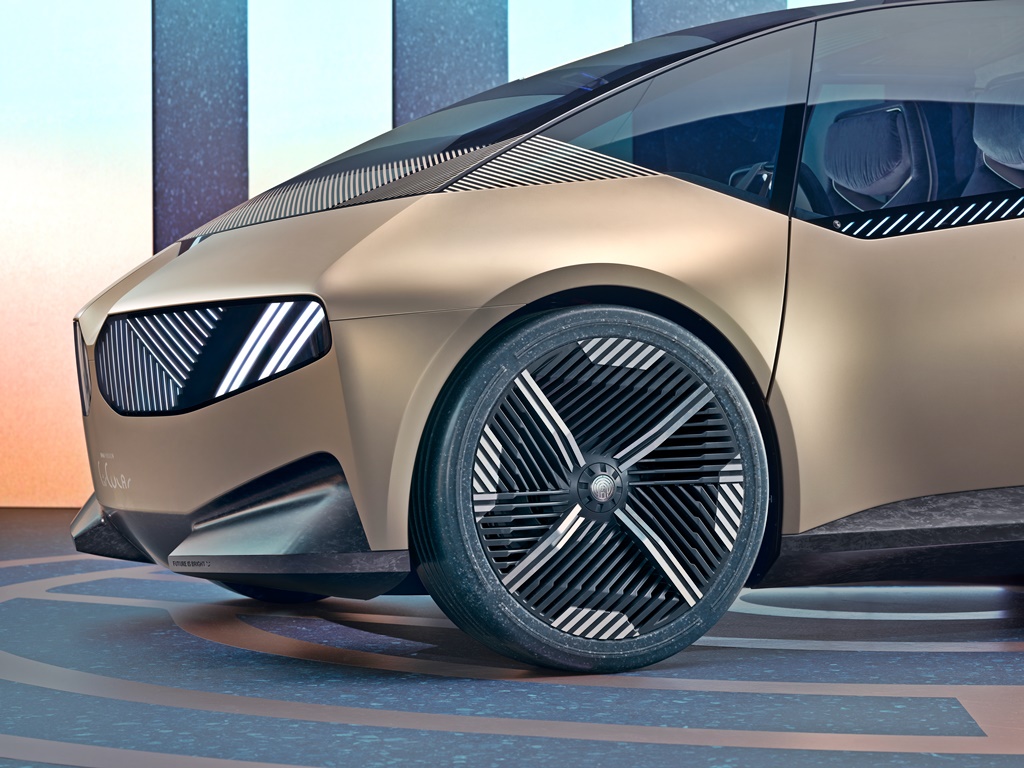
The tyres in ‘Vivid Blue Rubber’ are made from certified, sustainably cultivated natural rubber and have a slightly transparent appearance. Extra coloured, recycled rubber particles are added to the tyre compound for strengthening, creating an intriguing terrazzo effect and purposefully highlighting the reuse of materials.
The wheel rims are designed and manufactured with minimal materials use. Rim centres with maximum permeability provide brake cooling, while the more enclosed surfaces to the outer reaches of the wheels ensure the greatest possible aerodynamic efficiency. The wheels are fixed in place with a quick-release fastener at the centre of each wheel.
Only visible when looking from above, a narrow fin is integrated centrally in the rear section of the glass roof. It contains the communications and antenna technology, and provides information on the status of the vehicle (open/closed, charge level of the battery, etc.). It also integrates the high-mounted centre brake light.
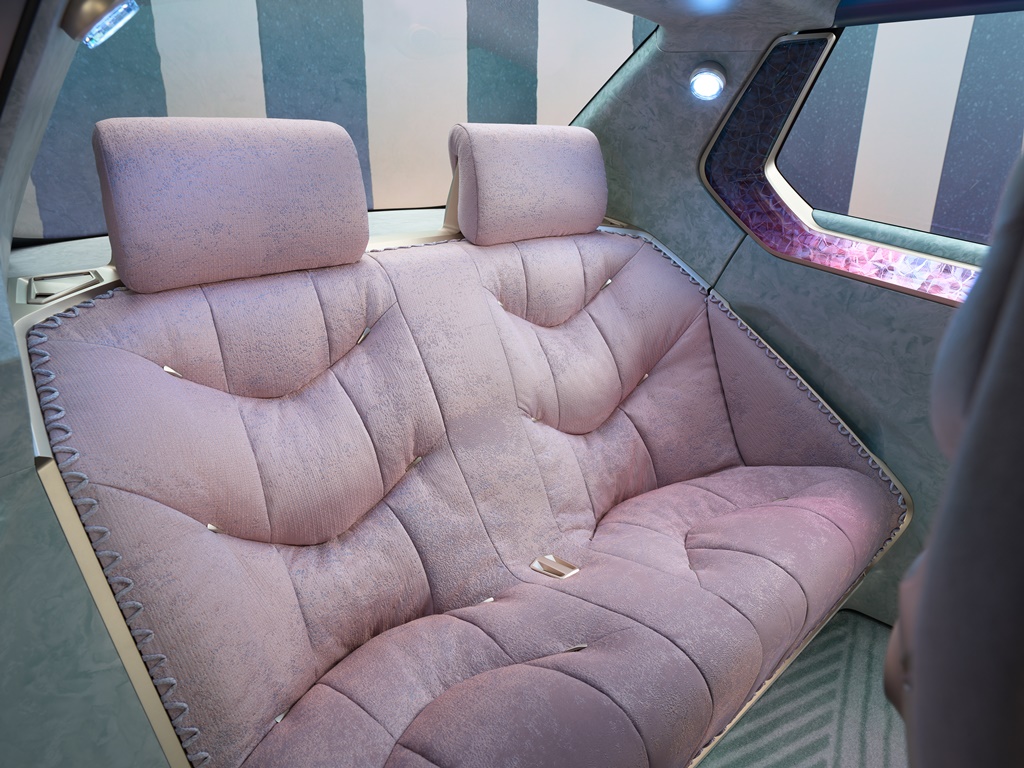
Luxurious ambience with recycled materials
Inside, the i Vision Circular is also true to employing materials and production processes that are indicative of a responsible approach to the environment and its resources. But that does not mean it cannot have a luxurious ambience. For this, the interior designers carried out purposeful selection of materials. This involves using not just the right basic materials in the form of mono-materials but also clever new joining techniques for them which avoid the use of glue in order to ensure optimum suitability for dismantling and sorting at a later stage.
In order to minimise the amount of waste and offcuts, all components and materials will be manufactured to fit exactly using processes such as 3D printing. Any surplus material will be systematically fed back into the materials cycle.
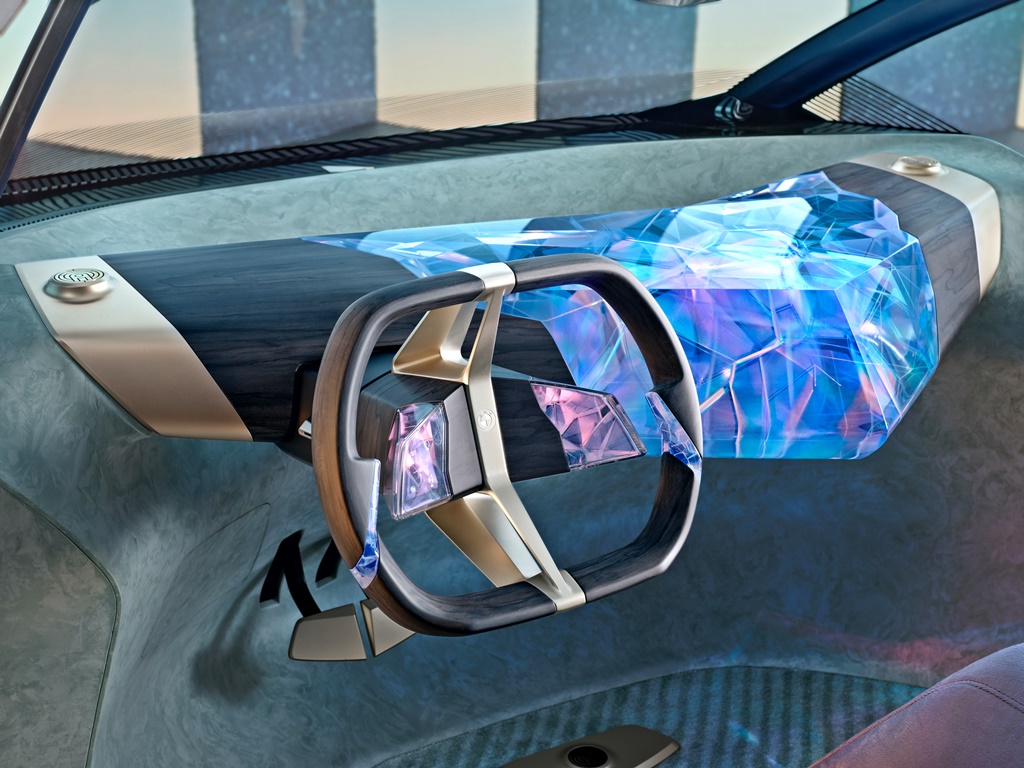
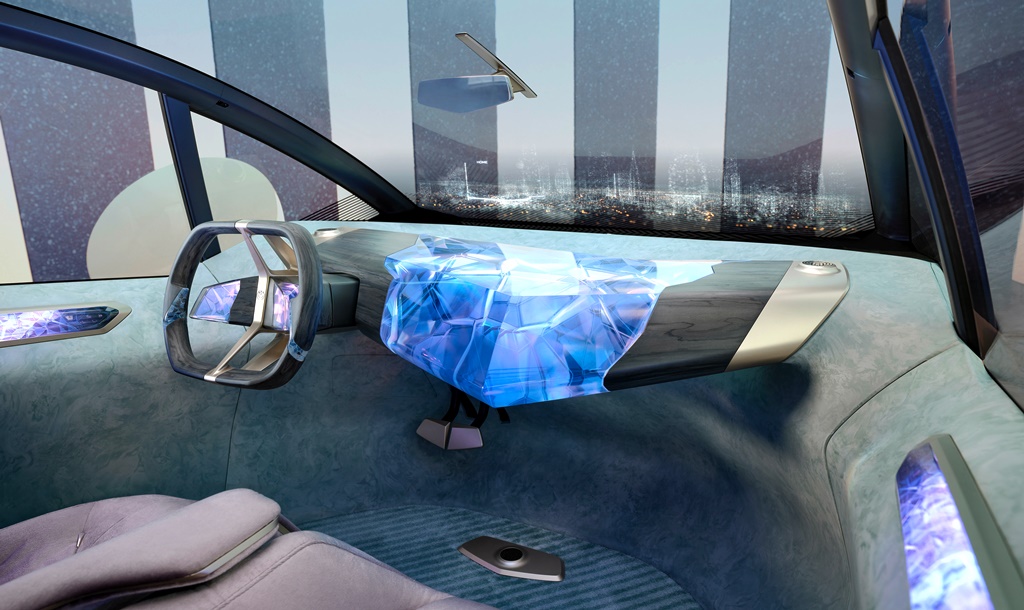
The instrument panel is turned into a next-generation ‘phygital’ (a newly coined term that refers to turning digitality into a haptic experience) user interface. Here, it takes the form of a hovering, V-shaped sculpture that projects out into the cabin. At its heart is a 3D-printed, crystal body with nerve-like structures running through it, great visual depth and an enthralling lighting effect. This is where the vehicle’s “thinking” is visualised, allowing the user to see its intelligence at work.
The information area you would normally expect to find in a central information display is located above the instrument panel, at the bottom of the windscreen. This display area takes the Head-Up Display to a whole new level. All relevant information is projected onto the bottom area of the windscreen across its entire width. Driving displays for the driver can be found here together with communications functions and entertainment features for the passengers.
3D-printed steering wheel
The steering wheel forms a link between past and future at the same time as reducing the quantity of material and components. The rim has been 3D-printed from bio-based material, with the wood powder variant shown here giving the steering wheel a natural and warm feel. The unconventional, central positioning of the vertical spoke in gold-bronze adds a modern twist.
The display and operating surface below the windows visible on the outside of the car can be found on the inside too, forming a connecting element between interior and exterior. Here again, it extends back into the rear of the car and around the Hofmeister kink. Featuring the same crystal appearance as the instrument panel and ambient lighting, this element in the sidewall adds to the intriguing and mystical aura produced in the cabin.
BMW makes it clear that the i Vision Circular concept is not the basis or any future model. It has a range of next-generation EVs under development, referred to as ‘Neue Klasse’ (German for ‘New Class’) which may adopt some of the ideas from the sustainability-focused concept car.
BMW brand logo modernised with visual style of today to suit digital age