‘Kei’ cars are vehicles in a category that was created in 1949 in Japan. The regulations limit their dimensions to a very small size, suited for the narrow roads of the country’s cities but also permitted for use on highways. They are very small – no more than 3.4 metres in length, 1.48 metres in width, and 2 metres in height – and even their engine sizes are limited to 660 cc (in Japan).
Having small engines, kei cars have obviously been very economical and as a segment, the amount of pollution from such vehicles would be lower than the other segments too. Due to the fuel efficiency of kei cars, the need to electrify them has not been as urgent as for larger cars but electrification is necessary in coming years.
To prepare for this new era, Nissan Motor has been having a joint project with Mitsubishi Motors Corporation (MMC) through an existing 50/50 joint venture known as NMKV Co., Ltd. It’s not known what ‘NMKV’ stands for though it could be ‘Nissan Mitsubishi Kei Vehicles’. The company handles product planning and project management for minivehicles sold in the Japan market.
The NMKV Model
NMKV uses its unique ‘NMKV Model’ to create highly competitive products while dispersing risks of development costs. The source of the NMKV Model is the value-creation abilities through organically combining the resources, technology, and expertise of the two parent companies.
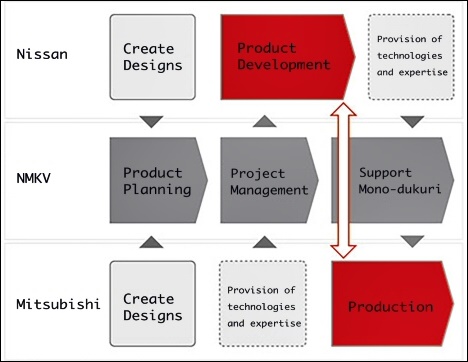
Expertise in electric vehicles and kei cars
Nissan Motor and MMC each have their own strategies for kei cars. One aims to display a significant presence as an automobile company in the segment while the other wants to fully utilize the high level of development capability of such vehicles that it has built up to this point. With NMKV, corporate lines can be crossed to share the automobile development expertise that has accumulated inside each company.
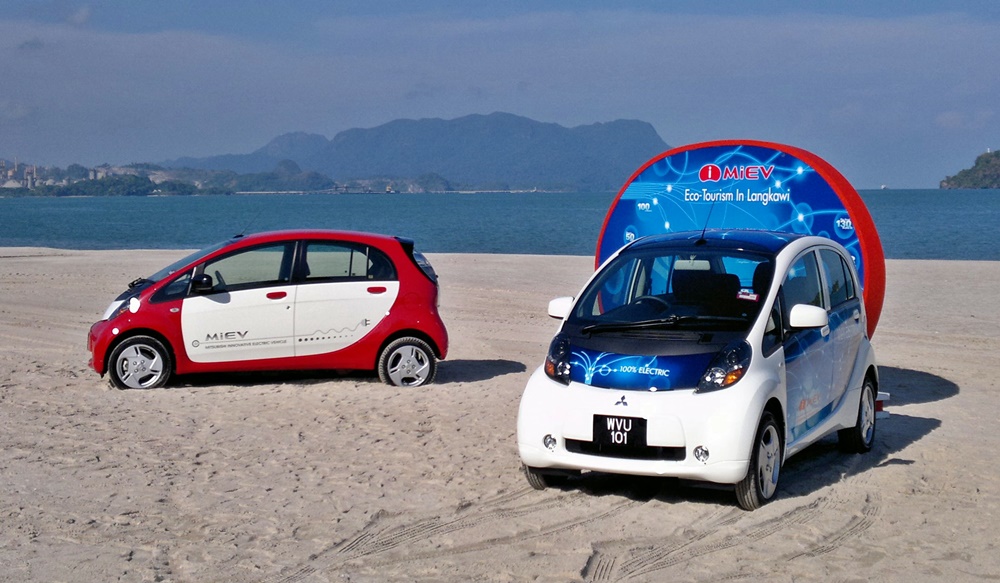
MMC, for example, has built up expertise in electric kei cars, having introduced the first one in Japan in 2009. This was the i-MiEV and it was also the world’s first mass-produced electric car. Nissan too has a long history of making electric cars, with its corporate history including an electric model known as the TAMA which was produced way back in 1947.


“We are a highly unique company of a type never before seen in Japan. We inherit the genes of both companies, and fuse together the experience and knowledge that both have cultivated. Our mission is to serve as a catalyst for both companies to make ‘1 + 1 = 3’, or even ’1 + 1 = 5’, and accomplish things that were not possible for the companies to accomplish individually in the past,” said Junichi Endo, President & CEO of NMKV.
New electric minivehicle in 2022
NMKV is developing a new electric minivehicle to be launched by Nissan in the second quarter of 2022 which is said to redefine the popular car category in Japan (it accounts for about 30% of new vehicle sales). With a nominal battery capacity of 20 kWh, it will have strong acceleration with smooth driving and cabin quietness that are key characteristics of electric vehicles. It will be available with a variety of advanced technologies, including driver assistance technologies.
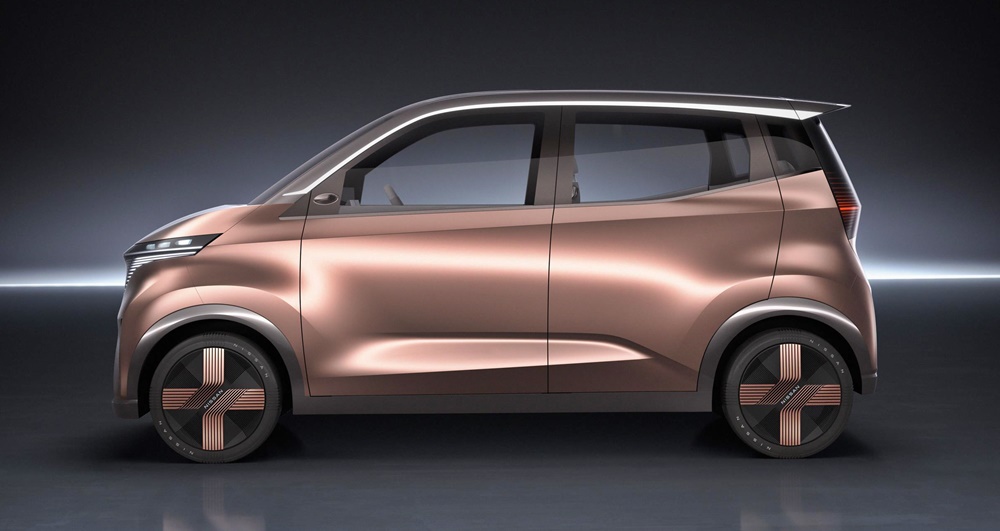

The range will be sufficient to cover daily usage in Japan and in any case, the charging network in the country is already quite extensive. In addition to its mobility uses, the vehicle will be able to provide electricity from its battery to a home and, in emergencies, act as a mobile power source.
At 3395 mm long, 1475 mm wide, and 1655 mm high, the minivehicle would qualify for kei car incentives and the purchase prices are forecast to start at approximately 2 million yen (about RM76,400).
To locate a showroom to view or purchase the latest Nissan LEAF EV in Malaysia, visit www.nissan.com.my.