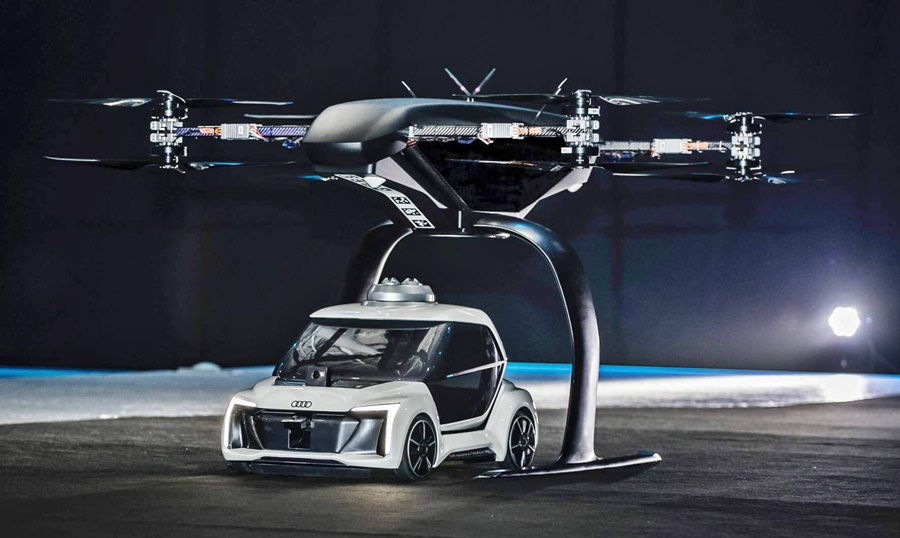
Although there have been prototypes of flying cars for many decades, it’s only in the past few years that the idea has become a more serious venture. Even Audi and Porsche have, with aerospace partners, looked into developing vehicles that can fly as well as be driven along roads. In many cases, it appears that the potential usage is not for personal, individual transport but as taxis or transporters.
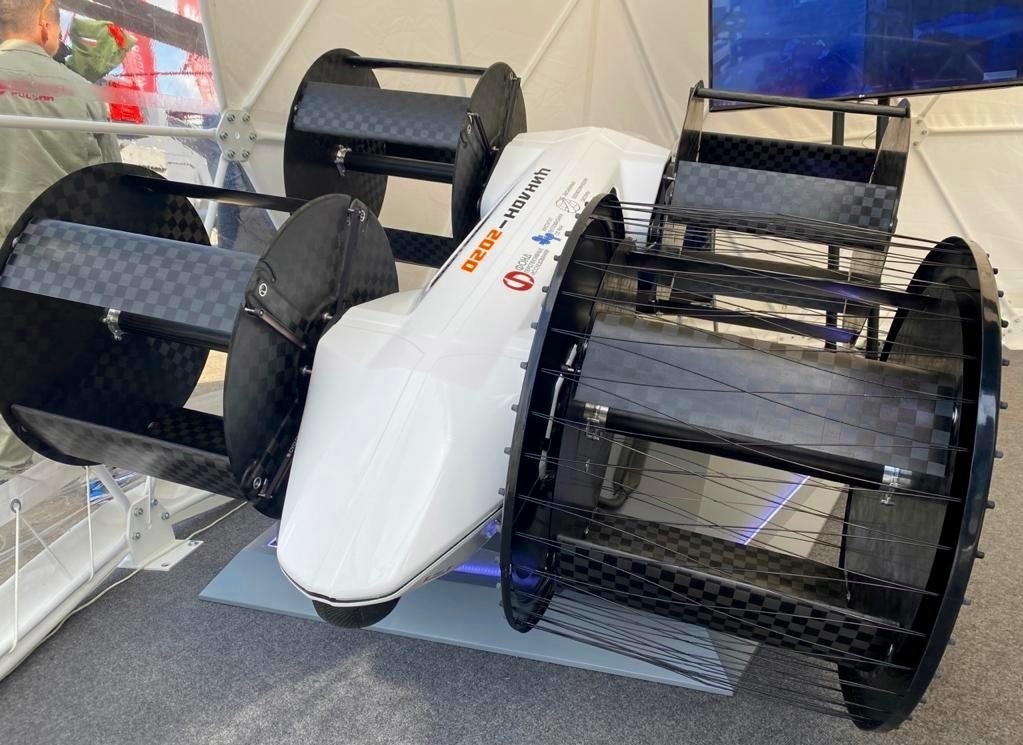
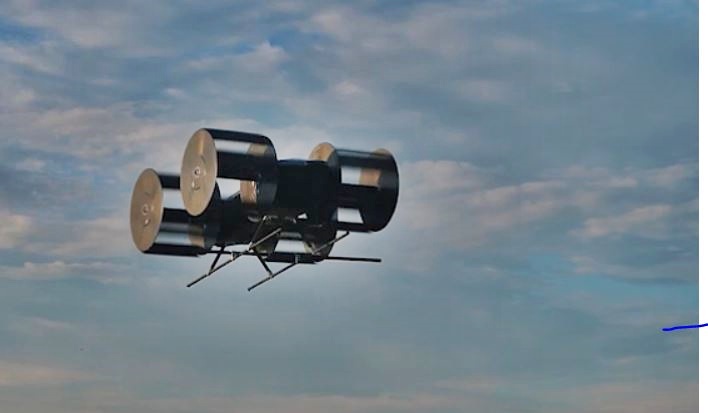
At the Russian Academy of Sciences, a flying car project is now underway under the framework of the Foundation for Advanced Research ‘Cyclone’. The project, undertaken by the academy’s Siberian branch of the Institute of Thermophysics, is for the development of an aeromobile called the Cyclocar.
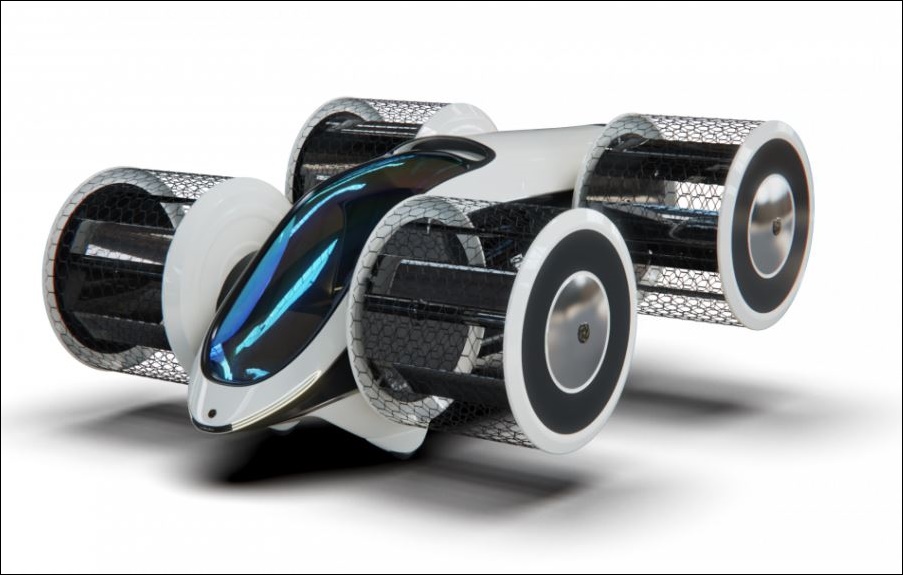
Cyclic propellers and hybrid powerplant
The method of lifting the vehicle off the ground uses cyclic propellers which are powered by electric motors from a sequential hybrid powerplant with a petrol combustion engine or a turboshaft engine employing a gas turbine.
The advantages of using cyclical propellers are fast control of the thrust vector through 360 degrees, low noise level, and compactness. A cyclic propulsion device is one of the most complex aerodynamic devices to design but scientists and engineers of the Novosibirsk Institute of Thermophysics have been able to solutions to the inherent problems.
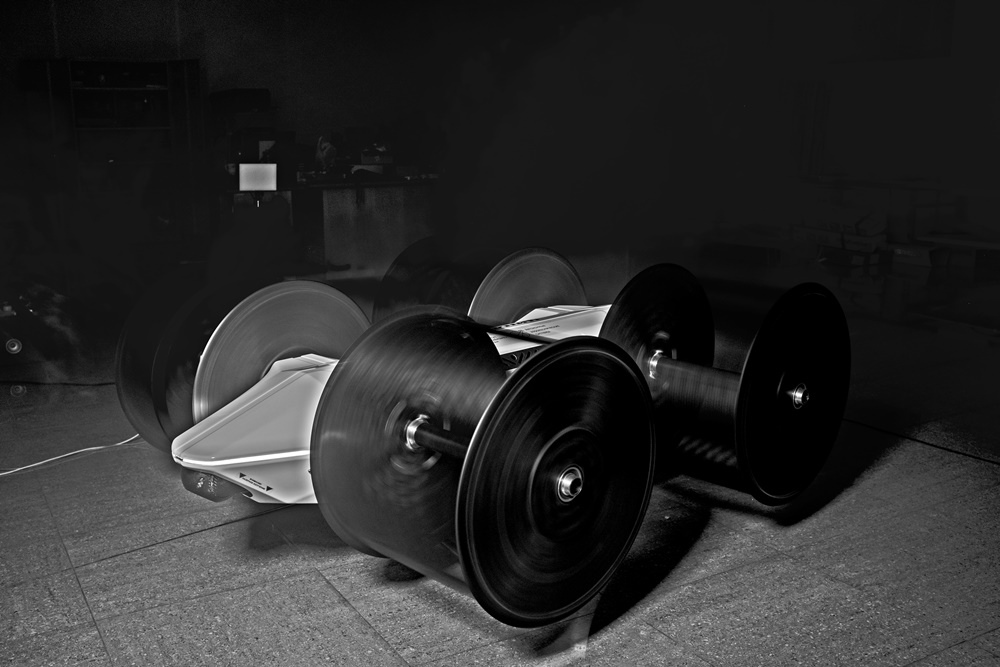
During the first stage of work, ground tests of a cyclic propeller with a diameter of 1.5 metres were carried out. The results obtained during the tests on traction and consumed electric power fully confirmed the viability of the concept for powering the Cyclocar.
As the pictures show, the cyclic propellers will be installed at the side of the body with their frames. Special attention is being given to the design of the propeller frames to prevent people from being close to them while they are spinning as well as to resist damage from foreign objects.
More compact than a helicopter
The dimensions are 6.2 metres in length and 6 metres in width. Besides the compact dimensions in comparison with helicopters, a useful capability is landing on an inclined surface (up to 30 degrees) and docking against vertical surfaces like buildings.
The Cyclocar is expected to be able to take a payload of 600 kgs with 6 persons on board. Its maximum speed will be up to 250 km/h and it will have a flying range of up to 500 kms. The present layout has boarding from both sides as well as the rear where there is a ramp that can be lowered at any angle. The interior configuration can be varied to carry long items or even medical modules for use in disaster areas.
Like driving a modern car
The designers expect that operating the Cyclocar will be no more difficult than driving a modern car. It can be flown by the operator on board or remotely controlled, with the possibility of being used like a drone. The pilot-operator can, if needed, use manual control or automatic control, depending on the situation.
The next phase will see prototypes being built for flight tests and a fully functional Cyclocar is expected to be ready for production in 2024. The vehicle is intended for use by the military rather than the civilian sector.

Klein Vision’s AirCar successfully completes flight tests in Slovakia (w/VIDEO)