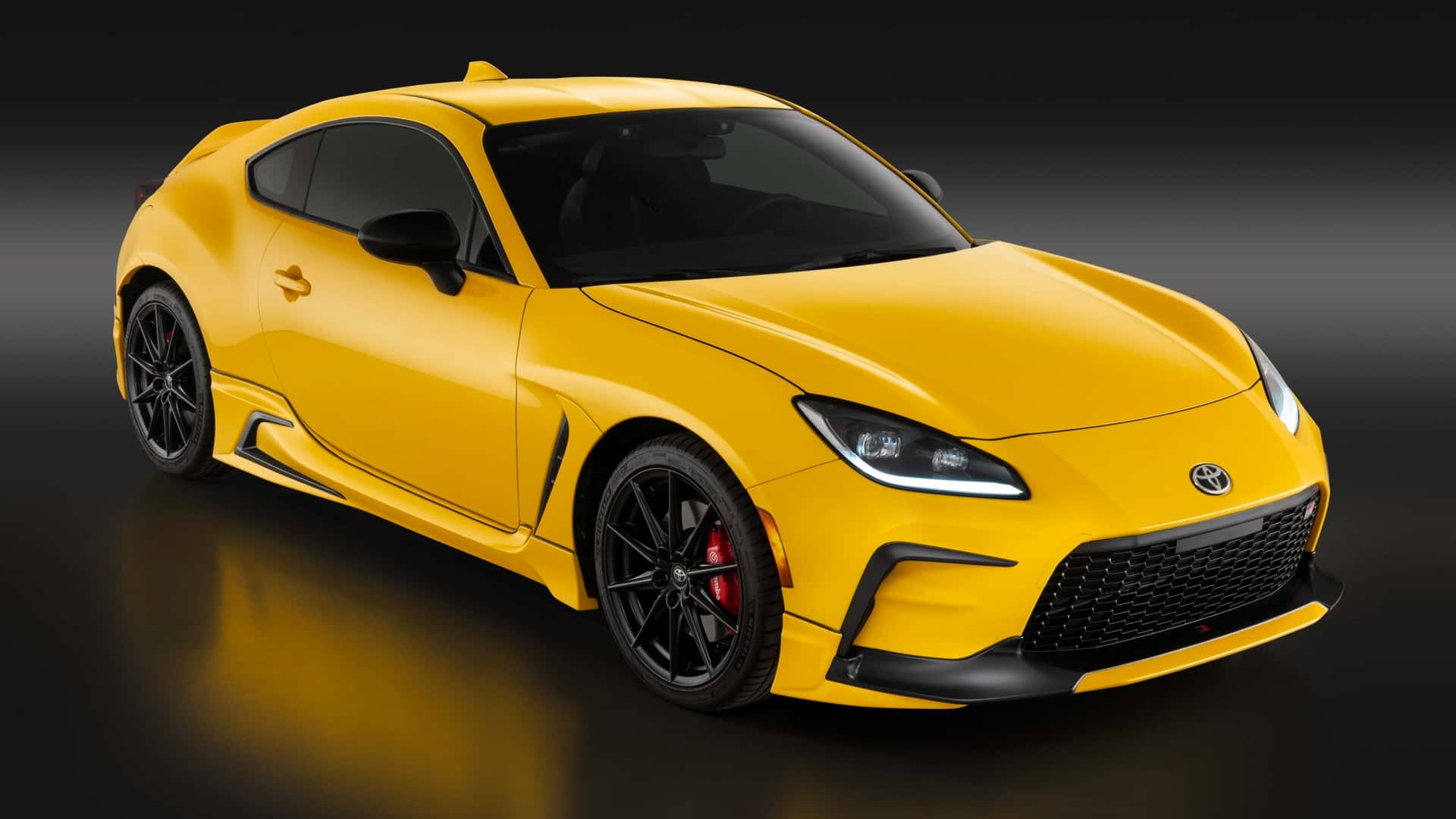
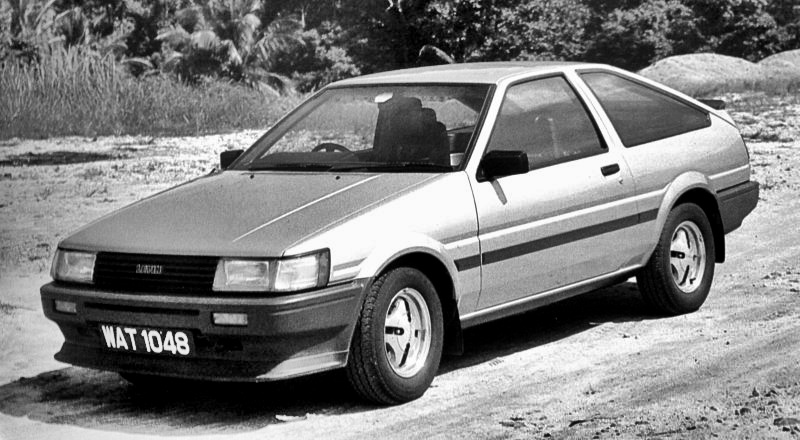
The Toyota AE86 – also known by names such as Levin, Sprinter Trueno, Corolla GT. GT 86 and Hachi-Roku – was originally launched in 1983 as a sporty coupe variant in the Corolla fifth generation of what would become the world’s bestselling model. It was not the first coupe variant of the Corolla, nor was it the only one, but somehow, that particular model has become legendary long after it ceased production.
Low-priced sporty variants faded away after the 1990s as the sportscar segment diminished in size, leading to most carmakers not favouring them as the volumes did not present a good business case. Enthusiasts missed the cars although many had grown older and gravitated towards SUVs. But there were still those who remembered the sportscars and Akio Toyoda, President of Toyota Motor Corporation since 2009, was one of them. Wanting to bring back fun-to-drive cars, he encouraged the development of a new and sporty range of models that began with the 86 in 2012.

The modern 86 was conceived in the same way as the original with front-engine and, rear-wheel drive, delivering the sort of driving experience that was long missed. A total of more than 200,000 units have been sold worldwide, some used for motorsports.
When the 86 was launched, the GR high-performance brand was not in existence yet (although GAZOO Racing was) but in recent years, the company has promoted this new brand and used for models like the 86, Supra and GR-Yaris besides GR-customised versions being available in Japan.
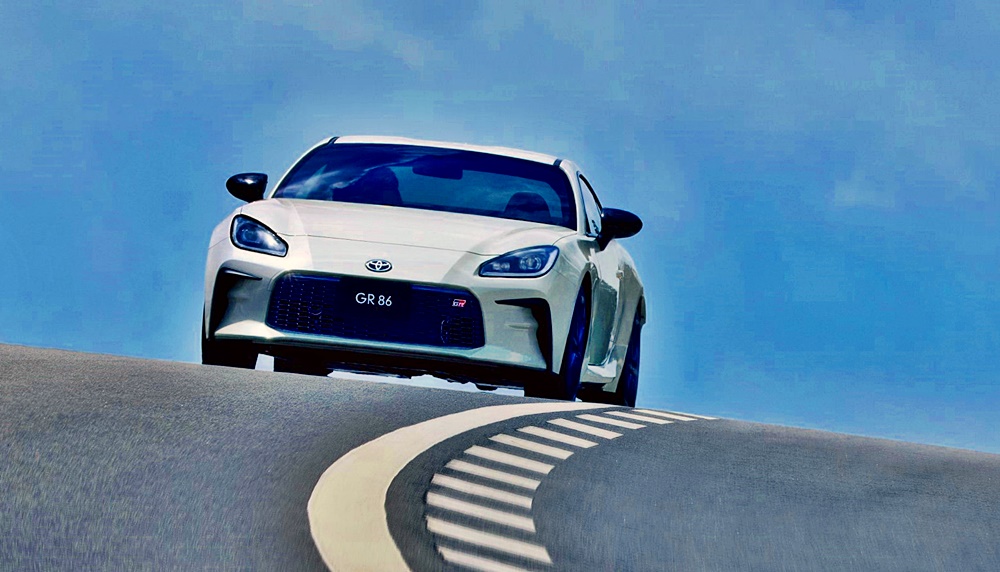
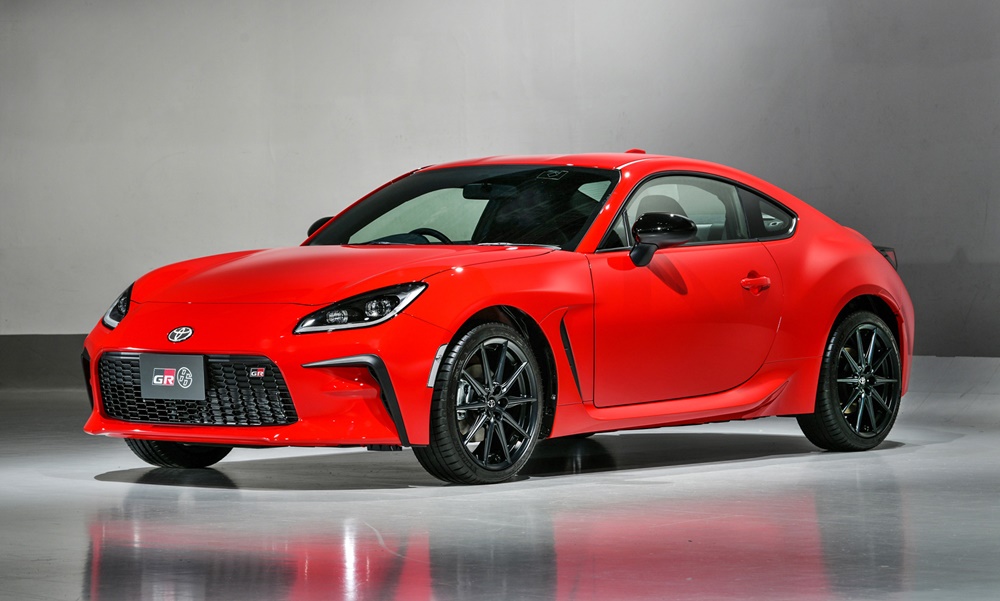
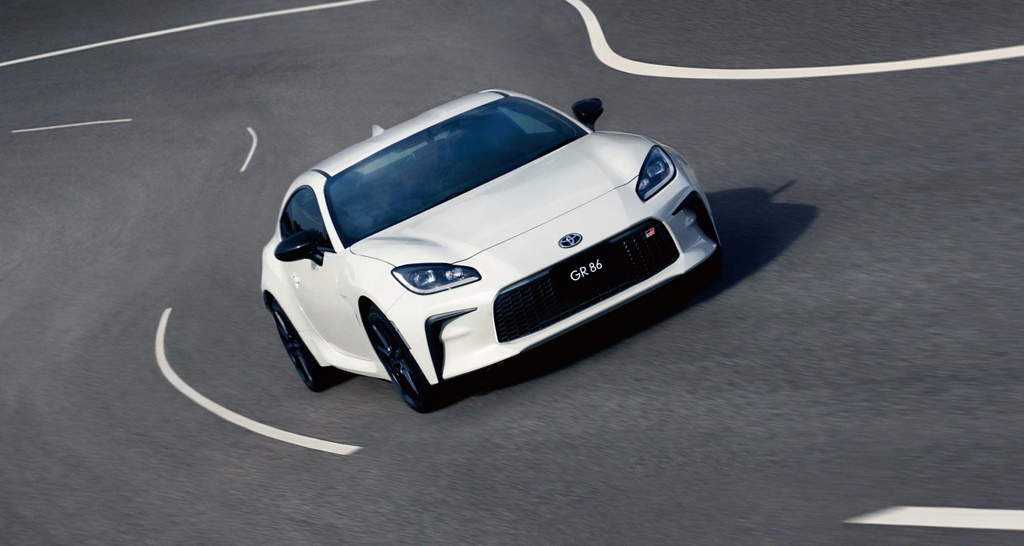
After a rather long 9-year run, the 86 goes into its second generation as the GR 86 and again, its development was shared with Subaru which sells their model as the BRZ. Collaborating with Subaru makes sense given the potential volumes for this sort of car, economies of scale can only be good for a business case if they are combined by the two brands. That’s part of the reason why the Supra is shared with BMW although the GR-Yaris was a separate matter as it was intended as a ‘Homologation Special’ to support motorsport activities.
The BRZ, which made its debut earlier, has its own following and engineers from each company approached chassis tuning with their own philosophies. While the extensive resources of Toyota have utilised in the car’s development, TOYOTA GAZOO Racing (TGR) has focussed on the dynamic qualities of the new 86 with the aim of making it better than before.
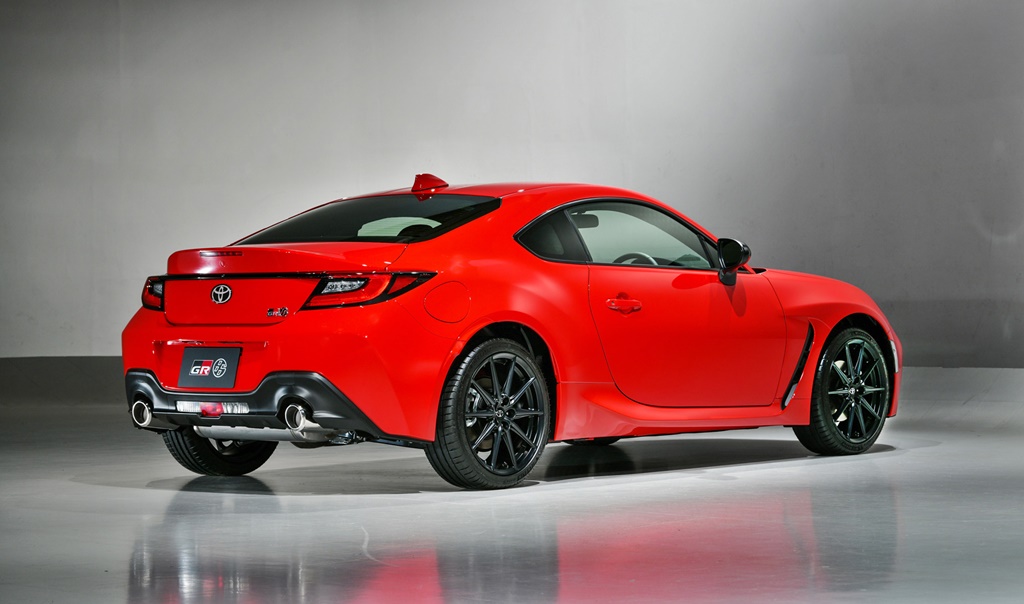
Same size, more aerodynamic
The dimensions of the new GR 86, which will go on sale in Japan in the fourth quarter of this year, are almost identical to the previous model. It has a generally similar appearance to the previous model with the sleek coupe profile. The front end has been reprofiled for better aerodynamics and gets a GR-specific Functional MATRIX Grille. Some of the aerodynamic components have been developed for 86 models that participate in motorsports and include air outlets, side sill spoilers, and other parts that improve steering responsiveness and stability.

Limiting both the overall height and hip-point of the vehicle helps lower the center of gravity and enhance turning performance, and so delivering the agility required. Under the skin, body rigidity has been improved, with torsional rigidity raised by approximately 50% over the previous model.
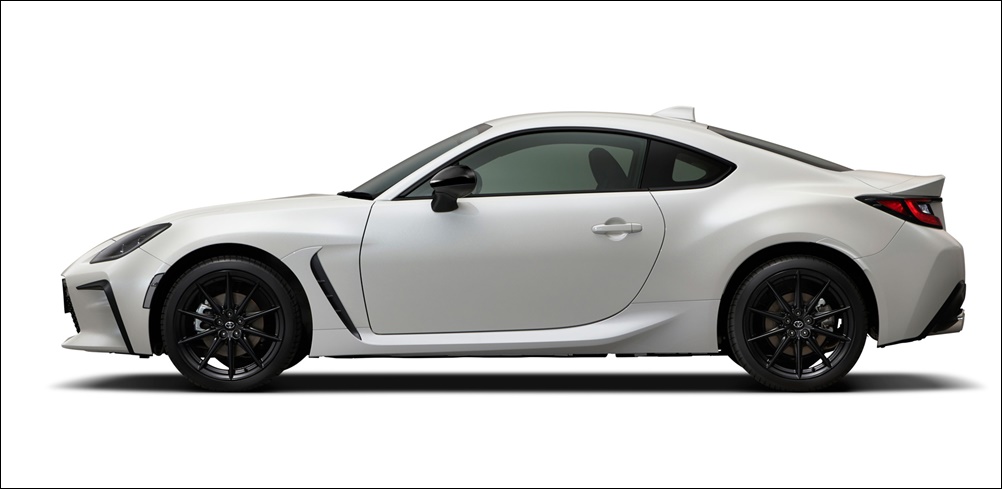

The use of aluminium for the roof panels results in a lower centre of gravity, while aluminium fenders and updated front seats and mufflers contribute to reduced weight. Keeping weight low has been a priority and is one reason why an all-wheel drive system has not been adopted (Subaru really wanted it but Toyota was against it).
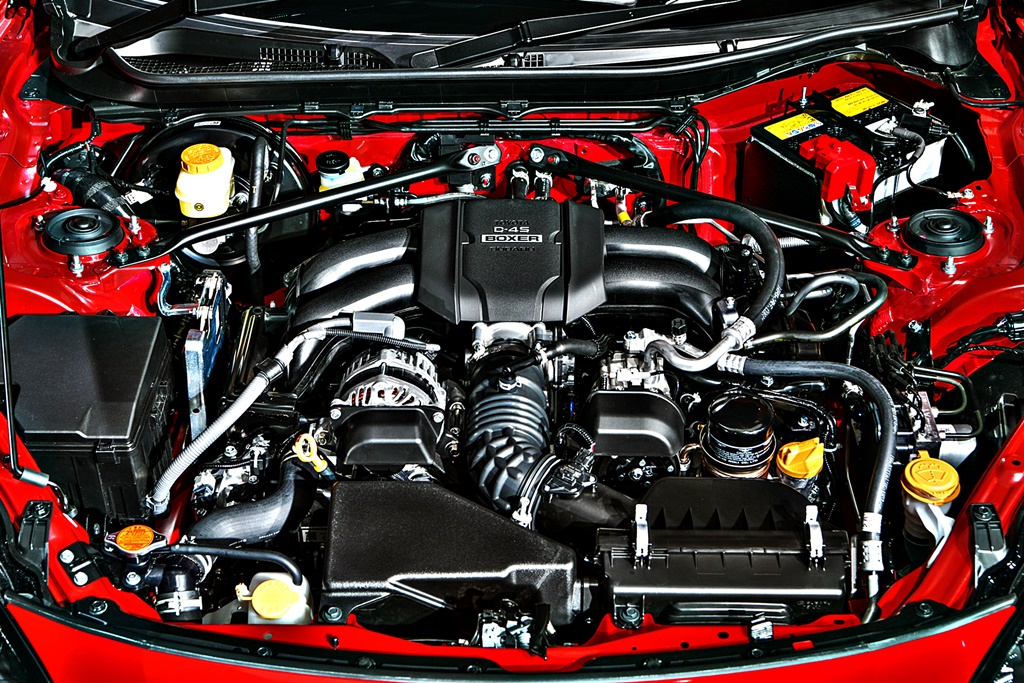
Bigger engine, same flat-four layout
As before, a horizontally-opposed flat-four engine is used and while this configuration is common in Subarus, it is unique for a Toyota. The flat-four layout places the mass of the engine further down, which is good for lowering the centre of gravity.
The displacement has been increased to 2.4 litres from the previous 2 litres – with no turbocharging – raising power output to 235 ps with 250 Nm of torque. Toyota has installed their own direct fuel injection and port injection system known as TOYOTA D-4S for fuel delivery. 0 to 100 km/h acceleration is claimed to be 6.3 seconds, quicker than the 7.4 seconds before, and customers have a choice of a 6-speed manual or automatic transmission.
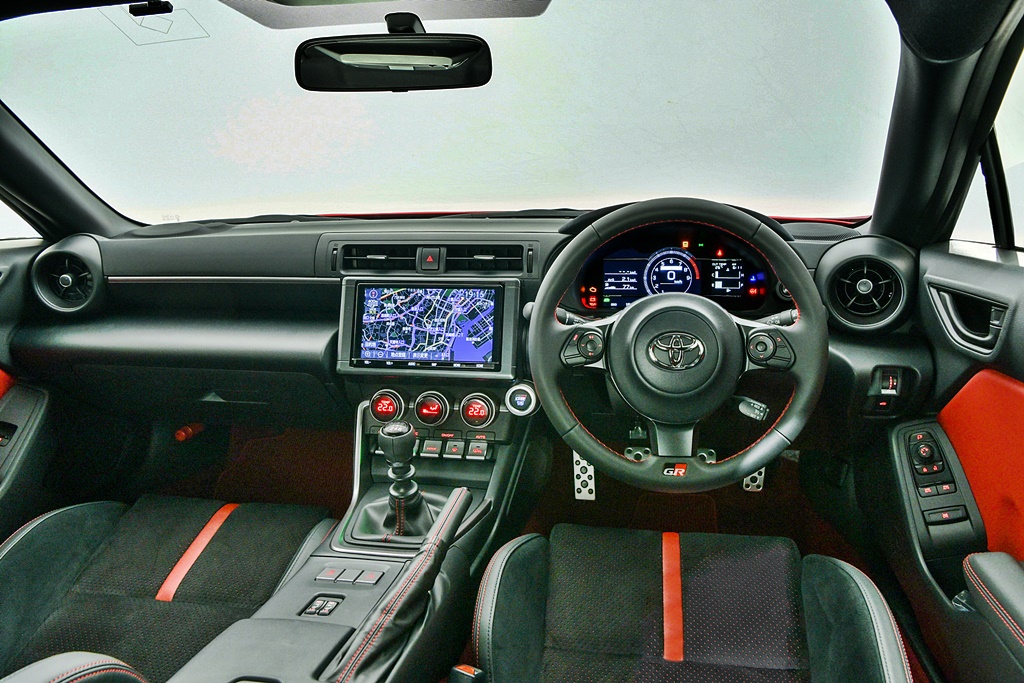
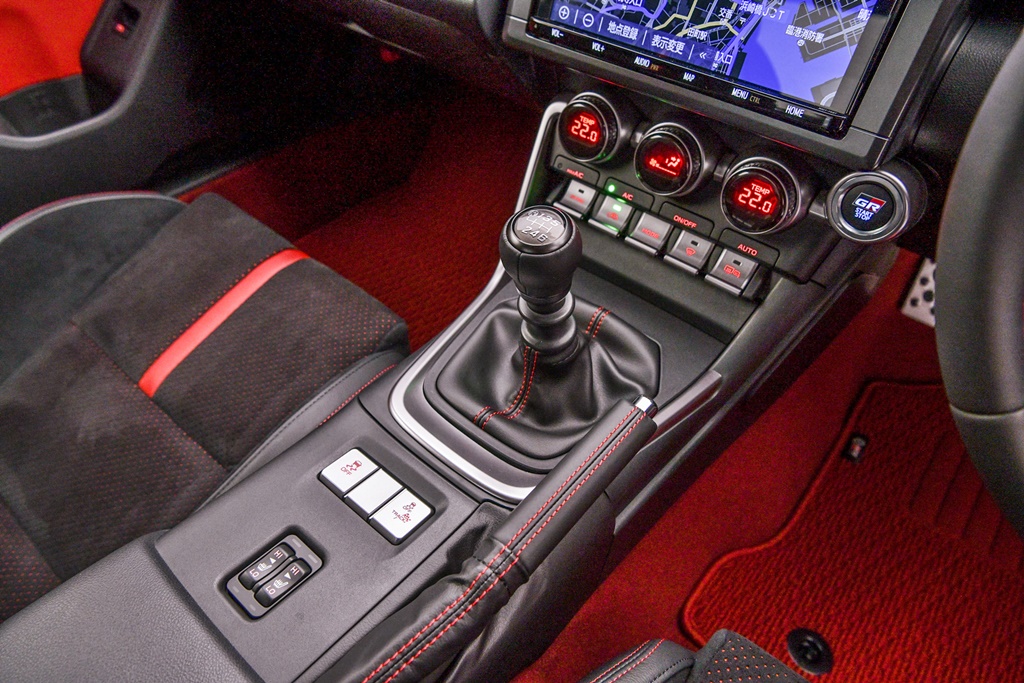
More comfort-oriented cabin
The previous 86 interior may have been designed with a rather purist approach, so it had a stripped-down look like a racing car. However, for this new generation, there appears to be a bit more ‘comfort-oriented’ philosophy with a 7-inch TFT screen that has an opening animation sequence inspired by the piston movements of the engine.
The cockpit has been designed with the hard driving in mind, and sightlines as well as the seating position have all been set from experiences in racing. While the centre display is a touchscreen, the interior designers have provided either rotary knobs or rocker switches, both of which are easier for the driver to operate while driving (especially if wearing gloves).
Subaru Eyesight system used
Although Toyota has its own Toyota Safety Suite (TSS), Subaru’s EyeSight Driver Assist Technology is used for the GR 86 with automatic transmission. Like TSS, the Eyesight system has active safety technologies using radar and camera sensors to help the driver avoid a collision or reduce the effects of one.