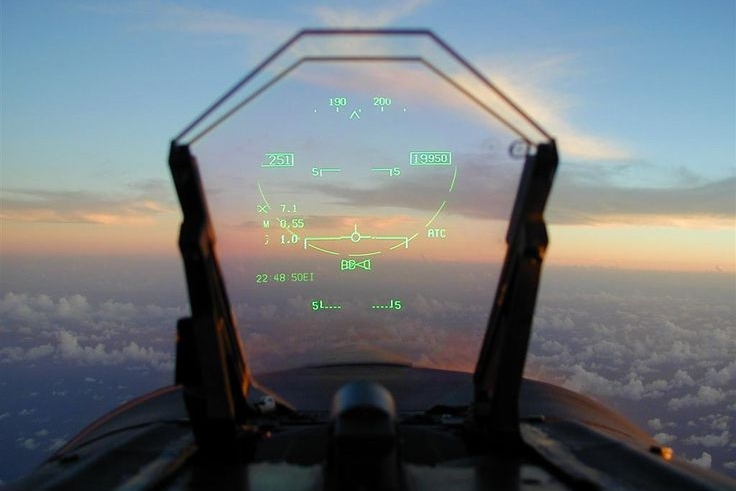
The Head-Up Display (HUD) was originally developed for use in fighter jets, providing pilots with important operating information without having to look down at instruments. This was important at the speeds they were flying, more so when in combat where they had to be looking ahead (or around) all the time.
The value of HUDs eventually saw them being installed in commercial aircraft, providing pilots with an additional ‘screen’ ahead of them so they could still view the runway ahead when landing. The system also caught the attention of engineers in the auto industry who thought it would be a good idea to use in cars. By projecting information on the windscreen, the driver could stay focussed on the road ahead and still be informed of things like speed and other functions.

The earliest use of the HUD in a car was in a Nissan Silvia in the mid-1980s and General Motors also put it in some of its models. However, the early HUDs were simple with just a few items of information. There were initial issues of visibility in bright sunlight which limited their wider use, apart from the cost. As such, while they continued to be offered, only very expensive models had them, usually as an option.
Some manufacturers came up with a low-cost approach which did not need any special windscreen glass. Instead, a flip-up see-through panel was installed on top of the dashboard ahead of the steering wheel. Information was projected onto this from inside the dashboard, which was visible to the driver. In a way, it was a return to the earliest concept of the HUD which was basically a reflector sight installed in fighter planes in World War II.
A genuine innovation
With advancements in electronics and other technologies, the HUD for cars has also evolved and with costs dropping as volume increases, it is slowly becoming available in lower segments. Volkswagen is the first car manufacturer in the world to introduce this technology in the compact segment (initially in the new ID.3 and ID.4 electric models), and it includes augmented reality (AR) as well.
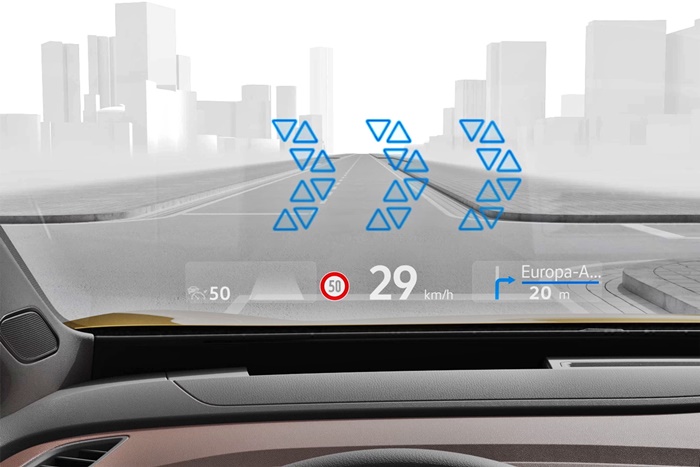
With AR, the virtual and real worlds are merged in the HUD panel. The innovative system superimposes selected symbols onto the outside world and displays them dynamically. It’s a new chapter in driver information displays and a genuine global innovation.
Two fields, two levels.
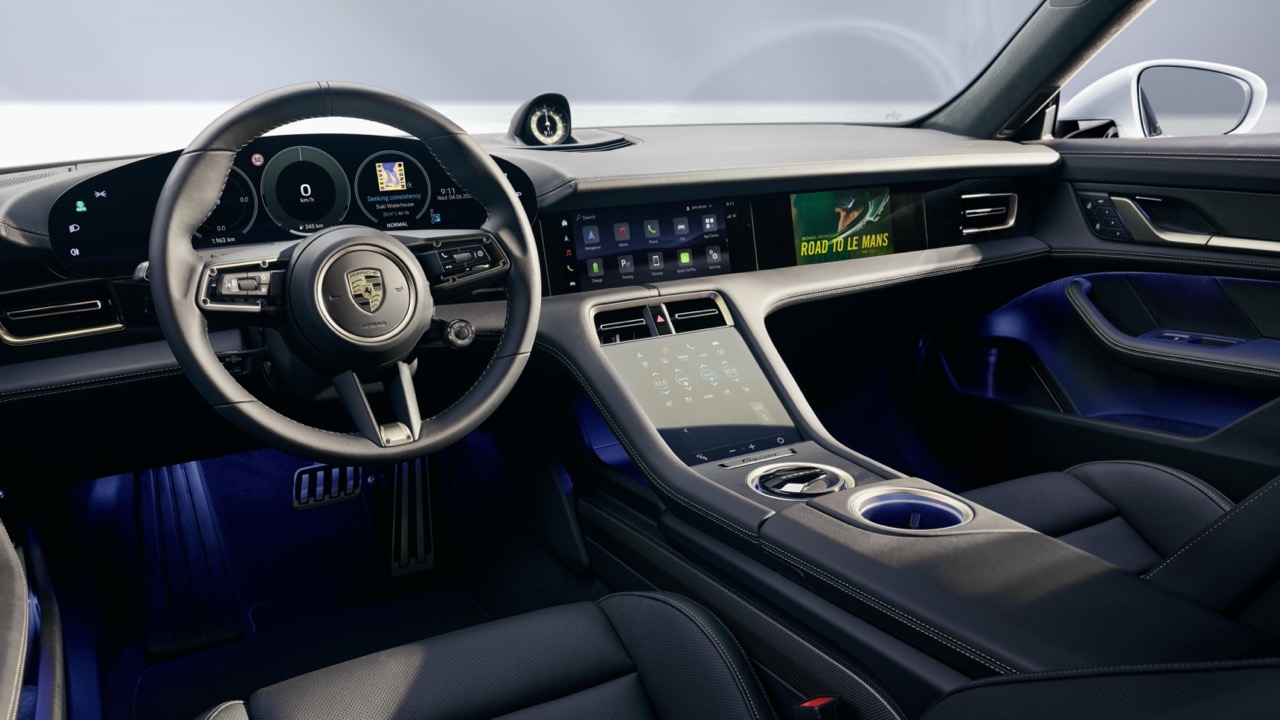
The AR HUD projects important information onto the windscreen – separated into two fields and levels. The large window for the dynamic displays is located in the driver’s field of view at a virtual distance of around 10 metres and has a diagonal measuring around 1.8 metres. Information from the driver assist systems as well as the turn arrows and starting points and destinations of the navigation system are displayed in this far-range window.
The close-range window is located as a flat band under the large far-range window. This shows the driving speed, road signs, and assist and navigation symbols as static displays. They appear to ‘float’ around 3 metres in front of the driver.
All displays are positioned perfectly in line with the real world outside the vehicle and are shown dynamically. When the vehicle approaches a junction where it should turn off according to the navigation route, the driver sees two indications: in the first step, an advance notification on the road level, and then three arrows located at the junction.
The closer the driver gets to the junction, the larger the arrows become. At the same time, their textures fade in order to ensure a clear view of the road. When developing all displays, Volkswagen followed the basic concept of “Less is more”. This ensures that the driver is not overwhelmed with distracting information under any circumstances.
The Lane Assist function is also visualised in the far-range window. If the vehicle moves closer to a boundary line at the edge of the road without indicating, this line is displayed in orange. Two green lines appear after switching on Travel Assist, which keeps the car in the middle of the lane. When following another vehicle, the display marks the vehicle in front with a coloured stripe as soon as Adaptive Cruise Control or Travel Assist is activated. When the assist systems are switched off, the driver sees a red warning signal if they drive dangerously close to the vehicle in front.
Media error: Format(s) not supported or source(s) not found
Download File: https://www.piston.my/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/VW-AR-HUD.mp4?_=1The technical heart
The technical heart of the AR HUD is the picture generation unit display located deep inside the dash panel. The beam bundles generated by an especially bright LCD display are transmitted onto two flat mirrors, and special lenses separate the portions for the close and far range display levels. The flat mirrors deflect the beams onto a large, electrically adjustable concave mirror. From here, the beams reach the windscreen and thus enter the driver’s field of view. The driver sees the symbols with the same sharp definition as the real world at an apparent distance of just under 10 metres.
The images are generated by an AR creator located in one of the two central computers in the ID. models. The AR creator calculates the positioning of the symbols corresponding to the surroundings. To make these calculations, it receives information from the raw data of the front camera, radar sensor and navigation map. The displays that appear in the large window are stabilised with respect to the vehicle’s movements and adapted to the geometry of the optical projection system.

“We have introduced a genuine innovation not in a premium vehicle, but in the compact models of the all-electric ID. family. Making pioneering technologies available to a large number of customers is a core competency of Volkswagen,” said Frank Welsch, Member of the Board of Management for Development at Volkswagen.