Car-buyers all over the world are always concerned about the safety standards of the car they are interested in getting. After all, they will be using it daily and while no one wants to have an accident, it can happen unexpectedly and when it does, that’s when the protective systems and engineering become vital in minimising injuries.
Today, buyers can be better informed about how safe a model is, thanks to the New Car Assessment Programme (NCAP) which started in the European car industry 24 years ago. The program, conducted by the independent Euro NCAP organisation, involved crash tests and other assessments of new vehicles which were analysed and star ratings would be awarded, depending on the performance in the tests.
NCAP for ASEAN region
Since then, as awareness grew in other parts of the world, including Malaysia, regional NCAPs were established. This was an important move as there would be some models which might be sold or developed for specific regions. In ASEAN, the Malaysian Institute of Road Safety Research (MIROS), an agency under the Transport Ministry, was instrumental in starting a NCAP for the region. The ASEAN NCAP is recognised and part of the Global NCAP organisation which shares information and discusses matters relating to motor vehicle safety standards.

While consumers have come to know about ASEAN NCAP ratings as they are publicised in articles as well as advertisements, the ratings are not mandatory for Type Approval of a vehicle to be permitted for sale in Malaysia. Nevertheless, because NCAP ratings are easy to understand and provide consumers with useful information on how safe a model is, manufacturers strive to achieve the best results and get a 5-star rating, the maximum currently awarded.
Adapted from Geely Binyue
For this reason, when the Proton X50 began development, its performance in the ASEAN NCAP was targeted to be no less than 5 stars. The X50, being adapted from Geely’s Binyue SUV model, already had sound engineering but it was not as straightforward as simply changing the badge and making styling changes here and there. To become a Proton model required a new engineering programme which included meeting the highest ASEAN NCAP standards.
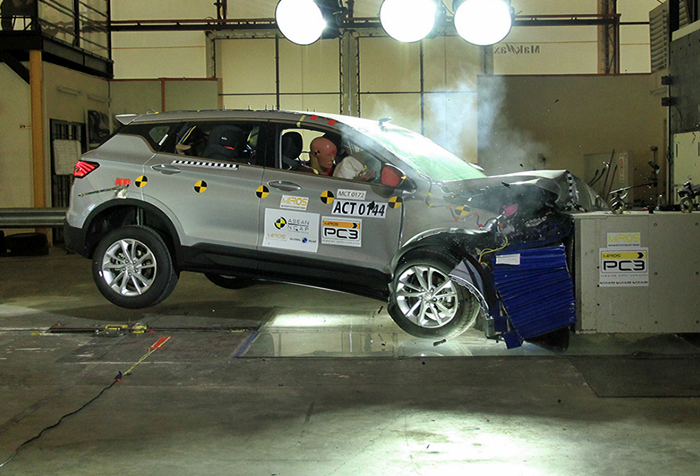
The task fell to the Safety and Intelligent Drive team at Proton, headed by Zanita Zainuddin. To ensure a 5-star rating, crucial, yet subtle changes had to be made, involving performance tuning, material replacement and parts repositioning. One crucial change made was on the bodyshell of the X50. In initial frontal collision tests during development, the front floorboard often experienced tearing, certainly unacceptable by any standard. To overcome this, the engineers had to reinforce the area with ultra-high-strength steel, thereby shifting the force of impact to other areas that do not present any threat to occupant safety. Overall, 40% of the body, including the front, side and back, was made using a combination of high-strength steel variants.

Another change was on the driver’s footrest, next to the accelerator and brake pedals. It was not a simple matter converting from the lefthand drive of the Binyue to the righthand drive for the X50. In fact, Geely had not developed a righthand drive variant so Proton would have to re-engineer certain areas for the conversion.
The engine is always placed under the bonnet towards the right side of the vehicle, regardless of the driving side. Therefore, during a collision, the driver of a righthand-drive Proton X50 would be more vulnerable to foot injury as compared to the driver of a lefthand drive Geely Binyue. To safeguard the driver’s resting foot from such harm, the footrest for the X50 had to be modified to ensure that the foot remains on the footrest by reducing slippage.
Improving for ASEAN NCAP from C-NCAP
Being a model primarily for the China market, the Binyue was developed to meet the requirements of C-NCAP, which is the NCAP for that country. Although there are common criteria among all the NCAPs, there are also some differences with ASEAN NCAP.
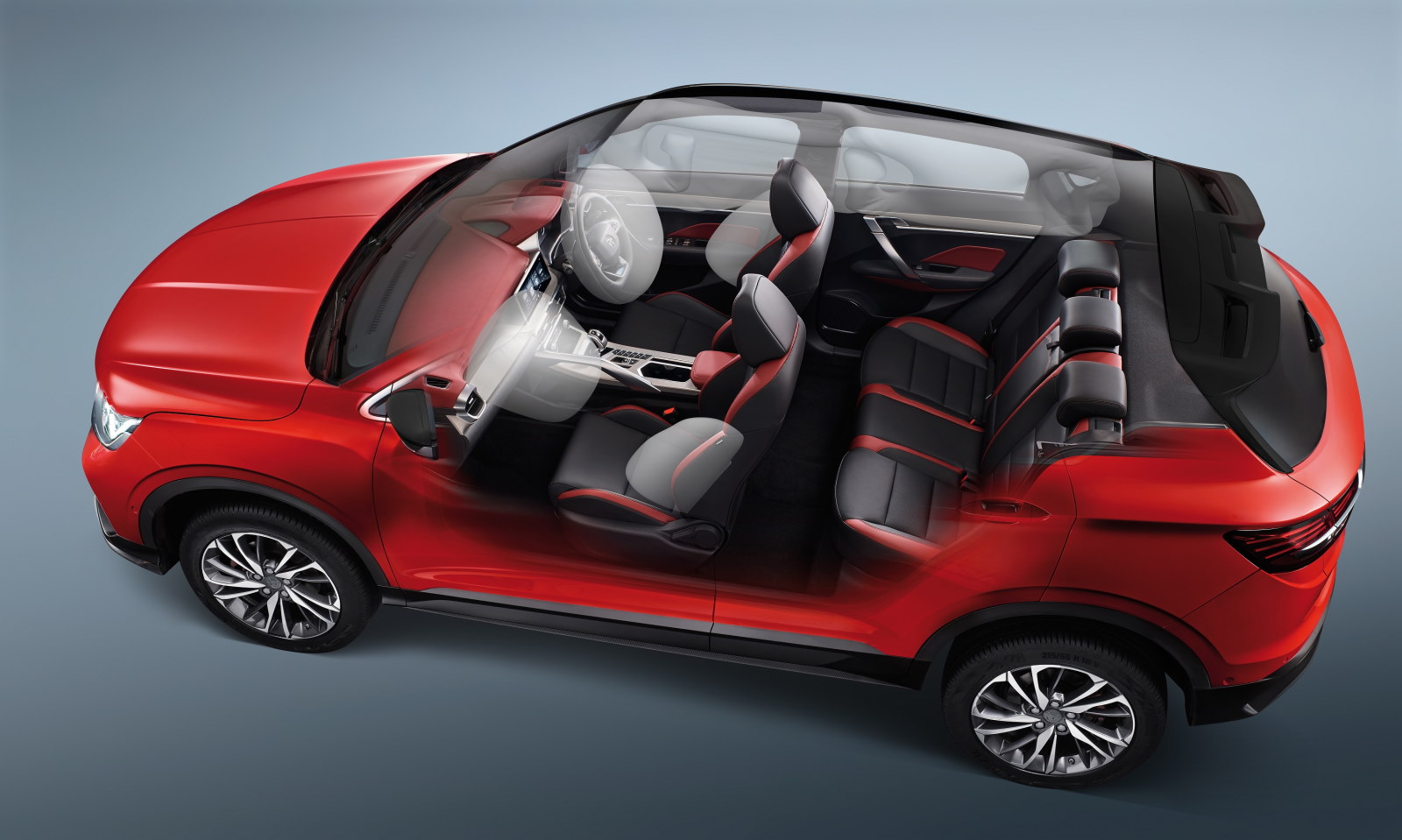
One example is the curtain airbags. ASEAN NCAP emphasizes that the static deployment of curtain airbags covers a range of body types for the different people that may be in the vehicle. Therefore, the curtain airbags for the X50 had to be adjusted to provide additional cushioning to the head area during impact, primarily during side collisions. Since this greatly improves occupants’ safety, it was highly recommended that the additional provision be incorporated in future Geely models.
Child Occupant Protection
C-NAP is also less focussed on the issue of compatible seats for child occupants, which is an important area in ASEAN NCAP referred to as Child Occupant Protection (COP) and contributory to the overall assessment. Zanita’s team made a changes which included lengthening the hook on the ISOFIX attachment point for compatible childseats. This not only made it easier to install the seat but also to readjust its angle to ensure secure positioning. The work done by Proton in such areas has been shared with Geely and will help it to be ready for such requirements if introduced by C-NAP in 2021.
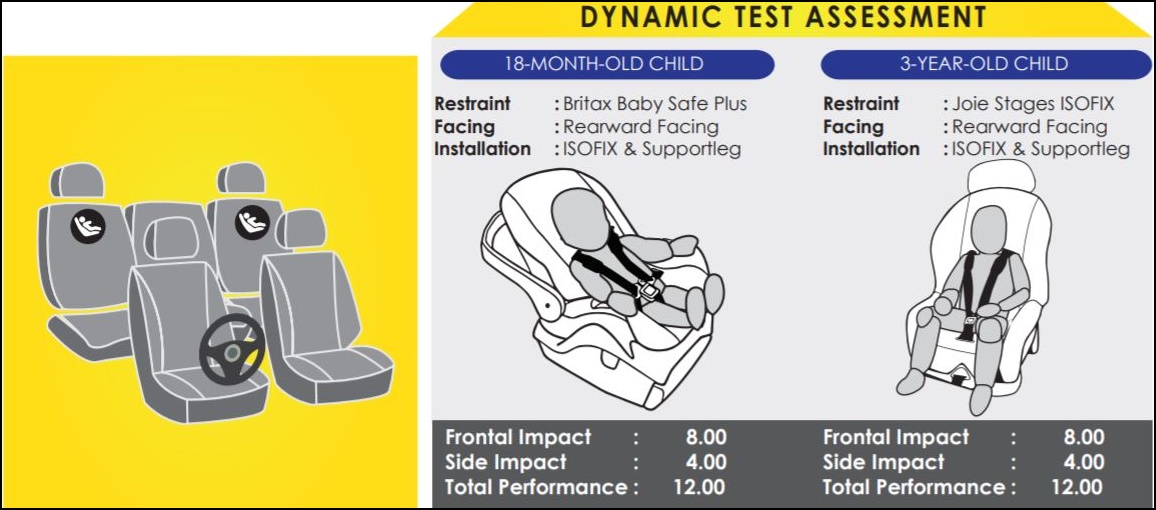
Related: Full ASEAN NCAP Report for Proton X50
Benefits of being in the Geely Group
Geely and Proton have both benefited from each brand being subjected to different safety and market standards. The best practices are being gathered and shared, ultimately benefitting consumers who get to enjoy not only a comfortable ride but also a very safe one. Additionally, having Volvo – widely acknowledged as the world leader in automotive safety – as part of the group means being able to get assistance in advancing safety technologies.
“Proton has always emphasized safety as one of its unique selling points, unbiased to any country or platform. It is not surprising then that we continue to challenge ourselves so that this DNA is inherent throughout our range of models, be it our locally produced car or the current joint development with our partner Geely,” said Zanita.



























