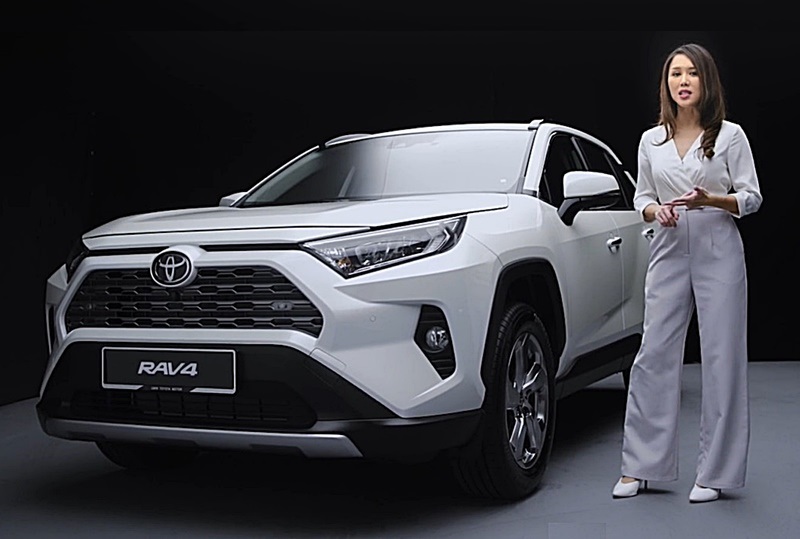
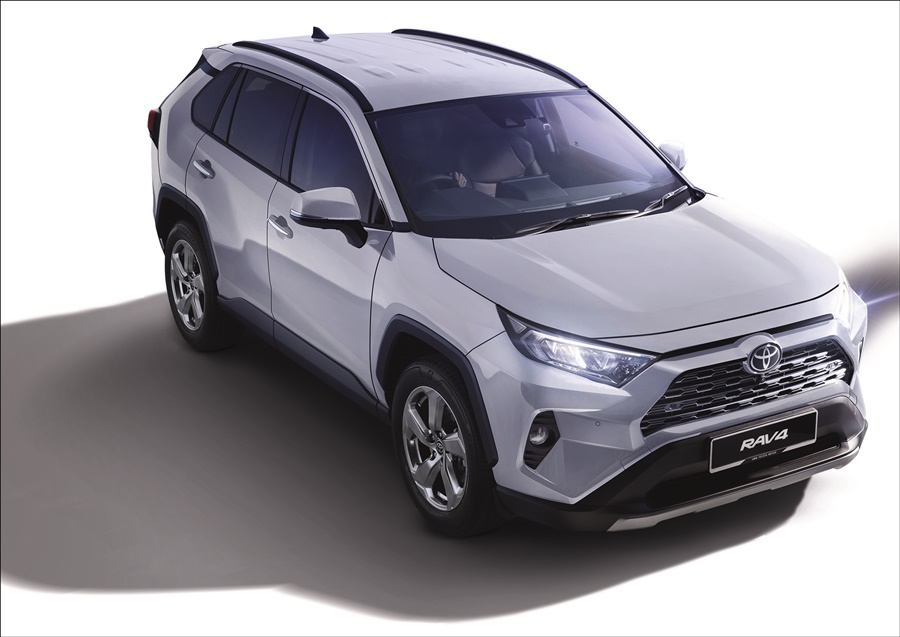
The Toyota RAV4 is a historically significant model in Toyota’s line-up. Introduced in 1994, it came at a time when motorists were beginning to appreciate SUVs and created a new segment in the car market almost overnight.
While the earlier SUVs (which were also rather big) were traditionally based on chassis-on-frame construction, Toyota designed the RAV4 with a monocoque bodyshell – the same as a passenger car. So it handled like a car and was also almost as comfortable; for many making the switch to the RAV4, the transition was easy as it felt like a passenger car when driven.

The RAV4 set off an ‘explosion’ in the SUV segment and in the years that followed, virtually every manufacturer would introduce a SUV (if it didn’t have one) or expand its SUV range. Demand kept growing and even the luxury segment began to have SUVs.
In 2019, the RAV4 was the world’s best-selling SUV and to date, over 10 million units have been sold worldwide. Now comes the fifth generation of the model which got off to a good start by being voted Japan’s Car of the Year 2019-2020.
The all-new RAV4 imported by UMW Toyota Motor is available in two variants with 2.0-litre and 2.5-litre engines, priced at RM196,436 and RM219,664.50 (Peninsular Malaysia price, excluding insurance premium). The vehicles are imported as Completely Built-Up (CBU) units from Japan and come with a 5-year/unlimited mileage warranty. [Click here for price list]
The prices are higher than the popular rivals in the local market but bear in mind that the RAV4 is imported as CBU from Japan whereas competitors in the same class such as the Honda CR-V and Mazda CX-5 are assembled locally with lower tax imposed on them (apart from getting incentives from the government for investments in local assembly). And the strength of the ringgit (or lack of it) these days also has an impact on pricing.
Evolving with trends
Over the years, the RAV4 has grown in size from the original design. The latest generation, with an overall length of 4600 mm, it is 445 mm longer than the first generation, while the overall width of 1855 mm is 160 mm wider. The wheelbase of 2690 mm is 280 mm longer. This moved the RAV4 up a notch is size categorisation and Toyota filled its place with the more compact C-HR.
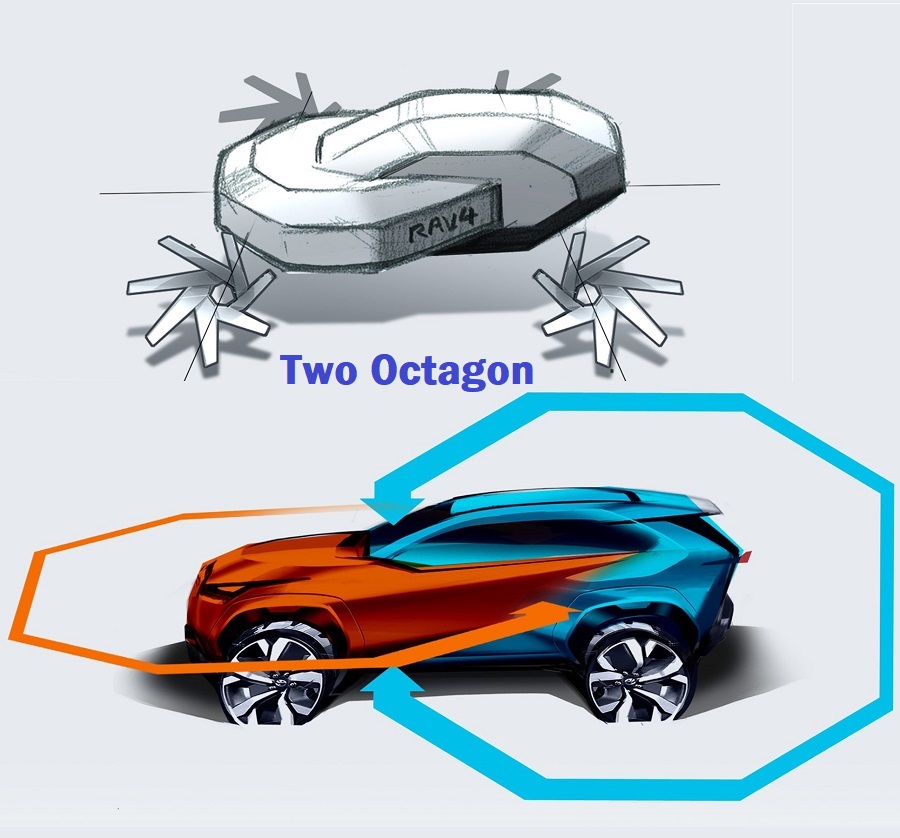
The styling also evolved with trends although even the first generation was stylish in its own way. The latest fifth generation has an octagonal theme giving a chiseled appearance with a front end that is bolder.
The door mirrors have been repositioned from the window panel to the door panel, increasing forward visibility around the A-pillars and contributing to a general increase in all-round visibility for better situational awareness.
The RAV4 rides on 18-inch alloy wheels, wrapped with 225/60R18 dual-purpose tyres. Unlike the earlier RAV4s, the spare wheel is no longer on the rear door – which used to be a must for the SUV image. These days, apart from a few models, the spare wheel is carried on board and in the case of the RAV4, it’s a space-saver type for emergency use only. Thankfully, it isn’t hung under the vehicle like the traditional SUVs.
Joining the TNGA era
While the original RAV4 departed from traditional SUV construction by having a unitary monocoque structure, the latest model has TNGA, which stands for Toyota New Global Architecture. This is the brand new platform developed for use in a wide range of new Toyota models.
The TNGA structure is also monocoque and is 57% more rigid. With the adoption of a ring structure, the torsional rigidity of the body has increased. Contributing to the rigidity is the reinforcement in many areas, strengthening the structure. This enhances agility while also providing a smoother, quieter ride.
Adopting the TNGA platform allowed the engineers to position the powertrain lower down which means a lower centre of gravity for better stability. Using high-strength hot-stamped steel and aluminium have also reduced weight in the upper body, again helping to shift the centre of gravity downwards. A new saddle-style fuel tank distributes weight of the fuel evenly side-to-side.
The suspension consists of MacPherson struts at the front and trailing wishbones, a straightforward layout which is clearly oriented towards on-road driving rather than off-road motoring. Handling and comfort were the priorities and a select group of takumi (highly trained master craftsmen) helped to refine the ride comfort, focusing on tuning details.
A new steering system is installed in the RAV4. The new parallel-type electric power steering system is rack-mounted rather than column-mounted, unlike the previous model. The new design helps enhance turning response and gives a natural feel that can help reduce fatigue on long drives.
The engineers also gave a lot of attention to reducing noise levels in the cabin, this aspect being important to the perception of quality. The reinforcements in the structure help, along with low noise features like integrating the floor silencer and expanding the surface area of damping materials.
Practical interior with car ambience
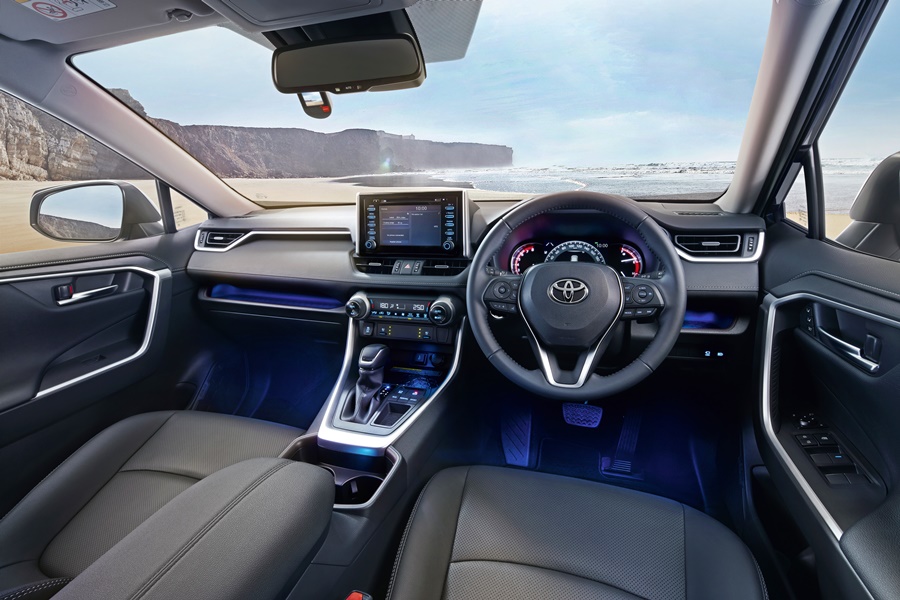
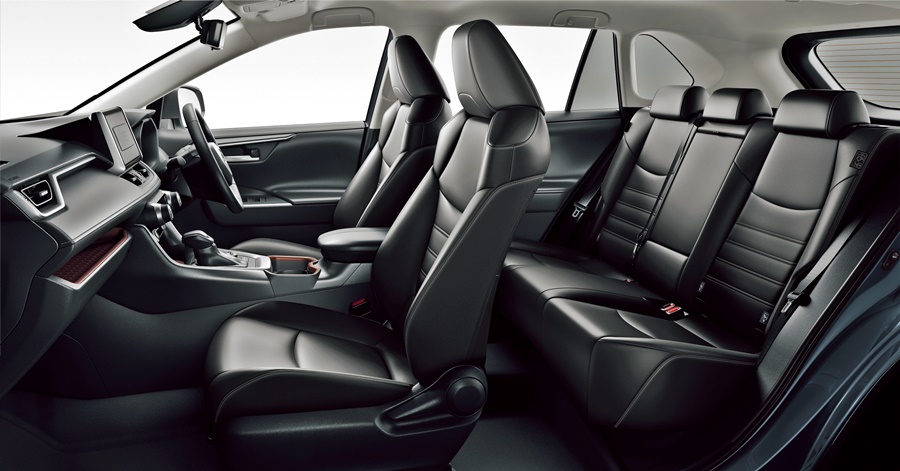
With the new platform, the interior designers took the opportunity to do a complete redesign of the cabin. As with earlier RAV4s, the interior concept focusses on practicality but blends in modern passenger car ambience with many convenience features.
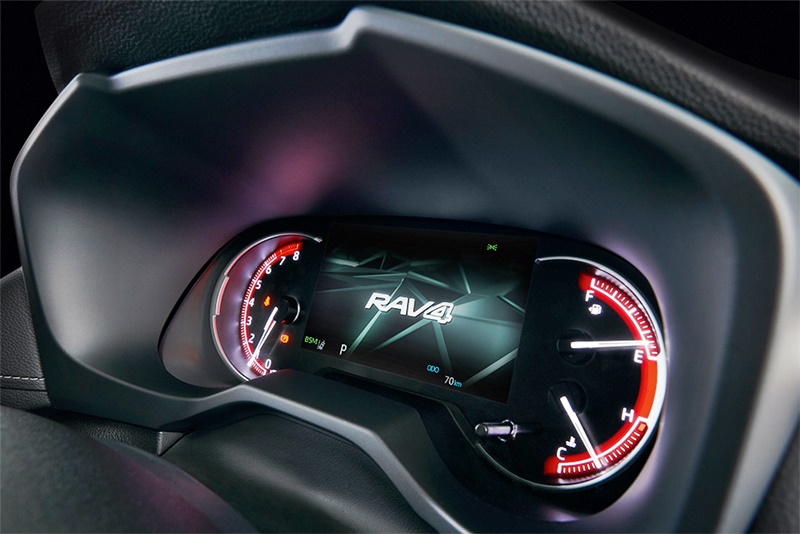
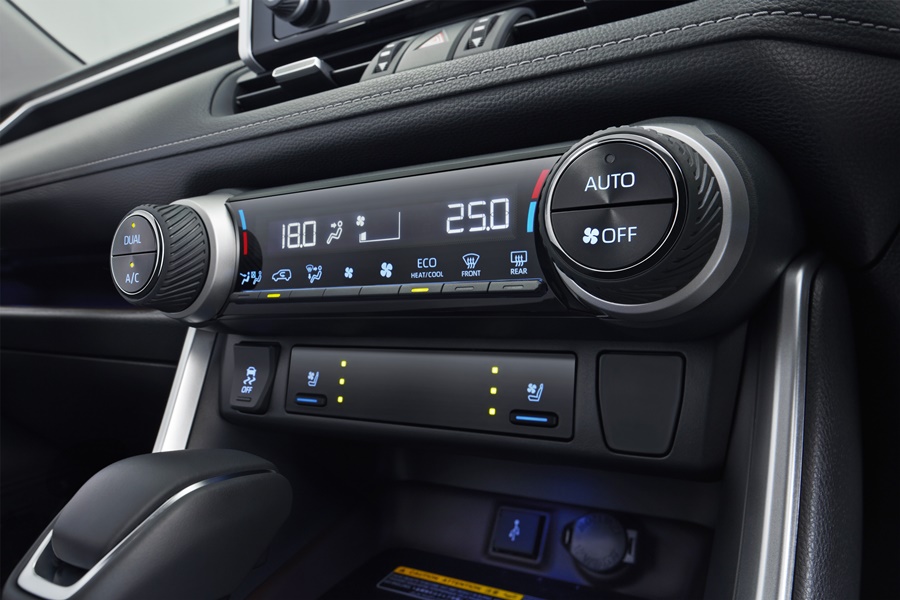
The new dashboard layout incorporates a slimmed-down instrument panel which is installed low, giving the driver better visibility. Bright and clear Optitron meters (originally developed for the Lexus luxury models) are used on the instrument panel. The TFT Combination Meter can be switched between analog and digital displays.
Infotainment is right up to date with a 7-inch display and a range of connectivity options such as Mirrorlink, Miracast, AUX and Bluetooth. AppleCarPlay and Android Auto are also available so occupants can connect their compatible smartphone and access apps from the dashboard. There’s also voice command which enables management of certain features or handsfree telephony.
Seating comfort is improved with thicker cushions and enlarged lumbar support pads and there’s also a Seat Ventilation System installed – something which you usually find on luxury models.
Large cargo space with auto-opening door
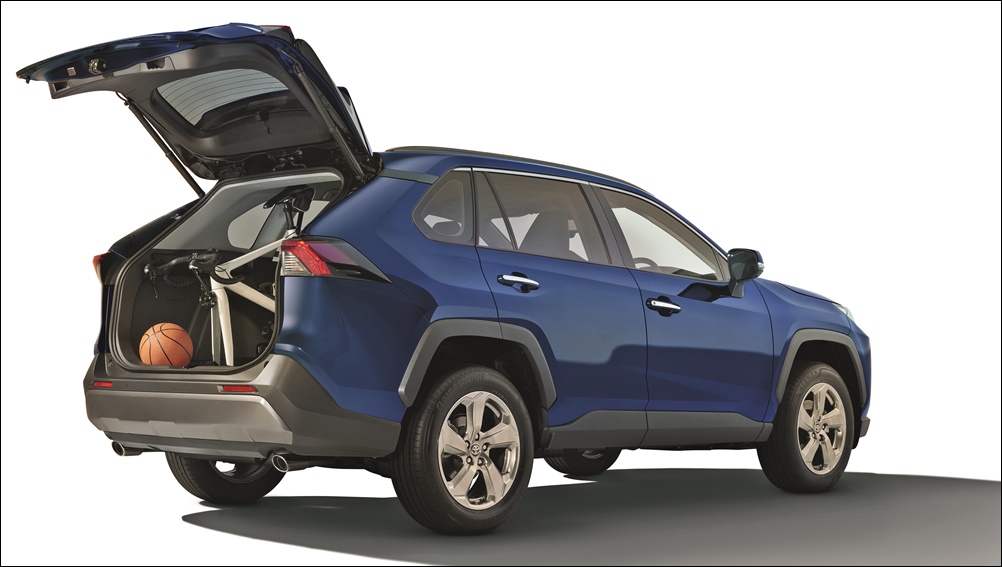
The RAV4 is a 5-seater with two rows of seats, and the back row can be folded flat to increase the cargo floor length for more cargo volume. The cargo area is large enough to even accommodate a 62-inch bicycle with the front wheels having to be removed.
Where the earliest RAV4s had side-hinged rear doors, the door for latest one is top-hinged. There are pros and cons to this as a top-hinged door requires extra space behind the vehicle to open whereas you can open a side-hinged door a bit to put things in. But what will be greatly appreciate is not just powered operation for opening and closing but also a handsfree operation. Placing a foot under the rear bumper will unlatch the door and it raises automatically – a great feature to have when both your hands are full.
Feedback from owners of earlier generations told the new RAV4 development team that many owners have outdoor activities. This led them to come up with useful features to support such activities. For example, the inside handle of the rear door can be used for clothes hangers or camping lights. The wide and long ceiling can be used as a storage area with a nylon strap strung across the passenger grips. Numerous hooks are available to secure irregular-sized luggage as well.
A new engine family
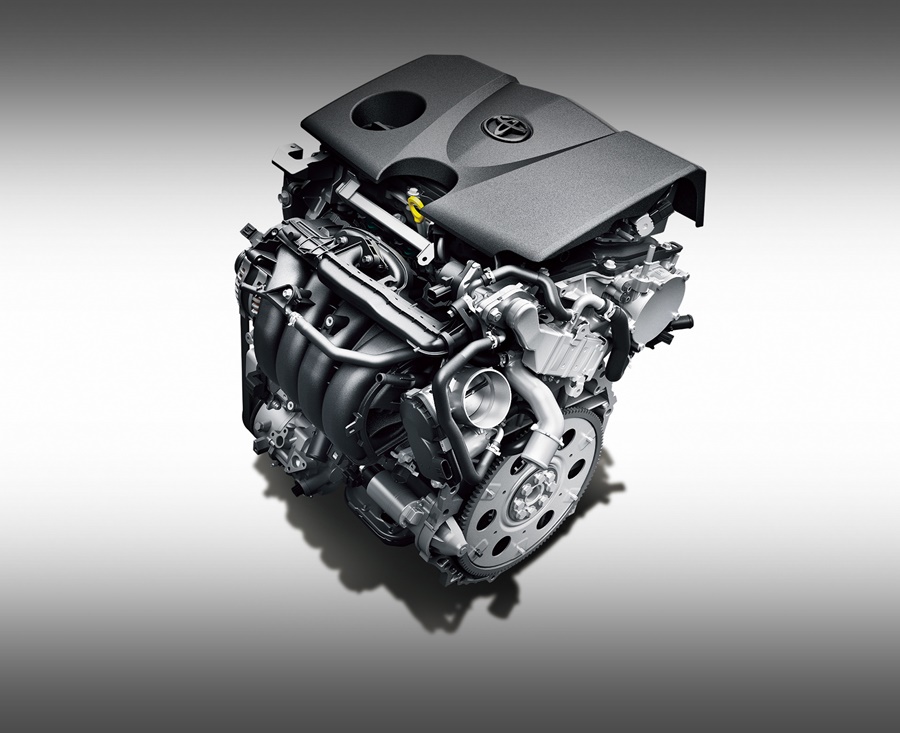
With this new generation, the RAV4 gets an entirely new powertrain with Dynamic Force engines. Lighter and more powerful, these 4-cylinder petrol engines have a combination of a very high compression ratio (13:1), advanced D4-S fuel injection (combining direct and secondary port injectors), high-speed combustion technologies, VVT-iE intelligent variable valve-timing (both sides), and ultra-low internal friction. The thermal efficiencies are as high as 40%, double the average of most internal combustion engines.
The 2.5-litre version produces up to 207 ps/243 Nm of torque while the 2.0-litre engine produces up to 173 ps/207 Nm. The bigger engine is mated to an 8-speed automatic transmission (Direct Shift 8-AT) but for the 2-litre unit, there’s a CVT with Sequential Shiftmatic.
For both transmissions, the driver can choose from Eco, Normal and Sport modes to suit driving preference or conditions. Selection of the preferred mode is done by pressing switches on the centre console. Paddle shifters are also provided (both variants), allowing the driver to make manual selections without removing the hands from the steering wheel.
Both variants have front-wheel drive rather than 4-wheel drive. When the RAV4 was first introduced, SUVs all had 4-wheel drive although there were also 2-wheel drive variants available, especially for the flatter regions of the US market. But as time went on, manufacturers found that the new generation of SUV buyers didn’t seem to care much for 4WD. Omitting 4WD meant weight reduction, with cost savings which could be used to provide more features. Those who had to have 4WD could still get it in more expensive variants but the majority were satisfied with 2WD.
Integrated active safety systems
Like most of the latest Toyota models, active safety systems are no longer independent elements but integrated to work together to help the driver avoid accidents and maintain better control of the vehicle. Besides the now-standard provision of systems such as ABS, Traction Control and Vehicle Stability Control, Toyota has developed an integrated package known as Toyota Safety Sense (TSS) which is used in the RAV4 and many of the Toyota’s latest models.
TSS consists of four driver-assistance systems – Pre-Collision System, Lane Departure Alert with Lane Tracing Assist, Dynamic Radar Cruise Control at All Speeds (DRCC), and Automatic High Beam (AHB). Lane Tracing Assist operates using the camera and radar to recognize lane markers or the preceding vehicle’s driving path. It estimates the vehicle’s position in the lane and then implements steering assist to remain in the lane, even on roads with curves.

DRCC is a more advanced form of cruise control which can vary the cruising speed depending on conditions, while AHB detects the headlights of an oncoming vehicle or tail lights of a vehicle ahead and automatically switches to low beams.
Other safety features and systems in the RAV4 include Blind Spot Monitor with Rear Cross Traffic Alert both of which alert the driver when other vehicles are in the blind spot during changing lanes and reversing.
Besides the camera used for the TSS, there are also six other cameras around the vehicle. The first two are the Driving Video Recorders (DVR) mounted in the front and rear positions inside the cabin and the other four cameras are tiny one installed around the body for 360-degree coverage. The driver can view the surrounding areas next to the vehicle while parking, a great benefit in narrow or tight parking spaces.
Apart from the engine immobilizer and alarm system, UMWT also installs a Vehicle Telematics System (VTS) in the RAV4. This system uses GPS/GSM for tracking so if the vehicle is stolen, its location can be identified quickly and the authorities informed to recover the vehicle. The service provider for the VTS can also provide emergency assistance from its 24-hour command centre.
Visit www.toyota.com.my to find out more about the new RAV4 and where to view it.