The age of autonomous cars – vehicles that can operate without human control – is coming. It’s not charging at us but with the amount of investment and R&D going into such technology, there will come a time when the companies are ready to sell autonomous vehicles. The introduction won’t be global, just as electric vehicles are not sold everywhere even though they have reached commercialisation.
While autonomous technologies have improved substantially, they still ultimately view the drivers around them as obstacles made up of ones and zeros, rather than human beings with specific intentions, motivations, and personalities. For all their fancy sensors and intricate data-crunching abilities, even the most cutting-edge cars lack something that (almost) every teenager with a ‘P’ licence has: social awareness.
A team led by researchers at the Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL) of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) has been exploring whether self-driving cars can be programmed to classify the social personalities of other drivers. This could help them better predict what different cars will do — and, therefore, be able to drive more safely among them.
In a new paper, the scientists integrated tools from social psychology to classify driving behaviour with respect to how selfish or selfless a particular driver is. Specifically, they used something called social value orientation (SVO), which represents the degree to which someone is selfish (‘egoistic’) versus altruistic or cooperative (‘prosocial’). The system then estimates drivers’ SVOs to create real-time driving trajectories for self-driving cars.
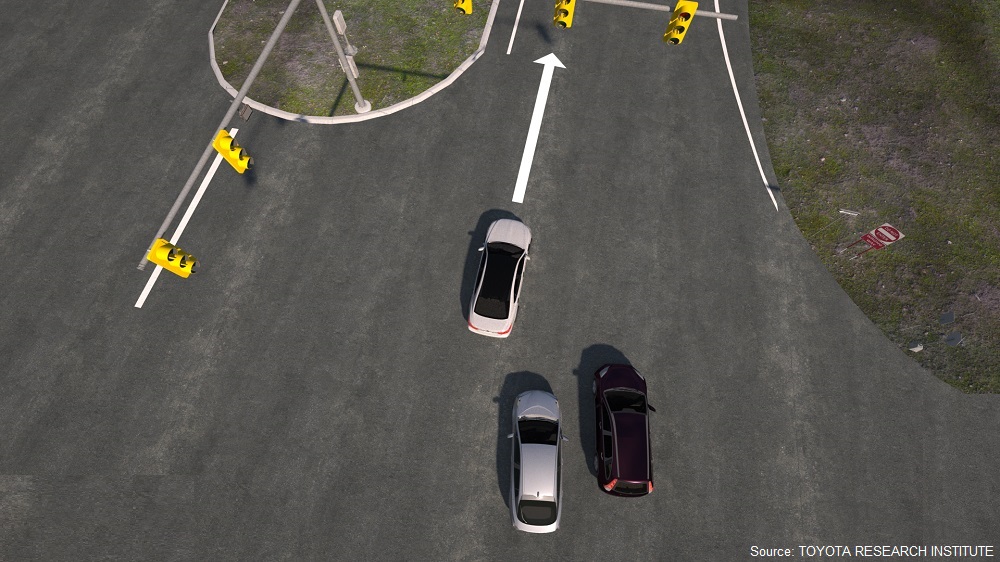
Testing their algorithm on the tasks of merging lanes and making unprotected turns to the left (on US roads where vehicles travel on the right), the team showed that they could better predict the behaviour of other cars by a factor of 25%. For example, in the left-turn simulations, their car knew to wait when the approaching car had a more egoistic driver, and to then make the turn when the other car was more ‘prosocial’.
While not yet robust enough to be implemented on real roads, the system could have some intriguing use cases, and not just for the cars that drive themselves. Say you’re a human driving along and a car suddenly enters your blind spot — the system could give you a warning in the rear-view mirror that the car has an aggressive driver, allowing you to adjust accordingly. It could also allow self-driving cars to actually learn to exhibit more human-like behaviour that will be easier for human drivers to understand.

“Working with and around humans means figuring out their intentions to better understand their behaviour,” said graduate student Wilko Schwarting, who was lead author on the new paper published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. “People’s tendencies to be collaborative or competitive often spills over into how they behave as drivers. In this paper, we sought to understand if this was something we could actually quantify.”
Schwarting’s co-authors included MIT professors Sertac Karaman and Daniela Rus, as well as research scientist Alyssa Pierson and former CSAIL postdoc Javier Alonso-Mora.
A central issue with today’s self-driving cars is that they’re programmed to assume that all humans act the same way. This means that, among other things, they’re quite conservative in their decision-making at 4-way stops and other intersections. While this caution reduces the chance of fatal accidents, it also creates bottlenecks that can be frustrating for other drivers, not to mention hard for them to understand. This may be why the majority of traffic incidents have involved getting rear-ended by impatient drivers.
“Creating more human-like behaviour in autonomous vehicles (AVs) is fundamental for the safety of passengers and surrounding vehicles, since behaving in a predictable manner enables humans to understand and appropriately respond to the AV’s actions,” said Schwarting.
To try to expand the car’s social awareness, the CSAIL team combined methods from social psychology with game theory, a theoretical framework for conceiving social situations among competing players. The team modeled road scenarios where each driver tried to maximize their own utility and analyzed their ‘best responses’ given the decisions of all other agents.
Based on that small snippet of motion from other cars, the team’s algorithm could then predict the surrounding cars’ behaviour as cooperative, altruistic, or egoistic — grouping the first two as ‘prosocial’. People’s scores for these qualities rest on a continuum with respect to how much a person demonstrates care for themselves versus care for others.
In the merging and left-turn scenarios, the two outcome options were to either let somebody merge into your lane (‘prosocial’) or not (‘egoistic’). The team’s results showed that, not surprisingly, merging cars are deemed more competitive than non-merging cars.
The system was trained to try to better understand when it’s appropriate to exhibit different behaviours. For example, even the most deferential of human drivers knows that certain types of actions — like making a lane-change in heavy traffic — require a moment of being more assertive and decisive.
“By modeling driving personalities and incorporating the models mathematically using the SVO in the decision-making module of a robot car, this work opens the door to safer and more seamless road-sharing between human-driven and robot-driven cars,” said Rus.

The research was supported by the Toyota Research Institute for the MIT team. The Netherlands Organization for Scientific Research provided support for the specific participation of Mora.