The new company formed by the merger of Fiat Chrysler Automobiles (FCA) and the PSA Group will see 14 brands – mainly European – coming under one group. That’s a lot of brands to manage and in an age when economies of scale are paramount, there’s the big question mark of whether some brands will be discontinued. Or if they are retained, will they lose their uniqueness and be just badge-engineered products that are needed for certain regions where the brand has been popular?
Carlos Tavares (currently PSA’s chief), who will be the CEO of the new combined company, has said that no brand will be axed while acknowledging that it will be a challenge to manage so many brands. But these are early days and the new company has not even started business; once the new management starts to look at the numbers and formulates long-term plans, it may be necessary to make the hard decisions and cut off some brands that just cannot deliver revenues.
A struggle to be kept in existence
One brand that many worry about is Alfa Romeo. The sporty Italian brand has a history spanning over 100 years and has a strong following of alfisti all over the world. Fiat acquired it in 1986 but struggled to get it to make money for the past 20 years. When former FCA CEO Sergio Marchionne was alive, he tried to boost the brand but three efforts still failed. His successor, Mike Manley, was less sentimental about the brand and had announced decreased investments for it.
There is a glimmer of hope for Alfa Romeo though, simply because 61-year old Tavares is a true car guy. His first job after university was as a test driver at Renault and apart from a strong personal interest in cars, he also goes racing on many weekends (though that may have to be sacrificed in future). So while he is also known as a cost-cutter like his former boss (Carlos Ghosn), he may well make a decision ‘from the heart’ and keep the Italian brand going somehow.

Trying unconventional ideas like the SZ
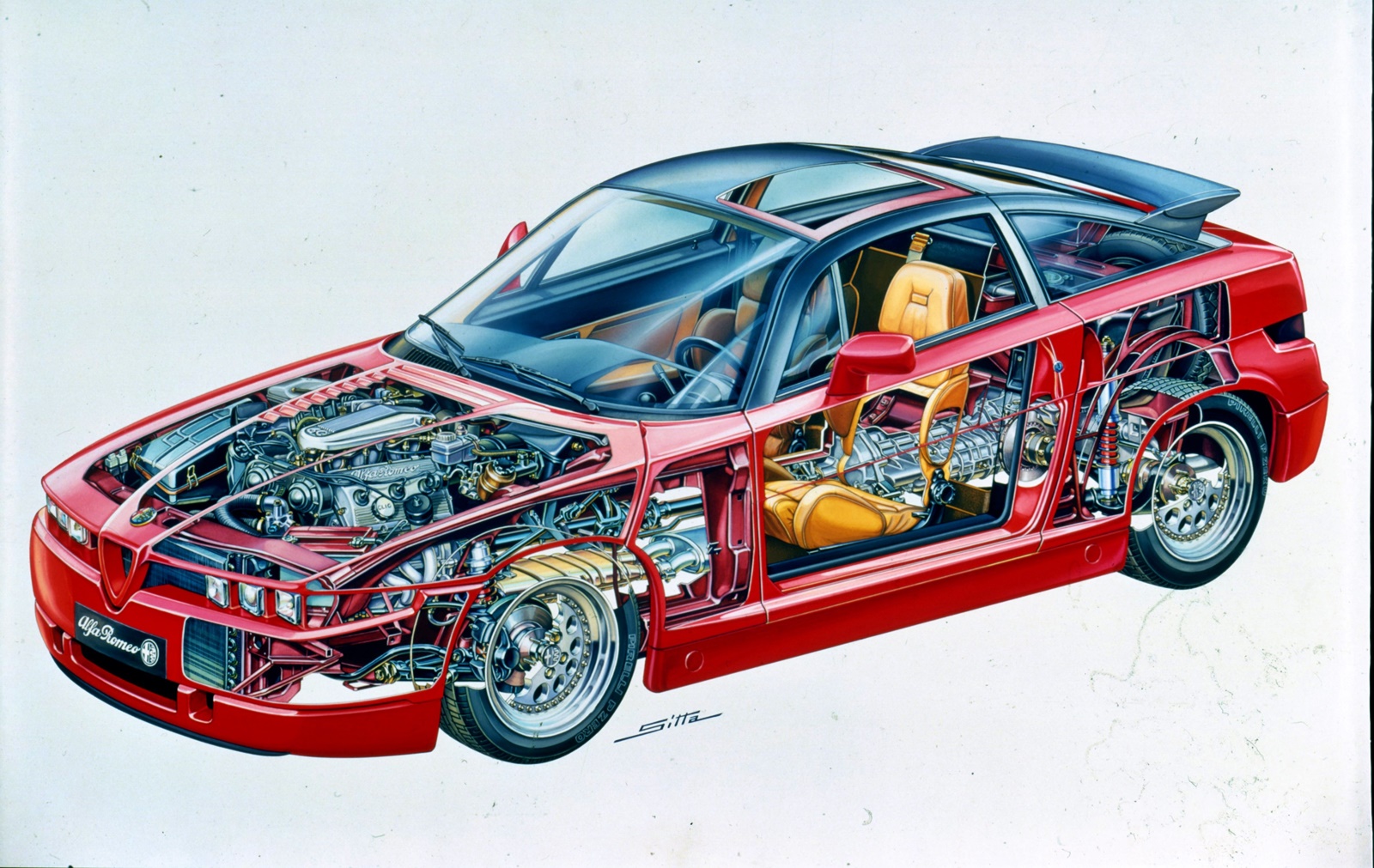
He may look at unconventional ideas to breathe new life into Alfa Romeo, as Vittorio Ghidella, President of Fiat in 1986, did when he initiated the ‘Experimental Sportscar, 3.0 litre engine (ES30) project. Ghidella specified a puristic coupe with the sporty performance and sensational design as the target for the development contract.
Three teams took care of the second point of the task description in parallel – the Alfa Romeo design department, Fiat Centro Stile and design studio Zagato (responsible for some of the most spectacular and most successful models from Alfa Romeo in racing). This team of three was also given a low weight and the most efficient aerodynamics including ground effect possible, as in a Formula 1 racing car, which was supposed to suck the finished model onto the road through the wind.
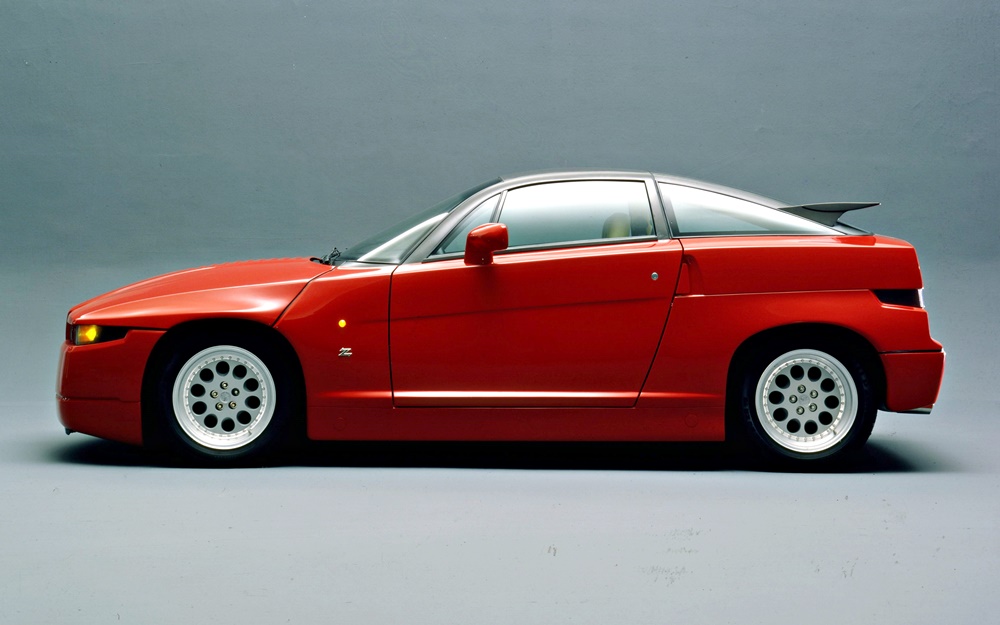
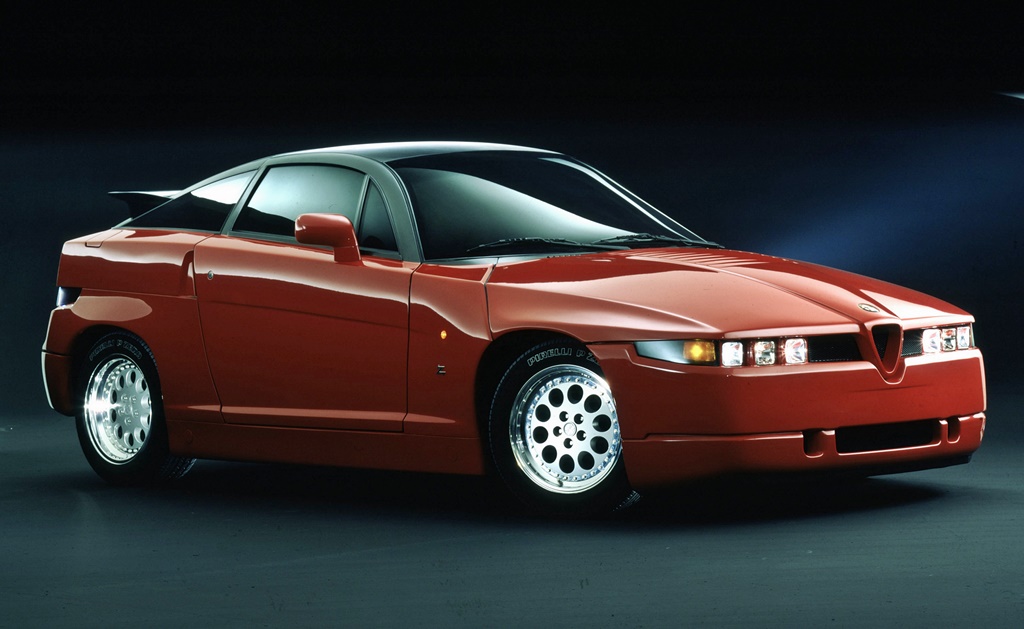
The result was an avant-garde design with narrow, square triple headlights, a distinctive wedge shape with a high beltline and a short hatchback. The ES30 was undoubtedly the most radical thing there was at the time as a production vehicle. The coupe corresponded entirely to the aesthetics at the time of Italian design in furniture and fashion.
The elaborate body was made of a glassfibre-reinforced synthetic resin. A new process ensured a particularly smooth surface. A steel skeleton served as the load-bearing structure, which, in addition to high torsional rigidity, also guaranteed low weight. The light metal aluminium was used for the roof skin. The finished car would finally weigh a comparatively low 1,256 kgs.
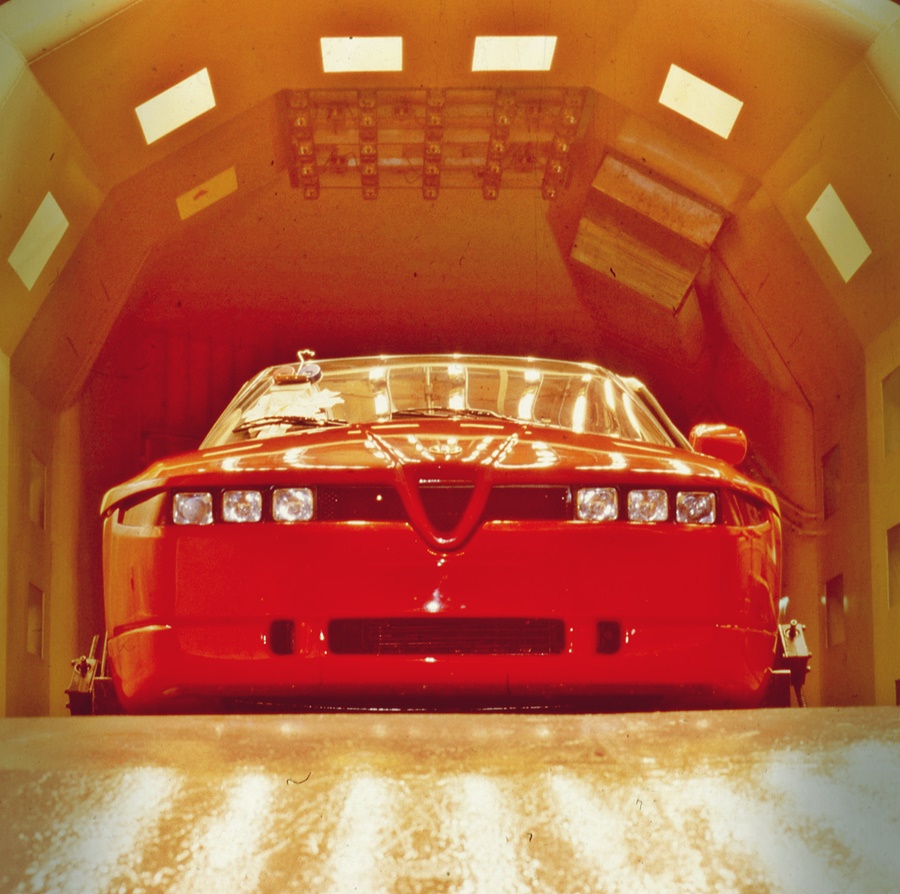
The drag coefficient of 0.30 was also excellent for the time. Wind tunnel tests indicated a top speed of 245 km/h and a time of 7.5 seconds for the sprint from 0 to 100 km/h. In order to achieve the required ground effect, however, the body had to have such a low ground clearance (around 6 cm) that it would have led to problems with, for example, driveways. The solution was an electrical level control, with the help of which the body could be raised by 5 cm when necessary.
Alfa Romeo 75 technology
As the other requirement was to keep the development costs low, the team used the proven technology of the Alfa Romeo 75. However, the chassis with the gearbox on the rear axle (transaxle design) was in some places know-how the Alfa Romeo racing department adapted to the desired performance. The torsion spring bars on the front axle gave way to conventional McPherson struts, stiff Uniball joints instead of the conventional rubber elements, eliminating inherent movements in the chassis.
The technicians selected the V6 petrol engine with 3 litres displacement from the 75 America model as the drive source. They increased its output to 210 bhp through sharper camshafts and newly programmed engine electronics (Bosch Motronic).
Zagato even developed a racing version of the ES30, which appeared in its own one-make cup in 1993 as part of some Formula 1 races. But the comfortable driving behaviour also proved itself in everyday life, even long tours were a pleasure in the two-seater coupe.
After just 19 months of development, just in time for the planned world premiere at the Geneva Motor Show in March 1989, the ES30 project was ready for production. Since production at Zagato was to take place in the Milan suburb of Rho, the company remembered a legendary combination of letters – SZ for ‘Sprint Zagato’. Despite the relatively high base price, 1,036 cars were sold between 1989 and 1993.