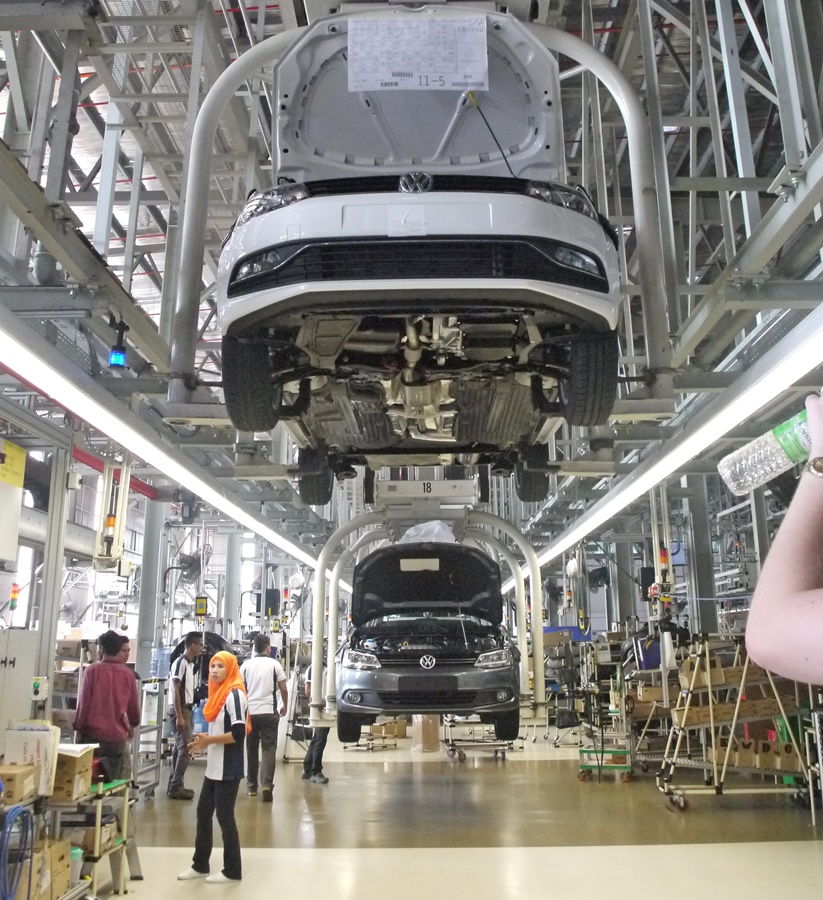
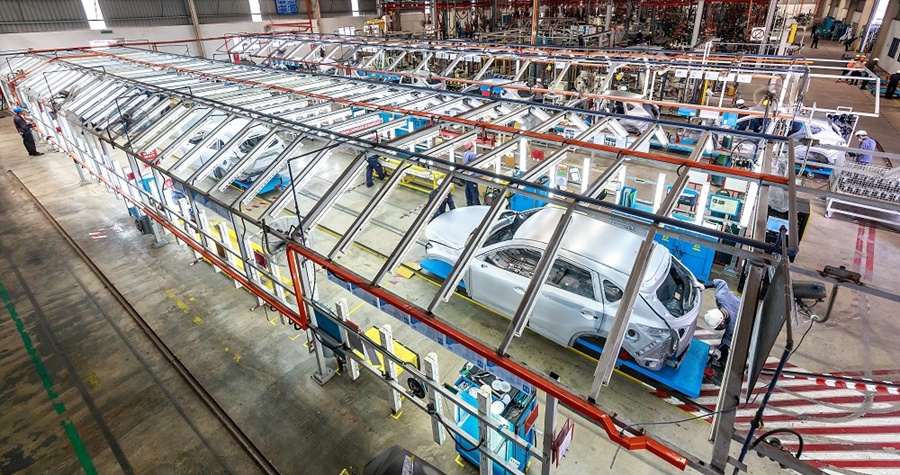
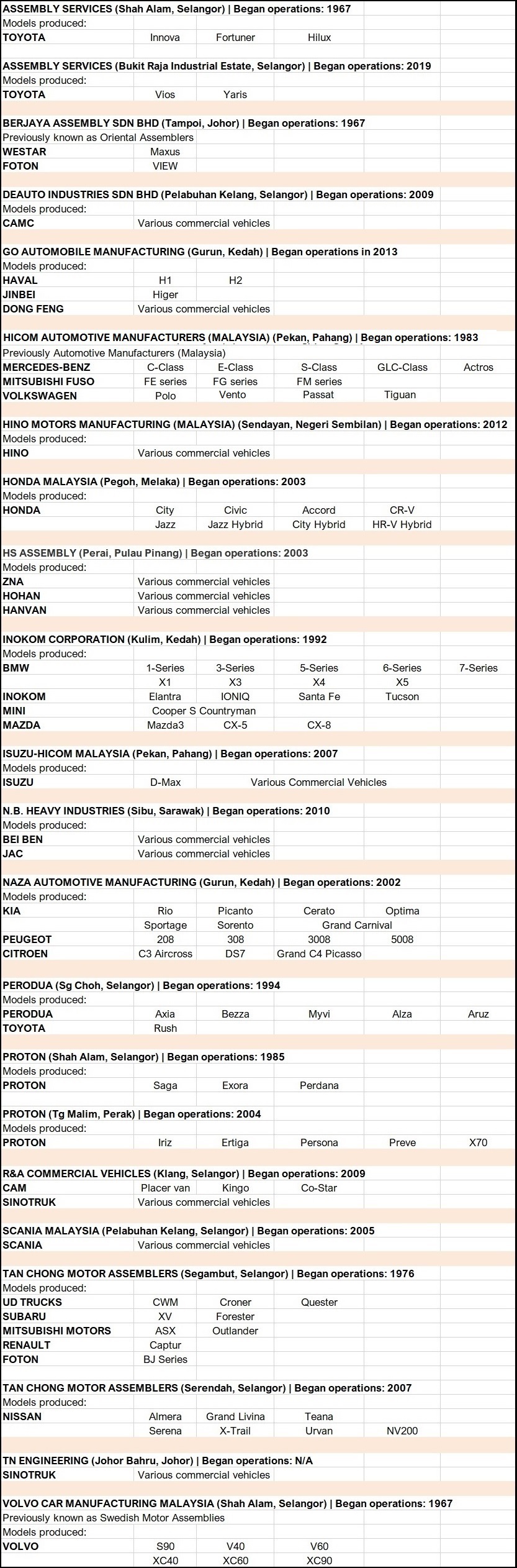
Local assembly of vehicles has been going on since the mid-1960s when the government offered incentives to carmakers to build factories and assemble their vehicles in Malaysia, or have the vehicles assembled under contract by other parties. The move was to put Malaysia on the path towards industrialisation and the auto industry was to serve as a catalyst, as it had in countries like Japan and Germany.
From a handful of factories in the late 1960s, mainly in Selangor and Johor, the network of assembly plants spread across the country to states like Pahang and Perak, and even East Malaysia. The number of factories has risen and fallen as market conditions have changed over the past 50 years, and there are 22 active plants today which collectively produced 380,940 units of passenger and commercial vehicles during the first 8 months of this year.
From the start, the government encouraged the sourcing of parts locally as well to develop the auto industry in a comprehensive way. Incentives were also given for using more local parts as well as for investments made to grow local assembly. However, where exports are concerned, Malaysia has not been as strong as Thailand and Indonesia and it is only in the past decade that a few carmakers have started to use Malaysian plants as regional production hubs for some models.